
Assertion: Chain isomerism is observed in compounds containing four or more than four carbon atoms.
Reason: Only alkanes show chain isomerism.
[A] If both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
[B] If both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
[C] If assertion is correct and reason is incorrect.
[D] If assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Answer
573.6k+ views
HINT: To answer this, you need to remember what chain is. In chain isomerism, one isomer might be a straight chain and the other branched but their chemical formula will be the same. You can use this to answer the given question.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: To answer this, firstly we have to discuss what chain isomerism is.
- Chain isomerism – When two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but not the same carbon skeleton, then the compounds are known as chain isomers and the phenomenon is known as chain isomerism.
Chain isomerism is shown when the compound can exist in a long straight chain or a branched chain. Let us take an example of pentane. Chemical formula of pentane is ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}$. It can exist as isomers like iso-pentane and neopentane.
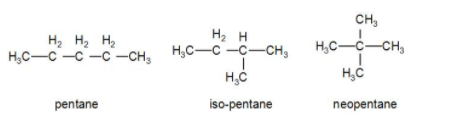
Pentane, isopentane and neopentane are examples of chain isomers. They have the same chemical formula i.e. ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}$ but the structure is different.
Now, if we take a 3 membered chain, like propane, we cannot form any such isomers for it. So, the minimum number of carbon atoms required for this isomerism is 4.
So, the assertion is correct.
Now, let us see the reason. For alkanes, n-butane is a straight chain compound whereas iso-butane is branched. For alkenes, oct – 1 – ene is straight chain but methyl hept – 1 – ene is branched. For alkynes, oct – 1 – yne is straight chain but methylhept – 1 – yne is branched. So, they show chain isomerism. So, the reason is incorrect as alkanes along with alkenes and alkynes can show chain isomerism. So, the reason is incorrect.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] assertion is correct and reason is incorrect.
NOTE: Isomerism is the phenomenon where two or more chemical compounds have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures. The compounds showing isomerism are known as isomers. Besides chain isomerism that we discussed above, there are other isomerisms shown by organic compounds. Chain isomerism is a structural isomerism. There are other isomers under this category like functional isomerism, ring-chain isomerism, metamerism and tautomerism. Besides structural isomerism, organic compounds also show stereoisomerism where the chemical formula and the sequence of bonding is the same but they differ in their spatial arrangements.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: To answer this, firstly we have to discuss what chain isomerism is.
- Chain isomerism – When two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but not the same carbon skeleton, then the compounds are known as chain isomers and the phenomenon is known as chain isomerism.
Chain isomerism is shown when the compound can exist in a long straight chain or a branched chain. Let us take an example of pentane. Chemical formula of pentane is ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}$. It can exist as isomers like iso-pentane and neopentane.

Pentane, isopentane and neopentane are examples of chain isomers. They have the same chemical formula i.e. ${{C}_{5}}{{H}_{12}}$ but the structure is different.
Now, if we take a 3 membered chain, like propane, we cannot form any such isomers for it. So, the minimum number of carbon atoms required for this isomerism is 4.
So, the assertion is correct.
Now, let us see the reason. For alkanes, n-butane is a straight chain compound whereas iso-butane is branched. For alkenes, oct – 1 – ene is straight chain but methyl hept – 1 – ene is branched. For alkynes, oct – 1 – yne is straight chain but methylhept – 1 – yne is branched. So, they show chain isomerism. So, the reason is incorrect as alkanes along with alkenes and alkynes can show chain isomerism. So, the reason is incorrect.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] assertion is correct and reason is incorrect.
NOTE: Isomerism is the phenomenon where two or more chemical compounds have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures. The compounds showing isomerism are known as isomers. Besides chain isomerism that we discussed above, there are other isomerisms shown by organic compounds. Chain isomerism is a structural isomerism. There are other isomers under this category like functional isomerism, ring-chain isomerism, metamerism and tautomerism. Besides structural isomerism, organic compounds also show stereoisomerism where the chemical formula and the sequence of bonding is the same but they differ in their spatial arrangements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




