
Assertion
Allylic and benzylic halides show high reactivity towards ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction
Reason
$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ and can show hyper conjugation
a.) Both assertion and the reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion
b.) Both assertion and the reason are correct and reason is not the correct explanation for assertion
c.) Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect
d.) Both assertion and reason are incorrect

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: ${{S}_{N}}1$ Reactions are substitution reaction in organic chemistry. These reactions are unimolecular, they have a stepwise mechanism. The 1 in ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction says that the rate determining step is unimolecular.
Complete step by step answer:
${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, it involves the attack of a positively charged or a partially positively charged atom or group by a nucleophile. Nucleophiles are species which are rich in electrons; they can donate an electron pair.
${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction follows the first order kinetics and it is a two-step reaction. The rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of the substrate. Carbocation is formed as an intermediate in the ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction after the removal of the leaving group. ${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction gives the mixture of product with the retention and inversion in configuration. This leads to racemization.
Mechanism of ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction is shown below:
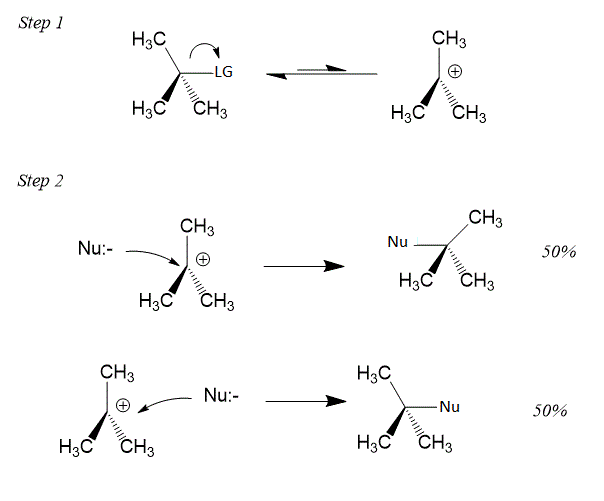
In both Allylic and benzylic halides carbocation is more stable, hence it becomes easy for the nucleophile to attack the carbocation and form a product.
The correct answer is option “A” .
Additional Information :
${{S}_{N}}2$ Reaction follows the second order kinetics and it is a single step reaction. The rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of the substrate and nucleophile. There is a formation of a single transition state in ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction. ${{S}_{N}}2$ Reaction leads to a back-side attack, which leads to the inversion of stereochemistry of the carbon atom, here a complete inversion of configuration takes place.
Note: Hyperconjugation is the interaction of the sigma bond, it can explain the stability of carbocations. Tertiary carbocation is more stable due to the presence of three methyl groups which distribute its positive charge. The order of stability of carbocation is:
Tertiary carbocation > secondary carbocation > primary carbocation
Complete step by step answer:
${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, it involves the attack of a positively charged or a partially positively charged atom or group by a nucleophile. Nucleophiles are species which are rich in electrons; they can donate an electron pair.
${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction follows the first order kinetics and it is a two-step reaction. The rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of the substrate. Carbocation is formed as an intermediate in the ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction after the removal of the leaving group. ${{S}_{N}}1$ Reaction gives the mixture of product with the retention and inversion in configuration. This leads to racemization.
Mechanism of ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction is shown below:

In both Allylic and benzylic halides carbocation is more stable, hence it becomes easy for the nucleophile to attack the carbocation and form a product.
The correct answer is option “A” .
Additional Information :
${{S}_{N}}2$ Reaction follows the second order kinetics and it is a single step reaction. The rate of the reaction depends upon the concentration of the substrate and nucleophile. There is a formation of a single transition state in ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction. ${{S}_{N}}2$ Reaction leads to a back-side attack, which leads to the inversion of stereochemistry of the carbon atom, here a complete inversion of configuration takes place.
Note: Hyperconjugation is the interaction of the sigma bond, it can explain the stability of carbocations. Tertiary carbocation is more stable due to the presence of three methyl groups which distribute its positive charge. The order of stability of carbocation is:
Tertiary carbocation > secondary carbocation > primary carbocation
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




