
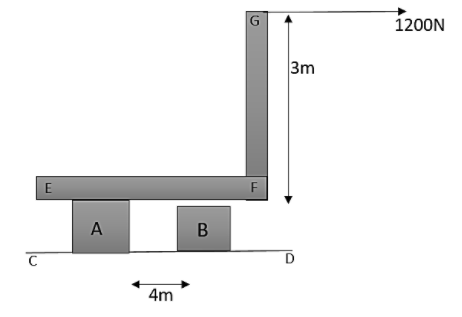
As shown in the figure below, A and B are two short steel rods each of cross-sectional area $5c{{m}^{2}}$. The lower ends of the rods A and B are welded to a fixed plate CD. The upper end of A is welded to the L−shaped piece EFG, which can slide without friction on the upper end of B. A horizontal pull of $1200N$ is exerted at G. Note that neglect the weight of EFG. Therefore the longitudinal stress in B is
A. tensile in nature and having a magnitude $180N{{m}^{-2}}$
B. tensile in nature and having a magnitude $240N{{m}^{-2}}$$180N{{m}^{-2}}$
C. compressive in nature and having a magnitude $180N{{m}^{-2}}$
D. compressive in nature and having a magnitude $240N{{m}^{-2}}$

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: First of all draw the diagram of the figure especially the L-shaped piece. Then draw the normal force acting in the diagram. At vertical equilibrium, these normal forces will be equal. Find the torque about E. then find the longitudinal stress acting in B with a help of a free body diagram.
Complete answer:
First of all let us draw the diagram as per the conditions mentioned in the question. Let the normal reaction at A be ${{N}_{1}}$ and at B be ${{N}_{2}}$.
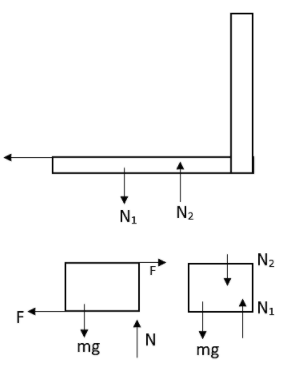
On the L-shaped piece these normal forces will be acting such as ${{N}_{1}}$ in the downward direction and ${{N}_{2}}$ in the upward direction.
In the vertical equilibrium, these normal forces will be equal.
${{N}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}$
The torque acting about E,
${{N}_{2}}\times 4=1200\times 3$
From this, we will get that,
${{N}_{2}}=900$
From the free body diagram,
The longitudinal stress acting over B can be written as,
$S=\dfrac{{{N}_{2}}}{5}=\dfrac{900}{5}=180Nc{{m}^{-2}}$
This will be compressive in nature also.
Therefore the correct answer for this question is option C.
Note:
The direction of the longitudinal stress acting over a steel rod will be parallel to the longitudinal axis of its centre line axis. This means that it is the stress acting in the direction of the rod’s length. Therefore it is also known as axial stress.
Complete answer:
First of all let us draw the diagram as per the conditions mentioned in the question. Let the normal reaction at A be ${{N}_{1}}$ and at B be ${{N}_{2}}$.

On the L-shaped piece these normal forces will be acting such as ${{N}_{1}}$ in the downward direction and ${{N}_{2}}$ in the upward direction.
In the vertical equilibrium, these normal forces will be equal.
${{N}_{1}}={{N}_{2}}$
The torque acting about E,
${{N}_{2}}\times 4=1200\times 3$
From this, we will get that,
${{N}_{2}}=900$
From the free body diagram,
The longitudinal stress acting over B can be written as,
$S=\dfrac{{{N}_{2}}}{5}=\dfrac{900}{5}=180Nc{{m}^{-2}}$
This will be compressive in nature also.
Therefore the correct answer for this question is option C.
Note:
The direction of the longitudinal stress acting over a steel rod will be parallel to the longitudinal axis of its centre line axis. This means that it is the stress acting in the direction of the rod’s length. Therefore it is also known as axial stress.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




