
As shown in the figure a chain mv is placed on a smooth quarter circular portion of radius $ R $ . End $ A $ is tied with wedge while remaining chain is free, then minimum work done required by external agent to make the chain horizontal keeping $ A $ point fixed is:
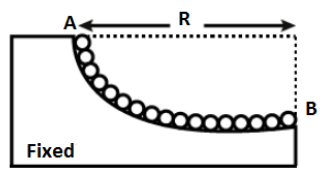
$ \left( A \right)mgR\left( {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right) \\
\left( B \right)mg\dfrac{{2R}}{\pi } \\
\left( C \right)mg\sqrt 2 \dfrac{{2R}}{\pi } \\
\left( D \right)None \\ $

Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint :In order to solve this question, we are going to consider a small mass element $ dm $ on the arc length, then, the corresponding amount of work done for displacement of mass from $ 0\,to\,R $ , which is equivalent to the initial potential energy and thereby finding the final potential energy, we get minimum work done.
The small mass element $ dm $ subtends an angle $ d\theta $ at the centre, can be found using formula
$ dm = \dfrac{m}{{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}}d\theta $
The potential energy is given by
$ dW = dmgh $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider a small mass element $ dm $ subtends an angle $ d\theta $ at the centre,
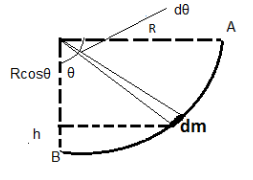
It is given by
$ dm = \dfrac{m}{{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}}d\theta $
So ,the potential energy is given by
$ dW = dmgh = \dfrac{{2m}}{\pi }gd\theta \left( {R - R\cos \theta } \right) $
Therefore, we can write that,
$ {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} d\theta \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\left[ {\left[ \theta \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} - \left[ {\sin \theta } \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = mgR\left[ {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right] \\ $
And the final potential energy is zero as the orientation becomes horizontal,
i.e., $ {U_f} = 0 $
Thus, it can be concluded that the minimum of work equal to $ {U_i} = mgR\left[ {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right] $ in joules has to be done by an external agent.
Hence, the correct answer is the option, $ \left( A \right)mgR\left( {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right) $ .
Note :
It is to be noted that when the chain is at the initial step it has a considerable amount of potential energy, we are given that the chain on being set free comes horizontal at the surface which gives the clue of the potential energy becoming zero at final step and the difference between them has given minimum work.
The small mass element $ dm $ subtends an angle $ d\theta $ at the centre, can be found using formula
$ dm = \dfrac{m}{{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}}d\theta $
The potential energy is given by
$ dW = dmgh $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider a small mass element $ dm $ subtends an angle $ d\theta $ at the centre,

It is given by
$ dm = \dfrac{m}{{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}}d\theta $
So ,the potential energy is given by
$ dW = dmgh = \dfrac{{2m}}{\pi }gd\theta \left( {R - R\cos \theta } \right) $
Therefore, we can write that,
$ {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\left( {1 - \cos \theta } \right)} d\theta \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\left[ {\left[ \theta \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} - \left[ {\sin \theta } \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = \dfrac{{2mgR}}{\pi }\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{2} - 1} \right] \\
\Rightarrow {U_i} = mgR\left[ {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right] \\ $
And the final potential energy is zero as the orientation becomes horizontal,
i.e., $ {U_f} = 0 $
Thus, it can be concluded that the minimum of work equal to $ {U_i} = mgR\left[ {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right] $ in joules has to be done by an external agent.
Hence, the correct answer is the option, $ \left( A \right)mgR\left( {1 - \dfrac{2}{\pi }} \right) $ .
Note :
It is to be noted that when the chain is at the initial step it has a considerable amount of potential energy, we are given that the chain on being set free comes horizontal at the surface which gives the clue of the potential energy becoming zero at final step and the difference between them has given minimum work.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




