
Arrange the given set of compounds in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, ${E^ + }$.

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Electrophiles are electron deficient species, so they want a nucleophile which donates electrons to them. The higher the electron density on a benzene ring, the higher is the reactivity towards electrophile. \[N{O_2}\] is an electron withdrawing group, it deactivates the benzene ring towards electrophilic by decreasing the electron density from the ring.
Complete step by step answer: Electrophiles are the reagents that participate in a reaction by accepting an electron pair in order to bond to nucleophiles.
The higher the electron density on a benzene ring, the more reactive is the compound towards an electrophile, ${E^ + }$ (Electrophilic reaction).
The presence of an electron withdrawing group that is, \[N{O_2}\] and \[C{l^ - }\] deactivates the aromatic ring by decreasing the electron density.
Since the\[N{O_2}\] group is more electron withdrawing due to the resonance effect than the \[C{l^ - }\] group due to the inductive effect.
As the number of electrons withdrawing nitro groups on the benzene nucleus increases, the electron density of the benzene ring decreases and the reactivity with an electrophile decreases.
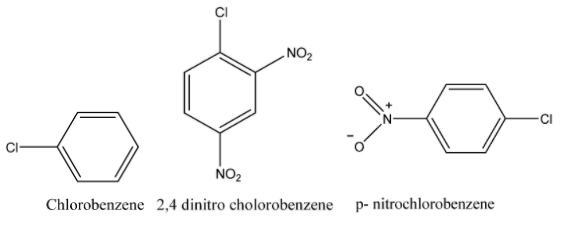
The decreasing order of relative reactivity with an electrophile is:
Chlorobenzene > p - nitro chlorobenzene > 2,4 - dinitrochlorobenzene
Note: Nitro group is a deactivating group and its presence on the benzene ring will deactivate it towards electrophile attack since electrophile seeks a centre of high electron density. Thus, a greater number of nitro groups present, the lesser will be the reactivity of the compounds towards electrophilic substitution.
Since the reagents and conditions employed in the reactions are electrophilic, these reactions are commonly referred to as Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
Complete step by step answer: Electrophiles are the reagents that participate in a reaction by accepting an electron pair in order to bond to nucleophiles.
The higher the electron density on a benzene ring, the more reactive is the compound towards an electrophile, ${E^ + }$ (Electrophilic reaction).
The presence of an electron withdrawing group that is, \[N{O_2}\] and \[C{l^ - }\] deactivates the aromatic ring by decreasing the electron density.
Since the\[N{O_2}\] group is more electron withdrawing due to the resonance effect than the \[C{l^ - }\] group due to the inductive effect.
As the number of electrons withdrawing nitro groups on the benzene nucleus increases, the electron density of the benzene ring decreases and the reactivity with an electrophile decreases.
The decreasing order of relative reactivity with an electrophile is:
Chlorobenzene > p - nitro chlorobenzene > 2,4 - dinitrochlorobenzene
Note: Nitro group is a deactivating group and its presence on the benzene ring will deactivate it towards electrophile attack since electrophile seeks a centre of high electron density. Thus, a greater number of nitro groups present, the lesser will be the reactivity of the compounds towards electrophilic substitution.
Since the reagents and conditions employed in the reactions are electrophilic, these reactions are commonly referred to as Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




