
Arrange the following in order of acidic character:
$I.)$
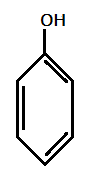
$II.)$
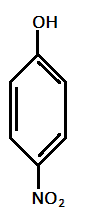
$III.)$
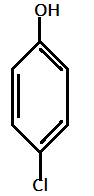
$IV.)$
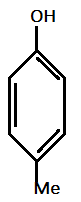
$V.)$





Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: If the functional group attached to the benzene ring in an aromatic compound is an electron withdrawing group then the compound will be less acidic and if the functional group attached to the aromatic compound is an electron donating group then the compound will be more acidic.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, all the compounds contain phenol groups with some different functional groups attached to them. As we know that an acid is that substance which will easily donate ${H^ + }$ ions. And after removing ${H^ + }$ from the acid the corresponding conjugate base is obtained. Therefore, the good acid will be that acid in which after removing ${H^ + }$ ions, the conjugate base will be stable. Thus, the more stable acid will have a more stable conjugate base.
Also, we know that after removing ${H^ + }$ from the acid, the conjugate base will get a negative sign and this conjugate base will be more stable if that negative sign will get more electron density.
As we know that an electron donating group will produce more electron density on the conjugate base which makes the conjugate base more stable and thus make the compound more acidic. And also, an electron withdrawing group will decrease the electron density on the conjugate base which makes the conjugate base less stable and thus make the compound less acidic.
Hence, the electron withdrawing group decreases the acidity and the electron donating group increases the acidity.
In the given compounds, $N{O_2}$ and $Cl$ are electron withdrawing groups with order of electron withdrawing as: $ - N{O_2} > - Cl$
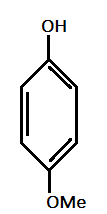
And methyl ($Me$) and Methoxy($OMe$) are electron donating groups with order of electron donating as : $ - OMe > - Me$.
Hence, most acidic compound is $V.)$ containing Methoxy($\text{OMe}$), second will be $IV.)$ containing $ - Me$ group, third will be $I.)$ containing no group , Fourth will be $III.)$ containing chlorine and then the $II.)$ which contains $ N{O_2 }$ group.
Therefore, the correct order of acidity is: $V > IV > I > III > II$.
Note:
Always remember that to see the acidity of a compound we will see whether the conjugate base of the given compound (which is obtained by removing hydrogen from that acid) is more stable or not.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, all the compounds contain phenol groups with some different functional groups attached to them. As we know that an acid is that substance which will easily donate ${H^ + }$ ions. And after removing ${H^ + }$ from the acid the corresponding conjugate base is obtained. Therefore, the good acid will be that acid in which after removing ${H^ + }$ ions, the conjugate base will be stable. Thus, the more stable acid will have a more stable conjugate base.
Also, we know that after removing ${H^ + }$ from the acid, the conjugate base will get a negative sign and this conjugate base will be more stable if that negative sign will get more electron density.
As we know that an electron donating group will produce more electron density on the conjugate base which makes the conjugate base more stable and thus make the compound more acidic. And also, an electron withdrawing group will decrease the electron density on the conjugate base which makes the conjugate base less stable and thus make the compound less acidic.
Hence, the electron withdrawing group decreases the acidity and the electron donating group increases the acidity.
In the given compounds, $N{O_2}$ and $Cl$ are electron withdrawing groups with order of electron withdrawing as: $ - N{O_2} > - Cl$
And methyl ($Me$) and Methoxy($OMe$) are electron donating groups with order of electron donating as : $ - OMe > - Me$.
Hence, most acidic compound is $V.)$ containing Methoxy($\text{OMe}$), second will be $IV.)$ containing $ - Me$ group, third will be $I.)$ containing no group , Fourth will be $III.)$ containing chlorine and then the $II.)$ which contains $ N{O_2 }$ group.
Therefore, the correct order of acidity is: $V > IV > I > III > II$.
Note:
Always remember that to see the acidity of a compound we will see whether the conjugate base of the given compound (which is obtained by removing hydrogen from that acid) is more stable or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




