
Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing metallic character: \[Sc,\text{ }Fe,\text{ }Rb,\text{ }Br,\text{ }O,\text{ }Ca,\text{ }F,\text{ }Te\]
A. \[Rb\text{ }>\text{ }Ca\text{ }>\text{ }Sc\text{ }>\text{ }Fe\text{ }>\text{ }Te\text{ }>\text{ }Br\text{ }>\text{ }O\text{ }>\text{ }F\]
B. \[Ca\text{ }>Rb\text{ }>\text{ }Sc\text{ }>\text{ }Fe\text{ }>\text{ }Br\text{ }>\text{ }Te\text{ }>\text{ }O\text{ }>\text{ }F\]
C. \[Rb\text{ }>\text{ }Sc\text{ }>\text{ }Ca\text{ }>\text{ }Fe\text{ }>\text{ }Te\text{ }>\text{ }Br\text{ }>\text{ }F\text{ }>\text{ }O\]
D. None of these
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:Metallic character is a periodic trend which could be observed in periodic tables.
The more loosely bound the electron is, the more metallic character it will have.
Complete step by step answer:
-Metallic character denotes the extent of the reactivity of a metal. In chemical reactions, metals tend to lose electrons, as we can see by their low ionization energies. Within a compound, metal atoms relatively attract electrons in a more lenient way, as indicated by their low electronegativities.
-Non-metals tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions and have a high affinity for electrons inside a compound. The most reactive non-metals exist in the upper right portion of the periodic table. As we know, the noble gases are a special kind of group because of their lack of reactivity, the element fluorine is the most reactive non-metal.
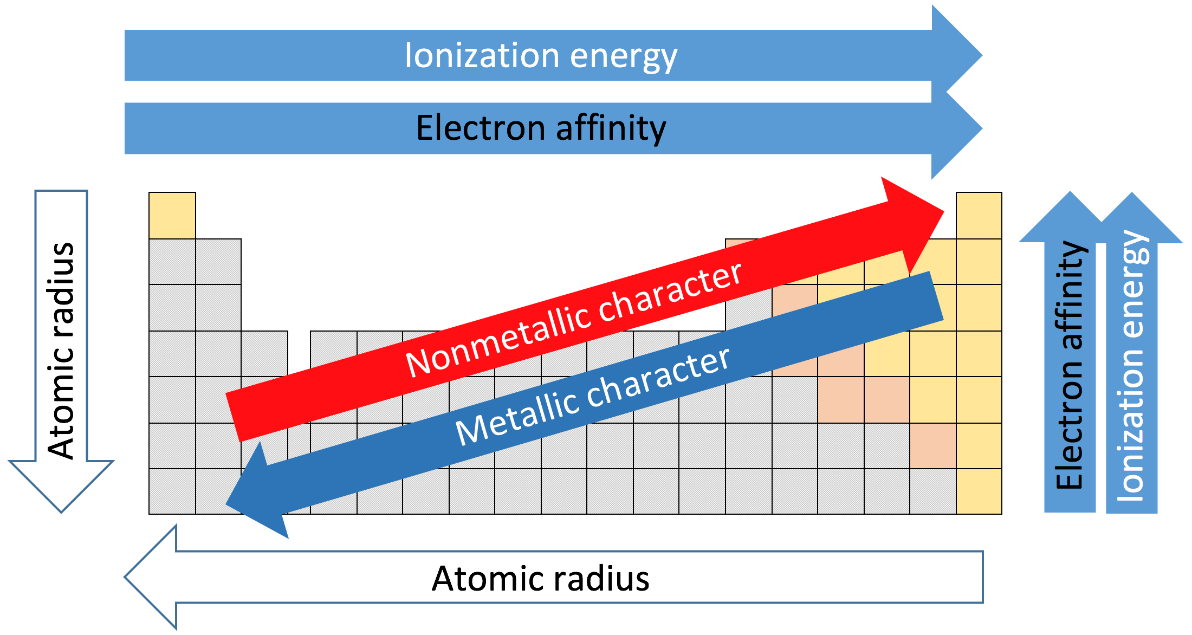
-The nuclear charge experienced by electrons, after it gets shielded by the other electrons, is called effective nuclear charge.
-From the figure above, we can see that, as we move from left to right across a period the metallic character decreases. This is because, when moving from left to right, one electron gets added in the same shell, and the effective nuclear charge experienced by each electron also increases as one neutron is also added to the nucleus. So, the ionisation energy also increases across a period, as it becomes difficult to separate the outer electrons from an isolated gaseous atom.
-Similarly, from the diagram we can see that, as we move from top to bottom in a group, the metallic character increases, as one more shell gets added each time we go down a group and the outermost electrons experience lesser effective nuclear charge, so it becomes easier to eject an electron from the outermost shell.
So the correct answer is \[Rb\text{ }>\text{ }Ca\text{ }>\text{ }Sc\text{ }>\text{ }Fe\text{ }>\text{ }Te\text{ }>\text{ }Br\text{ }>\text{ }O\text{ }>\text{ }F\].
Note:
When dealing with the metallic character of a compound, look for the ionisation enthalpy, as it can also give an idea about the metallic character of the element. if the element has higher ionisation enthalpy then it will have lower metallic character and vice versa.
The more loosely bound the electron is, the more metallic character it will have.
Complete step by step answer:
-Metallic character denotes the extent of the reactivity of a metal. In chemical reactions, metals tend to lose electrons, as we can see by their low ionization energies. Within a compound, metal atoms relatively attract electrons in a more lenient way, as indicated by their low electronegativities.
-Non-metals tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions and have a high affinity for electrons inside a compound. The most reactive non-metals exist in the upper right portion of the periodic table. As we know, the noble gases are a special kind of group because of their lack of reactivity, the element fluorine is the most reactive non-metal.

-The nuclear charge experienced by electrons, after it gets shielded by the other electrons, is called effective nuclear charge.
-From the figure above, we can see that, as we move from left to right across a period the metallic character decreases. This is because, when moving from left to right, one electron gets added in the same shell, and the effective nuclear charge experienced by each electron also increases as one neutron is also added to the nucleus. So, the ionisation energy also increases across a period, as it becomes difficult to separate the outer electrons from an isolated gaseous atom.
-Similarly, from the diagram we can see that, as we move from top to bottom in a group, the metallic character increases, as one more shell gets added each time we go down a group and the outermost electrons experience lesser effective nuclear charge, so it becomes easier to eject an electron from the outermost shell.
So the correct answer is \[Rb\text{ }>\text{ }Ca\text{ }>\text{ }Sc\text{ }>\text{ }Fe\text{ }>\text{ }Te\text{ }>\text{ }Br\text{ }>\text{ }O\text{ }>\text{ }F\].
Note:
When dealing with the metallic character of a compound, look for the ionisation enthalpy, as it can also give an idea about the metallic character of the element. if the element has higher ionisation enthalpy then it will have lower metallic character and vice versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




