
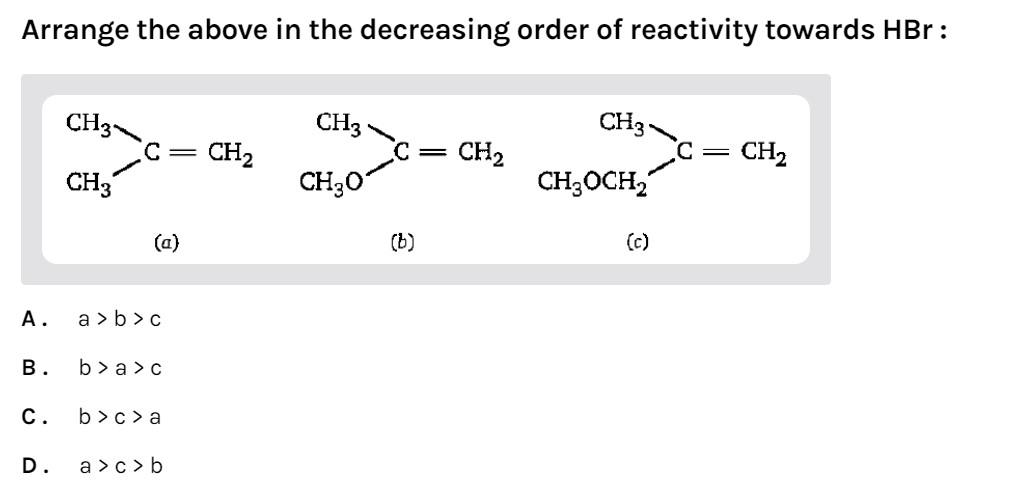
Arrange the above in the decreasing order of reactivity towards HBr:
(A)- (a) > (b) > (c)
(B)- (b) > (a) > (c)
(C)- (b) > (c) > (a)
(D)- (a) > (c) > (b)

Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The reactivity of alkenes towards HBr is dependent on the stability of the carbocation formed. So, any substituent which stabilizes the carbocation formed will increase the reactivity of that compound towards HBr.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s, see what the answer is:
-Groups like Methyl increase electron density on the carbon atom. Therefore, the more the number of methyl groups the greater the stability.
-High electronegative elements like Oxygen decrease electron density on the carbon atom. Therefore, it will decrease the reactivity towards HBr.
-The more the near oxygen is the more it will reduce electron density on the carbon atom and decrease the reactivity.
-In compound (a) there are 2 methyl groups. It will be more reactive towards HBr.
-In compound (b) the oxygen atom is directly attached to the double bonded carbon atom. It will be most reactive towards HBr as the carbocation formed will be resonance stabilized. Oxygen contains 2 lone pairs. Resonance occurs when a double bonded system is attached to an atom containing lone pairs.
-In compound (c) the oxygen atom is not directly attached to the double bonded carbon atom. So, resonance will not occur. It will be least reactive towards HBr.
So, the reactivity order will be (b) > (a) > (c)
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The addition of HBr to an alkene or alkyne is an electrophilic addition reaction. It follows Markovnikoff’s rule. It states that the hydrogen part of the acid attaches to the carbon atom having more number of hydrogens attached to it.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s, see what the answer is:
-Groups like Methyl increase electron density on the carbon atom. Therefore, the more the number of methyl groups the greater the stability.
-High electronegative elements like Oxygen decrease electron density on the carbon atom. Therefore, it will decrease the reactivity towards HBr.
-The more the near oxygen is the more it will reduce electron density on the carbon atom and decrease the reactivity.
-In compound (a) there are 2 methyl groups. It will be more reactive towards HBr.
-In compound (b) the oxygen atom is directly attached to the double bonded carbon atom. It will be most reactive towards HBr as the carbocation formed will be resonance stabilized. Oxygen contains 2 lone pairs. Resonance occurs when a double bonded system is attached to an atom containing lone pairs.
-In compound (c) the oxygen atom is not directly attached to the double bonded carbon atom. So, resonance will not occur. It will be least reactive towards HBr.
So, the reactivity order will be (b) > (a) > (c)
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The addition of HBr to an alkene or alkyne is an electrophilic addition reaction. It follows Markovnikoff’s rule. It states that the hydrogen part of the acid attaches to the carbon atom having more number of hydrogens attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




