
Why is the area under the Velocity time graph the distance?
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: The displacement of moving objects with constant velocity is equal to the product of the object velocity and the amount of time the object is in motion.
We need a velocity-time graph when the object’s velocity gets changed.
The area under the velocity-time graph is known as displacement.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw the distance-time graph of the body from the position \[{x_1}\] and \[{x_2}\] as drawn below,
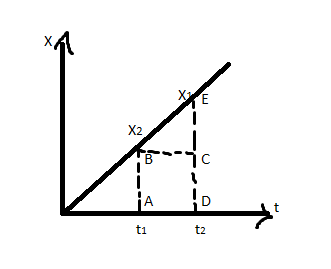
In the above diagram, the area under the curve is equal to the area of the triangle \[BCE\] and the area of the rectangle ABCD, this can be expressed as follows,
$A = (AB \times AD) + (\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times CE)$
Then this equation becomes,
$A = ({x_1})({t_2} - {t_1}) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}({t_2} - {t_1})({x_2} - {x_1})} \right)$
We have to solve the above equation then it becomes,
$A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {{x_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}{x_2} - \dfrac{1}{2}{x_1}} \right)$
After simplification the equations are,
$A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2}} \right)$
In the above equations When we consider the unit of term on the right-hand side, it gives
$A = meter \times \sec $
From this area under the distance-time graph gives nothing, Now draw the graph of the velocity of the body concerning the time
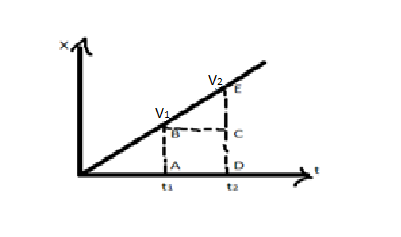
The expression for the area under the curve is as follows,
$A = (AB \times AD) + (\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times CE)$
The equation becomes,
$A = ({v_1})({t_2} - {t_1}) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}({t_2} - {t_1})({v_2} - {v_1})} \right)$
after solving the above equation,
\[A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {{v_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}{v_2} - \dfrac{1}{2}{v_1}} \right)\]
Hence it becomes,
\[A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {\dfrac{{{v_1} + {v_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
In the above equation, the right-hand side determines the unit we get,
\[A = \dfrac{{meter}}{{\sec }} \times \sec \]
\[A = meter\]
Here, the area under the curve of the velocity-time graph gives the distance covered by the object
Note:The velocity of the body is determined by the gradient curve in the distance-time graph.
The acceleration of the body is determined by the gradient curve in the velocity-time graph.
By integrating the curve we can calculate the area under the curve.
We need a velocity-time graph when the object’s velocity gets changed.
The area under the velocity-time graph is known as displacement.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw the distance-time graph of the body from the position \[{x_1}\] and \[{x_2}\] as drawn below,

In the above diagram, the area under the curve is equal to the area of the triangle \[BCE\] and the area of the rectangle ABCD, this can be expressed as follows,
$A = (AB \times AD) + (\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times CE)$
Then this equation becomes,
$A = ({x_1})({t_2} - {t_1}) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}({t_2} - {t_1})({x_2} - {x_1})} \right)$
We have to solve the above equation then it becomes,
$A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {{x_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}{x_2} - \dfrac{1}{2}{x_1}} \right)$
After simplification the equations are,
$A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2}} \right)$
In the above equations When we consider the unit of term on the right-hand side, it gives
$A = meter \times \sec $
From this area under the distance-time graph gives nothing, Now draw the graph of the velocity of the body concerning the time

The expression for the area under the curve is as follows,
$A = (AB \times AD) + (\dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times CE)$
The equation becomes,
$A = ({v_1})({t_2} - {t_1}) + \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}({t_2} - {t_1})({v_2} - {v_1})} \right)$
after solving the above equation,
\[A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {{v_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}{v_2} - \dfrac{1}{2}{v_1}} \right)\]
Hence it becomes,
\[A = ({t_2} - {t_1})\left( {\dfrac{{{v_1} + {v_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
In the above equation, the right-hand side determines the unit we get,
\[A = \dfrac{{meter}}{{\sec }} \times \sec \]
\[A = meter\]
Here, the area under the curve of the velocity-time graph gives the distance covered by the object
Note:The velocity of the body is determined by the gradient curve in the distance-time graph.
The acceleration of the body is determined by the gradient curve in the velocity-time graph.
By integrating the curve we can calculate the area under the curve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




