
What is the area of the given right-angled triangle?
I. Length of the hypotenuse is \[5\]cm.
ll. Perimeter of the triangle is four times its base
lll. One of the angles of the triangle is \[{60^0}\]
A. II only
B. III only
C. II or III only
D. II and III both
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: We are given that the length of the hypotenuse is \[5\]cm. The perimeter of the triangle is \[4\] times its base and one of the angles is \[{60^0}\]. We have to find the area of a right-angled triangle and tell which statement is correct regarding an area of the triangle.
So, firstly we will consider all statements and record the data provided then by using the area of the right-angle triangle formula and data recorded we will find out the area of a triangle.
After finding out the area of the triangle we will consider the statements and choose the best option which describes our answer.
Area of right-angled triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]base\[ \times \]height
Pythagoras theorem \[{h^2} = {p^2} + {b^2}\]where \[p\]is the perpendicular \[h\]is the hypotenuse and \[b\]is the base of the right-angled triangle.
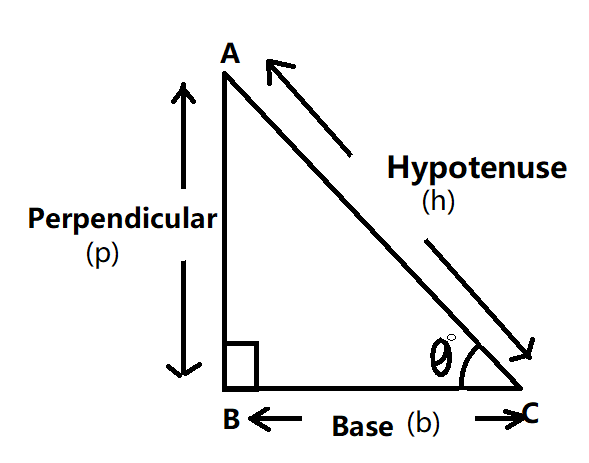
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we have \[3\] sets of the statement,
So,
>According to the first statement, we are given that
The length of the hypotenuse is \[5\]cm
Let \[h\]be the length of the hypotenuse
\[h = 5\]cm
>Now, according to the second statement, we are given that
The perimeter of the triangle is 4 times its base
Let us assume that perimeter is denoted by and the base is denoted by b”
So, according to the second statement,
\[P = 4b\]
We know that the perimeter of the right-angle triangle is equal to the sum of its side
\[
P = p + b + h \\
4b = p + b + h................(i) \\
\]
Now, putting\[h = 5\]cm in eq. \[(i)\], we get
\[3b = p + 5\]
From this, we can find the value of base and perpendicular using Pythagoras theorem
And hence, using the above we can have the values of the base, hypotenuse, and perpendicular which means that we can have the length of the sides by which using the formula area of the right-angled triangle we will put the values of base and height and we can find it.
Area of the right-angled triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]base\[ \times \]height
According to the statement\[III\], we are given that one angle is \[{60^0}\] which means that
\[\theta = {60^0}\]
We can take this in terms of \[\cos \]or \[\sin \]
The following figure will describe the statement third
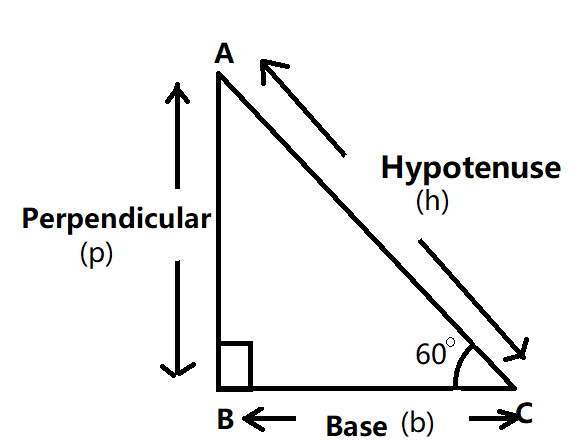
According to the statement, \[III\] we get,
\[\dfrac{p}{h} = \sin {60^0}and\dfrac{b}{h} = \cos {60^0}\]
And hence, using the above we can have the values of the base, hypotenuse, and perpendicular which means that we can have the length of the sides by which using the formula area of the right-angled triangle we will put the values of base and height and we can find it.
Since we can find the area of the triangle with both methods which provide both values of base and height
Therefore, II or III only is the correct answer. We are required to find a method so the option\[(D)\] cannot be true.
Hence we conclude that the option \[(C)\] is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students must avoid calculation mistakes as it can lead us to an incorrect solution. In this question we are only asked to consider the statements and find the correct area of the triangle, we have to not find the area of the triangle
Students must take care of the perpendicular and hypotenuse, the hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle and side opposite to the right angle.
So, firstly we will consider all statements and record the data provided then by using the area of the right-angle triangle formula and data recorded we will find out the area of a triangle.
After finding out the area of the triangle we will consider the statements and choose the best option which describes our answer.
Area of right-angled triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]base\[ \times \]height
Pythagoras theorem \[{h^2} = {p^2} + {b^2}\]where \[p\]is the perpendicular \[h\]is the hypotenuse and \[b\]is the base of the right-angled triangle.

Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we have \[3\] sets of the statement,
So,
>According to the first statement, we are given that
The length of the hypotenuse is \[5\]cm
Let \[h\]be the length of the hypotenuse
\[h = 5\]cm
>Now, according to the second statement, we are given that
The perimeter of the triangle is 4 times its base
Let us assume that perimeter is denoted by and the base is denoted by b”
So, according to the second statement,
\[P = 4b\]
We know that the perimeter of the right-angle triangle is equal to the sum of its side
\[
P = p + b + h \\
4b = p + b + h................(i) \\
\]
Now, putting\[h = 5\]cm in eq. \[(i)\], we get
\[3b = p + 5\]
From this, we can find the value of base and perpendicular using Pythagoras theorem
And hence, using the above we can have the values of the base, hypotenuse, and perpendicular which means that we can have the length of the sides by which using the formula area of the right-angled triangle we will put the values of base and height and we can find it.
Area of the right-angled triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]base\[ \times \]height
According to the statement\[III\], we are given that one angle is \[{60^0}\] which means that
\[\theta = {60^0}\]
We can take this in terms of \[\cos \]or \[\sin \]
The following figure will describe the statement third

According to the statement, \[III\] we get,
\[\dfrac{p}{h} = \sin {60^0}and\dfrac{b}{h} = \cos {60^0}\]
And hence, using the above we can have the values of the base, hypotenuse, and perpendicular which means that we can have the length of the sides by which using the formula area of the right-angled triangle we will put the values of base and height and we can find it.
Since we can find the area of the triangle with both methods which provide both values of base and height
Therefore, II or III only is the correct answer. We are required to find a method so the option\[(D)\] cannot be true.
Hence we conclude that the option \[(C)\] is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students must avoid calculation mistakes as it can lead us to an incorrect solution. In this question we are only asked to consider the statements and find the correct area of the triangle, we have to not find the area of the triangle
Students must take care of the perpendicular and hypotenuse, the hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle and side opposite to the right angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




