
Area of an isosceles triangle is given by the formula:
a is side, h is height and b is base of the triangle.
A.$$\dfrac{1}{2}bh$$
B.$$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$$
C.$$\dfrac{1}{4}b\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
D.None of the above
Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to find the area of the isosceles triangle by using a given area ‘a’, height ‘h’ and base ‘b’. For this, first we need to find the height of the isosceles triangle using a Pythagoras theorem and simplify by using a formula of the area of the triangle to get the required solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A triangle with two sides of equal length is an isosceles triangle. The two equal sides of an isosceles triangle are known as ‘legs’ whereas the third or unequal side is known as the ‘base’.
The area of a triangle is defined as the total region that is enclosed by the three sides of any particular triangle. Basically, it is equal to half of the base times height, i.e., $$Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$$ or $$A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$$.
Now, consider an isosceles triangle.
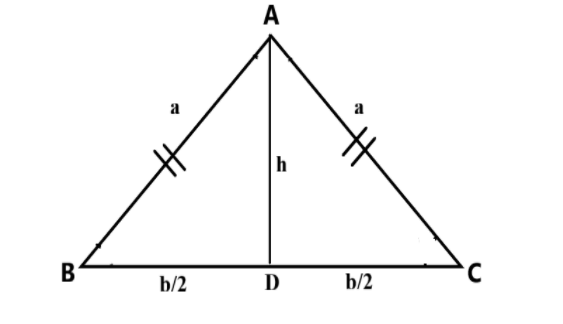
In the isosceles triangle $$\vartriangle ABC$$ and $$AD$$ be the height.
In $$\vartriangle ADC$$ is a right angled triangle, $$\angle D = {90^ \circ }$$
By the Pythagoras theorem $$hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}$$, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = \dfrac{{4{h^2} + {b^2}}}{4}$$
Multiply 4 on both the sides, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,4{a^2} = 4{h^2} + {b^2}$$
Subtract $${b^2}$$ on both the sides, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,4{a^2} - {b^2} = 4{h^2}$$
Divide 4 on both the sides
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,{h^2} = \,\dfrac{{4{a^2} - {b^2}}}{4}$$
Take square root on both the sides, then we get
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,h = \,\sqrt {\dfrac{{4{a^2} - {b^2}}}{4}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,h = \,\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
The height of the triangle $$\vartriangle ABC$$ is $$h = \,\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$.
Now, consider the formula of area of triangle i.e., $$A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$$
In $$\vartriangle ABC$$, $$BC$$ be the base of the triangle
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = BD + CD$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = \dfrac{b}{2} + \dfrac{b}{2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = b$$
The substitute the value of base and height in the formula of area of triangle, then we have
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times \dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
On simplification, we get
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,A = \dfrac{1}{4}b\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
Hence, the area of the isosceles triangle is $$\dfrac{1}{4}b\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember, Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“ i.e., $$hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}$$.
The area of the isosceles triangle can be calculated by using a Heron’s formula i.e., $$Area = \sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)} $$
Where ‘s’ is the half of the perimeter i.e.., $$s = \dfrac{{a + a + b}}{2} = a + \dfrac{b}{2}$$. On simplifying in formula we get the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A triangle with two sides of equal length is an isosceles triangle. The two equal sides of an isosceles triangle are known as ‘legs’ whereas the third or unequal side is known as the ‘base’.
The area of a triangle is defined as the total region that is enclosed by the three sides of any particular triangle. Basically, it is equal to half of the base times height, i.e., $$Area = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$$ or $$A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$$.
Now, consider an isosceles triangle.

In the isosceles triangle $$\vartriangle ABC$$ and $$AD$$ be the height.
In $$\vartriangle ADC$$ is a right angled triangle, $$\angle D = {90^ \circ }$$
By the Pythagoras theorem $$hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}$$, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = {h^2} + \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{4}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,{a^2} = \dfrac{{4{h^2} + {b^2}}}{4}$$
Multiply 4 on both the sides, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,4{a^2} = 4{h^2} + {b^2}$$
Subtract $${b^2}$$ on both the sides, then
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,\,4{a^2} - {b^2} = 4{h^2}$$
Divide 4 on both the sides
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,{h^2} = \,\dfrac{{4{a^2} - {b^2}}}{4}$$
Take square root on both the sides, then we get
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,h = \,\sqrt {\dfrac{{4{a^2} - {b^2}}}{4}} $$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,h = \,\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
The height of the triangle $$\vartriangle ABC$$ is $$h = \,\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$.
Now, consider the formula of area of triangle i.e., $$A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$$
In $$\vartriangle ABC$$, $$BC$$ be the base of the triangle
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = BD + CD$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = \dfrac{b}{2} + \dfrac{b}{2}$$
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,BC = b$$
The substitute the value of base and height in the formula of area of triangle, then we have
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times \dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
On simplification, we get
$$ \Rightarrow \,\,A = \dfrac{1}{4}b\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$
Hence, the area of the isosceles triangle is $$\dfrac{1}{4}b\sqrt {4{a^2} - {b^2}} $$.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember, Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“ i.e., $$hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}$$.
The area of the isosceles triangle can be calculated by using a Heron’s formula i.e., $$Area = \sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)} $$
Where ‘s’ is the half of the perimeter i.e.., $$s = \dfrac{{a + a + b}}{2} = a + \dfrac{b}{2}$$. On simplifying in formula we get the required area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





