
Area bounded by \[y\left| y \right|-x\left| x \right|=1,y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\] and \[y=\left| x \right|\] is
A. \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
B. \[\pi \]
C. \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
D. None of these
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:Now there are many methods to solve the question, but we use the graphical method. First we plot all the graphs of the equation given in the equation as:
\[y\left| y \right|-x\left| x \right|=1,y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\ and y=\left| x \right|\] with the graphs marked as colour of red, blue and green respectively as shown below.
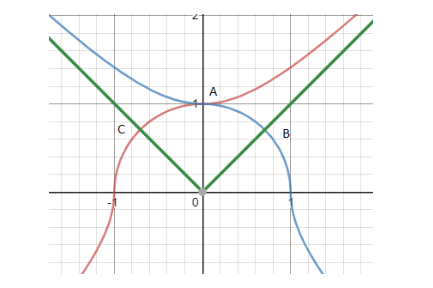
Complete step by step solution:
First find the coordinates in the graph where any two graphs are intersecting and then we find the integration of the three equations to find the area of the figure ABCD. Hence, we use the integration formula where we use the formula in terms of\[y\]:
First we find the equations in terms of \y\ for all the equation as:
\[y=\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}\, y=\sqrt{1-x\left| x \right|}\] and \[y=\left| x \right|\] and then we put the values of \[y\] in the formula given below as:
\[\Rightarrow \int\limits_{y}^{x}{\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}}+\int\limits_{B}^{A}{\sqrt{1-x\left| x
\right|}}+\int\limits_{b}^{a}{\left| x \right|}\]
Now we have put together a term for the area of the figure ABCD and to find the value of the area we will first find the limit of the points A,B,C and D. First let us equate \[y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\
and \,y=\left| x \right|\]:
\[\Rightarrow y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\ with \,y=\left| x \right|\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|\left| \left| x \right| \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\pm 0.707\] and with \[y=\left| x \right|\], we get the value of \[y=\pm 0.707\],
giving us the coordinates as:
C\[\left( -0.707,0.707 \right)\], B \[\left( 0.707,0.707 \right)\], D \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] and A\[\left( 1,1
\right)\].
Now placing the pointers in the above equation as:
\[\Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{-0.707}{\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}}+\int\limits_{0}^{0}{\sqrt{1-x\left| x
\right|}}+\int\limits_{0.707}^{0}{\left| x \right|}\]
Integrating the values of the integrations given above, we get the value of the area of ABCD as:
\[\Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{\sin }^{-1}}x}{2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+1}}{2} \right]_{0}^{-0.707}+\left[
\dfrac{{{\sin }^{-1}}x}{2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{0}+\dfrac{x\left| x
\right|}{2}_{0.707}^{0}+C\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}{2}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}+0+0-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
Changing the values of $\pi =3.14$ we get the final result as:
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.14}{8}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.14}{8}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 0.58\]unit square.
Therefore, the area of the figure ABCD is given as \[0.58\] unit square.
Note: When such questions are given point out the marks that are forming the enclosed area, and then find the area by integration of the equations given, the pointers or the limit are the x-coordinates.
\[y\left| y \right|-x\left| x \right|=1,y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\ and y=\left| x \right|\] with the graphs marked as colour of red, blue and green respectively as shown below.

Complete step by step solution:
First find the coordinates in the graph where any two graphs are intersecting and then we find the integration of the three equations to find the area of the figure ABCD. Hence, we use the integration formula where we use the formula in terms of\[y\]:
First we find the equations in terms of \y\ for all the equation as:
\[y=\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}\, y=\sqrt{1-x\left| x \right|}\] and \[y=\left| x \right|\] and then we put the values of \[y\] in the formula given below as:
\[\Rightarrow \int\limits_{y}^{x}{\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}}+\int\limits_{B}^{A}{\sqrt{1-x\left| x
\right|}}+\int\limits_{b}^{a}{\left| x \right|}\]
Now we have put together a term for the area of the figure ABCD and to find the value of the area we will first find the limit of the points A,B,C and D. First let us equate \[y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\
and \,y=\left| x \right|\]:
\[\Rightarrow y\left| y \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\ with \,y=\left| x \right|\]
\[\Rightarrow \left| x \right|\left| \left| x \right| \right|+x\left| x \right|=1\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\pm 0.707\] and with \[y=\left| x \right|\], we get the value of \[y=\pm 0.707\],
giving us the coordinates as:
C\[\left( -0.707,0.707 \right)\], B \[\left( 0.707,0.707 \right)\], D \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] and A\[\left( 1,1
\right)\].
Now placing the pointers in the above equation as:
\[\Rightarrow \int\limits_{0}^{-0.707}{\sqrt{1+x\left| x \right|}}+\int\limits_{0}^{0}{\sqrt{1-x\left| x
\right|}}+\int\limits_{0.707}^{0}{\left| x \right|}\]
Integrating the values of the integrations given above, we get the value of the area of ABCD as:
\[\Rightarrow \left[ \dfrac{{{\sin }^{-1}}x}{2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+1}}{2} \right]_{0}^{-0.707}+\left[
\dfrac{{{\sin }^{-1}}x}{2}+\dfrac{x\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}}{2} \right]_{0}^{0}+\dfrac{x\left| x
\right|}{2}_{0.707}^{0}+C\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{\pi }{4}}{2}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}+0+0-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
Changing the values of $\pi =3.14$ we get the final result as:
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.14}{8}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.14}{8}+\dfrac{-0.707\sqrt{0.5+1}}{2}-\dfrac{0.5}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 0.58\]unit square.
Therefore, the area of the figure ABCD is given as \[0.58\] unit square.
Note: When such questions are given point out the marks that are forming the enclosed area, and then find the area by integration of the equations given, the pointers or the limit are the x-coordinates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




