
What are the uses of distance time graphs?
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The distance time graph denotes the position of the body at any instant of time. The slope of the line in the distance time graph is the velocity of the body. Check whether the distance time graph can state the acceleration of the body.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss the distance time graph to answer this question. The distance time graph denotes the position of the body at any instant of time. The distance is plotted on the y-axis and the time is plotted on the x-axis on distance time graph as shown in the figure below.
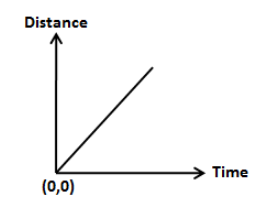
Now, let’s discuss the uses of distance time graphs. The slope of the curve shown in the above figure is,
\[m = \dfrac{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\]
Here, \[{x_2}\] is the distance of the final point, \[{x_1}\] is the distance of the initial point, \[{t_2}\] and \[{t_1}\] represents time for the respective positions.
We know that the right hand side of the above equation is the velocity of the body. Therefore, the use of the distance time graph is to predict the velocity of the body.
From the distance time graph, we can state the motion of the body. If the slope is steeper towards the distance axis, the gradient of the slope is more. Therefore, we can say that the body is moving faster. If the curve is other than a straight line, we can say that the motion of the body is not uniform.
We can state whether the body is accelerating or decelerating at a glance. If the straight line is steeper towards the distance axis, the body is accelerating and if the line is slanted towards the time axis, the body is decelerating.
Note: The speed of the body is the speed at a given instant of time. If you want to determine the speed of the body at 4 second, draw the line from 4s normal to the time axis joining the straight line and then draw the line from that point normal to the distance axis. The ratio of intersection point of the distance axis to the intersection point on the time axis is the instantaneous speed of the body. We cannot determine the exact acceleration of the body from the distance time graph at a glance.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss the distance time graph to answer this question. The distance time graph denotes the position of the body at any instant of time. The distance is plotted on the y-axis and the time is plotted on the x-axis on distance time graph as shown in the figure below.

Now, let’s discuss the uses of distance time graphs. The slope of the curve shown in the above figure is,
\[m = \dfrac{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\]
Here, \[{x_2}\] is the distance of the final point, \[{x_1}\] is the distance of the initial point, \[{t_2}\] and \[{t_1}\] represents time for the respective positions.
We know that the right hand side of the above equation is the velocity of the body. Therefore, the use of the distance time graph is to predict the velocity of the body.
From the distance time graph, we can state the motion of the body. If the slope is steeper towards the distance axis, the gradient of the slope is more. Therefore, we can say that the body is moving faster. If the curve is other than a straight line, we can say that the motion of the body is not uniform.
We can state whether the body is accelerating or decelerating at a glance. If the straight line is steeper towards the distance axis, the body is accelerating and if the line is slanted towards the time axis, the body is decelerating.
Note: The speed of the body is the speed at a given instant of time. If you want to determine the speed of the body at 4 second, draw the line from 4s normal to the time axis joining the straight line and then draw the line from that point normal to the distance axis. The ratio of intersection point of the distance axis to the intersection point on the time axis is the instantaneous speed of the body. We cannot determine the exact acceleration of the body from the distance time graph at a glance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




