
What are the two allotropes of oxygen?
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: We need to know that in chemistry, allotropy is when a compound/element exists in two more forms, and may differ in the structural arrangement of atoms or in the form of molecules having different numbers of atoms. Allotropes may be monotropic wherein one state is stable in all conditions, or enantiotropic where different states are stable in different conditions.
Complete answer:
As we know that many compounds including Carbon, Sulphur, Oxygen, tin, phosphorus display the property of allotropy. There are several allotropes of carbon.
Oxygen is an element of group $16$ and has the atomic number of $8$ . The two allotropic forms of Oxygen are:
1. Dioxygen: This is the most commonly found allotrope of Oxygen having the chemical formula of ${O_2}$. In nature Oxygen is mostly found in this form only. It constitutes about $21\% $ of the earth’s atmosphere. Dioxygen is a paramagnetic molecule having bond length of $121pm$ and a bond energy of $498KJ/mol$. The lewis dot structure of Dioxygen is:
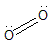
2. Ozone: Triatomic Oxygen is the most reactive allotrope of Oxygen which is destructive to materials like rubber, tissues, etc. It can be detected as a chlorine like smell that comes from rubber factories. Ozone is thermodynamically unstable unlike dioxygen. It is formed by the reaction of Dioxygen with atomic oxygen produced by splitting dioxygen by UV radiation in the upper atmosphere. Ozone absorbs strongly in the ultraviolet and functions as a shield to protect us from harmful UV rays. Ozone at ground level acts as a pollutant and can be harmful for humans. Ozone is a greenhouse gas and would contribute to global warming if present in the lower atmosphere.
Ozone is blue in colour and dark blue when it is condensed to liquid form and has a pungent ‘electric odour’. The reaction of formation of ozone is as follows:
${O_2} + {O^.} \to {O_3}$
The structure of ozone is:
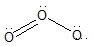
Note:
We also need to know that the other allotropic forms of oxygen are Tetra Oxygen and Solid oxygen. Tetraoxygen is one of the phases of ${O_8}$. One of the well-known solid oxygen is dark red ${O_8}$cluster. At very low temperatures, the solid oxygen phase also becomes superconducting.
Complete answer:
As we know that many compounds including Carbon, Sulphur, Oxygen, tin, phosphorus display the property of allotropy. There are several allotropes of carbon.
Oxygen is an element of group $16$ and has the atomic number of $8$ . The two allotropic forms of Oxygen are:
1. Dioxygen: This is the most commonly found allotrope of Oxygen having the chemical formula of ${O_2}$. In nature Oxygen is mostly found in this form only. It constitutes about $21\% $ of the earth’s atmosphere. Dioxygen is a paramagnetic molecule having bond length of $121pm$ and a bond energy of $498KJ/mol$. The lewis dot structure of Dioxygen is:
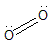
2. Ozone: Triatomic Oxygen is the most reactive allotrope of Oxygen which is destructive to materials like rubber, tissues, etc. It can be detected as a chlorine like smell that comes from rubber factories. Ozone is thermodynamically unstable unlike dioxygen. It is formed by the reaction of Dioxygen with atomic oxygen produced by splitting dioxygen by UV radiation in the upper atmosphere. Ozone absorbs strongly in the ultraviolet and functions as a shield to protect us from harmful UV rays. Ozone at ground level acts as a pollutant and can be harmful for humans. Ozone is a greenhouse gas and would contribute to global warming if present in the lower atmosphere.
Ozone is blue in colour and dark blue when it is condensed to liquid form and has a pungent ‘electric odour’. The reaction of formation of ozone is as follows:
${O_2} + {O^.} \to {O_3}$
The structure of ozone is:
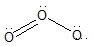
Note:
We also need to know that the other allotropic forms of oxygen are Tetra Oxygen and Solid oxygen. Tetraoxygen is one of the phases of ${O_8}$. One of the well-known solid oxygen is dark red ${O_8}$cluster. At very low temperatures, the solid oxygen phase also becomes superconducting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




