
What are the three parts of a nucleus?
Answer
477k+ views
Hint: When looking at a photograph of a cell, the nucleus is one of the most visible components. The nucleus is located at the centre of the cell and houses all of the cell's chromosomes, which encode genetic material. As a result, protecting this portion of the cell is extremely crucial.
Complete answer:
The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane that keeps all of the chromosomes within and distinguishes between the chromosomes and the various organelles and components of the cell that remain outside. Because RNA needs to travel between the nucleus and the cytoplasm on occasion, holes in the nuclear membrane allow molecules to enter and exit the nucleus. The nuclear membrane was previously considered to only enable molecules to leave the nucleus, but it has recently been shown that there is an active process for bringing molecules into the nucleus as well.
The chromosomes are stored in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, which is a double membrane-bound organelle. As a result, the nuclear membrane might be considered a component of the nucleus. It features holes that allow materials to move between the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm.
During interphase, chromatin material exists inside the nucleus in the form of a dispersed network. Chromatin material represents chromosomes that are hydrated and disorganized.
As a result, chromatin material might be considered the second portion of the nucleus.
The nucleolus is another key component of the nucleus. It is a compact spherical region within the nucleus that packages and synthesizes ribosomal subunits.
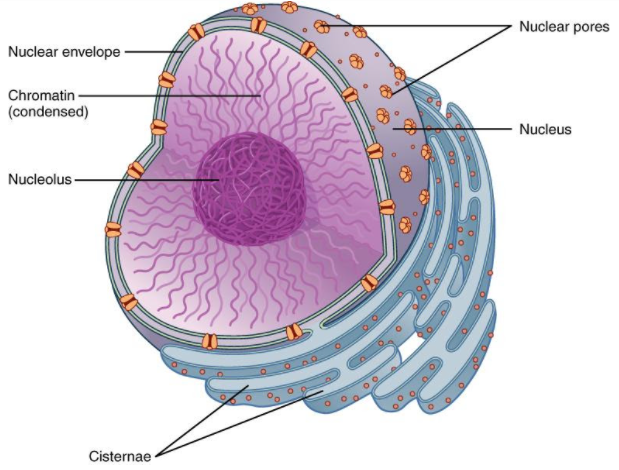
Note: The nucleus, which is surrounded by a network of fibrous intermediate filaments and wrapped in a double membrane known as the "nuclear envelope," contains virtually all of the cell's DNA. The nuclear envelope is a membrane that divides the nucleoplasm (fluid inside the nucleus) from the remainder of the cell. The nucleus' size is determined by the size of the cell in which it resides, with a nucleus generally accounting for around 8% of the total cell volume. In animal cells, the nucleus is the biggest organelle.
Complete answer:
The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane that keeps all of the chromosomes within and distinguishes between the chromosomes and the various organelles and components of the cell that remain outside. Because RNA needs to travel between the nucleus and the cytoplasm on occasion, holes in the nuclear membrane allow molecules to enter and exit the nucleus. The nuclear membrane was previously considered to only enable molecules to leave the nucleus, but it has recently been shown that there is an active process for bringing molecules into the nucleus as well.
The chromosomes are stored in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, which is a double membrane-bound organelle. As a result, the nuclear membrane might be considered a component of the nucleus. It features holes that allow materials to move between the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm.
During interphase, chromatin material exists inside the nucleus in the form of a dispersed network. Chromatin material represents chromosomes that are hydrated and disorganized.
As a result, chromatin material might be considered the second portion of the nucleus.
The nucleolus is another key component of the nucleus. It is a compact spherical region within the nucleus that packages and synthesizes ribosomal subunits.

Note: The nucleus, which is surrounded by a network of fibrous intermediate filaments and wrapped in a double membrane known as the "nuclear envelope," contains virtually all of the cell's DNA. The nuclear envelope is a membrane that divides the nucleoplasm (fluid inside the nucleus) from the remainder of the cell. The nucleus' size is determined by the size of the cell in which it resides, with a nucleus generally accounting for around 8% of the total cell volume. In animal cells, the nucleus is the biggest organelle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




