
What are the six trigonometric function values for $420^{\circ}$?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: We explain the process of finding values for associated angles. We find the rotation and the position of the angle for ${{420}^{\circ }}$. We explain the changes that are required for that angle. Depending on those things we find the solution.
Complete step by step solution:
We need to find the ratio value of six trigonometric functions for ${{420}^{\circ }}$.
For general form, we need to convert the value of x into the closest multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and add or subtract a certain value $\alpha $ from that multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to make it equal to x.
Let’s assume $x=k\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+\alpha $, $k\in \mathbb{Z}$. Here we took the addition of $\alpha $. We also need to remember that $\left| \alpha \right|\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Now we take the value of k. If it’s even then keep the ratio as it is and if it’s odd then the ratio changes to its particular form following the relation of $\sin \leftrightarrow \cos ,\sec \leftrightarrow \csc ,\tan \leftrightarrow \cot $.
Then we find the position of the given angle as quadrant value measured in counter clockwise movement from the origin and the positive side of X-axis.
The sign of the trigonometrical ratio is positive for the excess angle in their respective quadrants according to the below image.
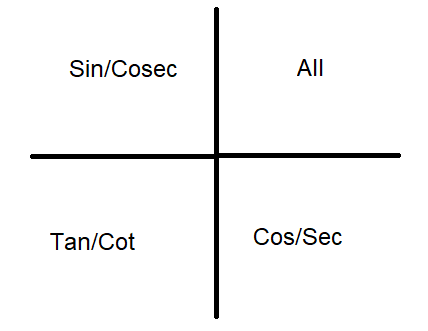
Depending on the sign and ratio change the final angle becomes $\alpha $ from x.
Now we find all six trigonometric function value for ${{420}^{\circ }}$.
The final form becomes
$\sin 420=\sin \left( 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+60 \right)=\sin \left( 60 \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\cos 420=\cos \left( 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+60 \right)=\cos \left( 60 \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\tan 420=\dfrac{\sin 420}{\cos 420}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=\sqrt{3}$
\[\csc 420=\dfrac{1}{\sin 420}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\]
$\sec 420=\dfrac{1}{\cos 420}=2$
$\cot 420=\dfrac{1}{\tan 420}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$.
Note:
We need to remember that the easiest way to avoid the change of ratio thing is to form the multiple of $\pi $ instead of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. It makes the multiplied number always even. In that case we don’t have to change the ratio. If $x=k\times \pi +\alpha =2k\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+\alpha $. Value of $2k$ is always even.
Complete step by step solution:
We need to find the ratio value of six trigonometric functions for ${{420}^{\circ }}$.
For general form, we need to convert the value of x into the closest multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and add or subtract a certain value $\alpha $ from that multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ to make it equal to x.
Let’s assume $x=k\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+\alpha $, $k\in \mathbb{Z}$. Here we took the addition of $\alpha $. We also need to remember that $\left| \alpha \right|\le \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Now we take the value of k. If it’s even then keep the ratio as it is and if it’s odd then the ratio changes to its particular form following the relation of $\sin \leftrightarrow \cos ,\sec \leftrightarrow \csc ,\tan \leftrightarrow \cot $.
Then we find the position of the given angle as quadrant value measured in counter clockwise movement from the origin and the positive side of X-axis.
The sign of the trigonometrical ratio is positive for the excess angle in their respective quadrants according to the below image.

Depending on the sign and ratio change the final angle becomes $\alpha $ from x.
Now we find all six trigonometric function value for ${{420}^{\circ }}$.
The final form becomes
$\sin 420=\sin \left( 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+60 \right)=\sin \left( 60 \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\cos 420=\cos \left( 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+60 \right)=\cos \left( 60 \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\tan 420=\dfrac{\sin 420}{\cos 420}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=\sqrt{3}$
\[\csc 420=\dfrac{1}{\sin 420}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\]
$\sec 420=\dfrac{1}{\cos 420}=2$
$\cot 420=\dfrac{1}{\tan 420}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$.
Note:
We need to remember that the easiest way to avoid the change of ratio thing is to form the multiple of $\pi $ instead of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$. It makes the multiplied number always even. In that case we don’t have to change the ratio. If $x=k\times \pi +\alpha =2k\times \dfrac{\pi }{2}+\alpha $. Value of $2k$ is always even.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




