
What are the organs of respiration in Arthropoda?
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: It is the largest phylum which includes insects and constitutes three fourth part of the animal kingdom.
Complete answer:
Arthropoda has a tracheal respiratory system in which the exchange of gases takes place at the tracheoles by the diffusion process. In this system, the tracheal carries oxygen directly to the body cells and does not require blood to transport it.
Structure:
Trachea: The respiratory system of arthropods consists of a network of the trachea. The trachea is an air tube lined with epithelial cells.
Taenidia: The cuticular lining of the trachea is spirally thickened that appears like ridges and form taenidia. It prevents the tracheal tubes from collapsing.
Spiracles: Trachea opens externally through ten pairs of small holes named spiracles present on the lateral side of the body. The opening of spiracles is regulated by sphincters.
Tracheoles: The tracheae further subdivided into finer branches called tracheoles which are air capillaries without inner taenidia ridges. Tracheoles are lined by a protein known as trachein and they are generally filled with a fluid in which oxygen dissolves and circulates to the tissues.
Tergo-sternal muscles: These paired muscles connect the dorsal side of the body to the ventral side and are responsible for breathing. On contraction, they compress the abdominal cavity forcing air to move out. During relaxed conditions, these muscles bring the abdominal cavity back into its original shape.
Book gills: In some arthropods, book gills in the form of respiratory organs are found for respiration. This structure is made up of a series of thin plates that are highly vascular that are arranged in a manner to each other like the pages of a book.
Note:
1. Many aquatic insects like mayfly and dragonfly larvae use tracheal gills for respiration in water.
2. Tracheal gills are leaf-like extensions that present on the terminal abdominal segments.
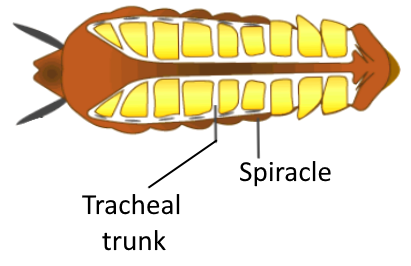
Figure: Tracheal respiration in Arthropoda
Complete answer:
Arthropoda has a tracheal respiratory system in which the exchange of gases takes place at the tracheoles by the diffusion process. In this system, the tracheal carries oxygen directly to the body cells and does not require blood to transport it.
Structure:
Trachea: The respiratory system of arthropods consists of a network of the trachea. The trachea is an air tube lined with epithelial cells.
Taenidia: The cuticular lining of the trachea is spirally thickened that appears like ridges and form taenidia. It prevents the tracheal tubes from collapsing.
Spiracles: Trachea opens externally through ten pairs of small holes named spiracles present on the lateral side of the body. The opening of spiracles is regulated by sphincters.
Tracheoles: The tracheae further subdivided into finer branches called tracheoles which are air capillaries without inner taenidia ridges. Tracheoles are lined by a protein known as trachein and they are generally filled with a fluid in which oxygen dissolves and circulates to the tissues.
Tergo-sternal muscles: These paired muscles connect the dorsal side of the body to the ventral side and are responsible for breathing. On contraction, they compress the abdominal cavity forcing air to move out. During relaxed conditions, these muscles bring the abdominal cavity back into its original shape.
Book gills: In some arthropods, book gills in the form of respiratory organs are found for respiration. This structure is made up of a series of thin plates that are highly vascular that are arranged in a manner to each other like the pages of a book.
Note:
1. Many aquatic insects like mayfly and dragonfly larvae use tracheal gills for respiration in water.
2. Tracheal gills are leaf-like extensions that present on the terminal abdominal segments.

Figure: Tracheal respiration in Arthropoda
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




