
What are the most probable velocities and the average velocity for a system that follows the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution ?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: We know that we can use Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics when a gaseous system will be in thermal equilibrium, which will give us the probability of a particle being in an energy state at a given temperature. There are three types of velocities associated with a particle in thermal equilibrium.
Complete answer:
We will consider only two velocities the most probable velocity and the average velocity as mentioned in the question:-
The most probable velocity $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ is the velocity which is velocity of the largest number of molecules, and is lower in magnitude compared to average velocity. The formula of $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\~ $ is :
$\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ = $\sqrt {\dfrac{{2RT}}{M}} $
Where $R$= Gas constant, $T$= temperature and $M$= molecular mass.
The average velocity , also known as the mean velocity $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ , is calculated as the total displacement over a given time. It is magnitude higher than that of most probable velocity, but its lesser number of molecules follow the average velocity. The magnitude of average velocity can be calculated by :
$\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ = $\sqrt {\dfrac{{8RT}}{M}} $,
Where $R$= Gas constant, $T$= temperature and $M$= molecular mass.
We can plot and represent these speeds as a graph as given below:
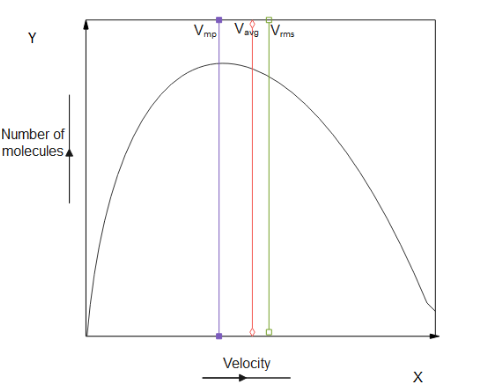
Note: There’s another type of velocity known as root mean square velocity, which is followed by the least number of electrons . It has the highest velocity among the types of velocity and its magnitude is given by : $V{}_{rms} = {\text{ }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{3RT}}{M}} $. The most important thing that has to be kept in mind is the graph and the formulas for different velocities. Calculating $V{}_{rms}$ is considering all the molecules speed and summing their squares, now the sum is square rooted and divided by the number of molecules.
Complete answer:
We will consider only two velocities the most probable velocity and the average velocity as mentioned in the question:-
The most probable velocity $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ is the velocity which is velocity of the largest number of molecules, and is lower in magnitude compared to average velocity. The formula of $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\~ $ is :
$\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ = $\sqrt {\dfrac{{2RT}}{M}} $
Where $R$= Gas constant, $T$= temperature and $M$= molecular mass.
The average velocity , also known as the mean velocity $\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ , is calculated as the total displacement over a given time. It is magnitude higher than that of most probable velocity, but its lesser number of molecules follow the average velocity. The magnitude of average velocity can be calculated by :
$\mathop \upsilon \limits^\_ $ = $\sqrt {\dfrac{{8RT}}{M}} $,
Where $R$= Gas constant, $T$= temperature and $M$= molecular mass.
We can plot and represent these speeds as a graph as given below:

Note: There’s another type of velocity known as root mean square velocity, which is followed by the least number of electrons . It has the highest velocity among the types of velocity and its magnitude is given by : $V{}_{rms} = {\text{ }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{3RT}}{M}} $. The most important thing that has to be kept in mind is the graph and the formulas for different velocities. Calculating $V{}_{rms}$ is considering all the molecules speed and summing their squares, now the sum is square rooted and divided by the number of molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




