
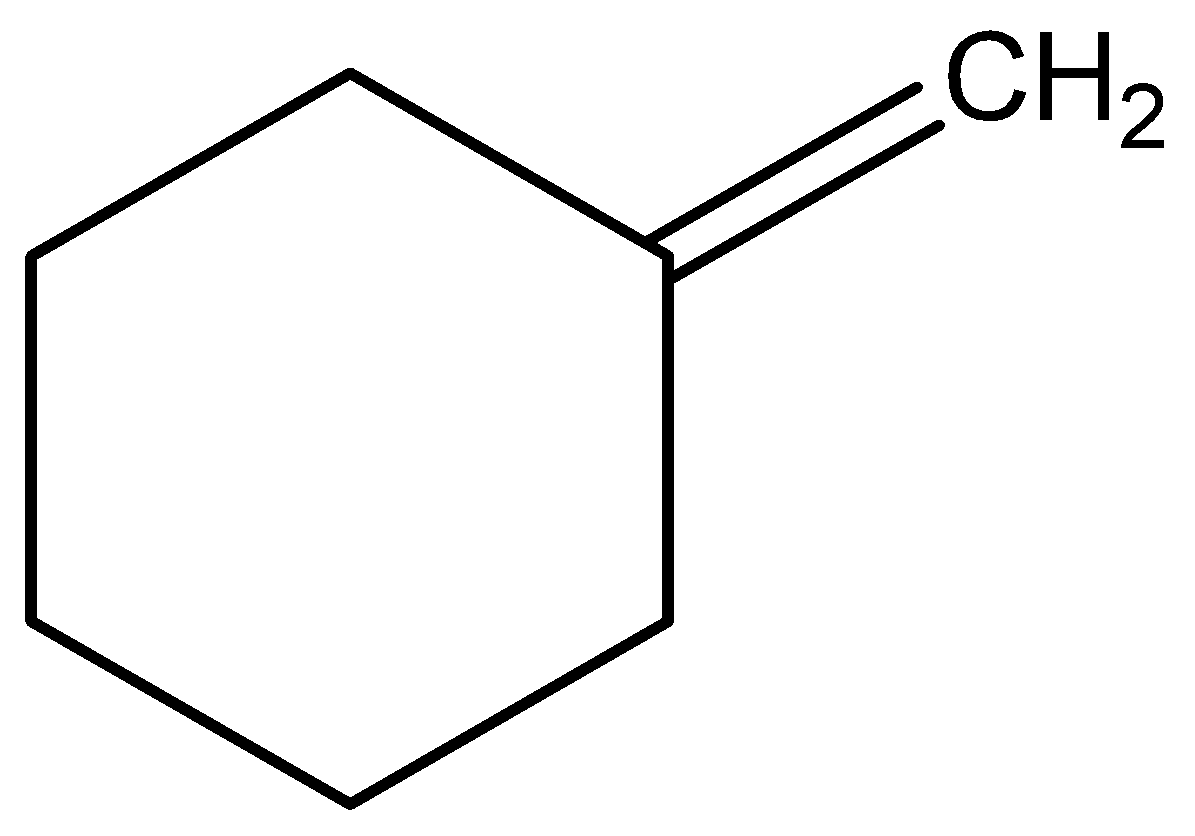
What are the major organic products when the following molecule is treated with ozone and then with \[\dfrac{{Zn}}{{{H_2}O}}\]?
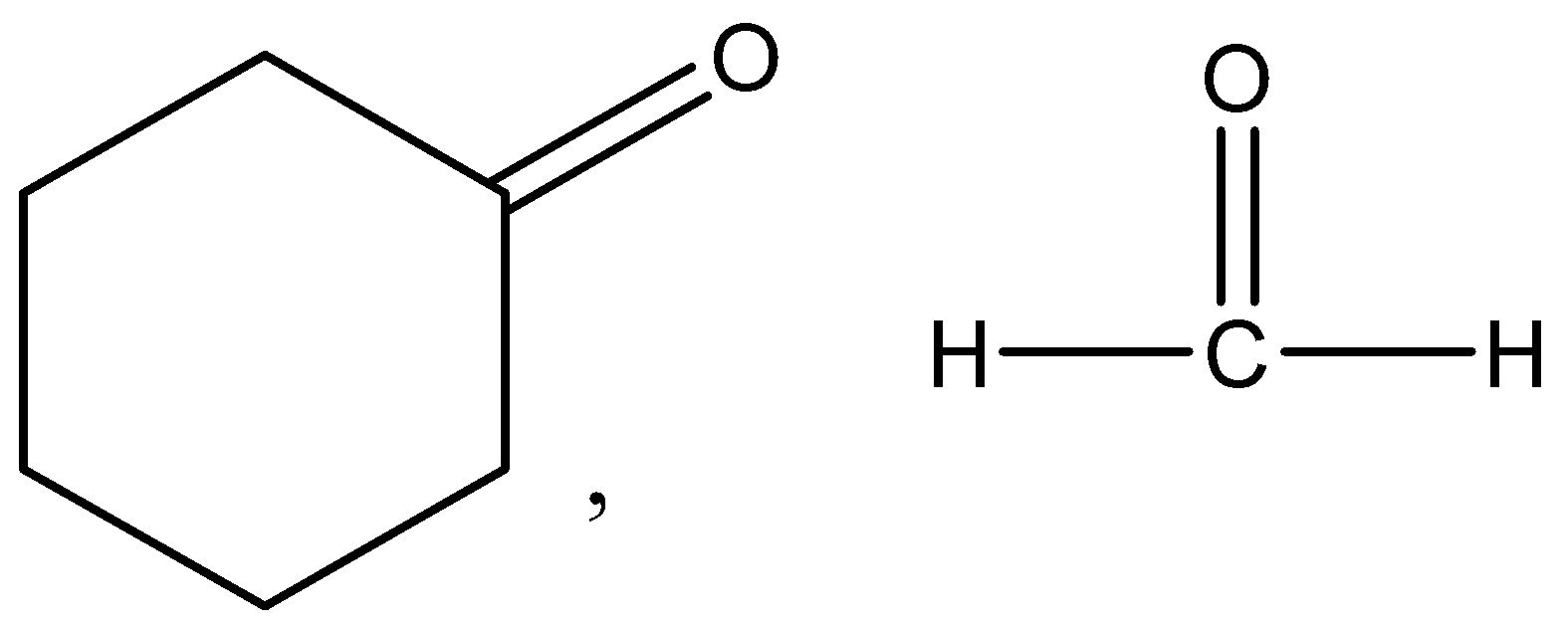
A.
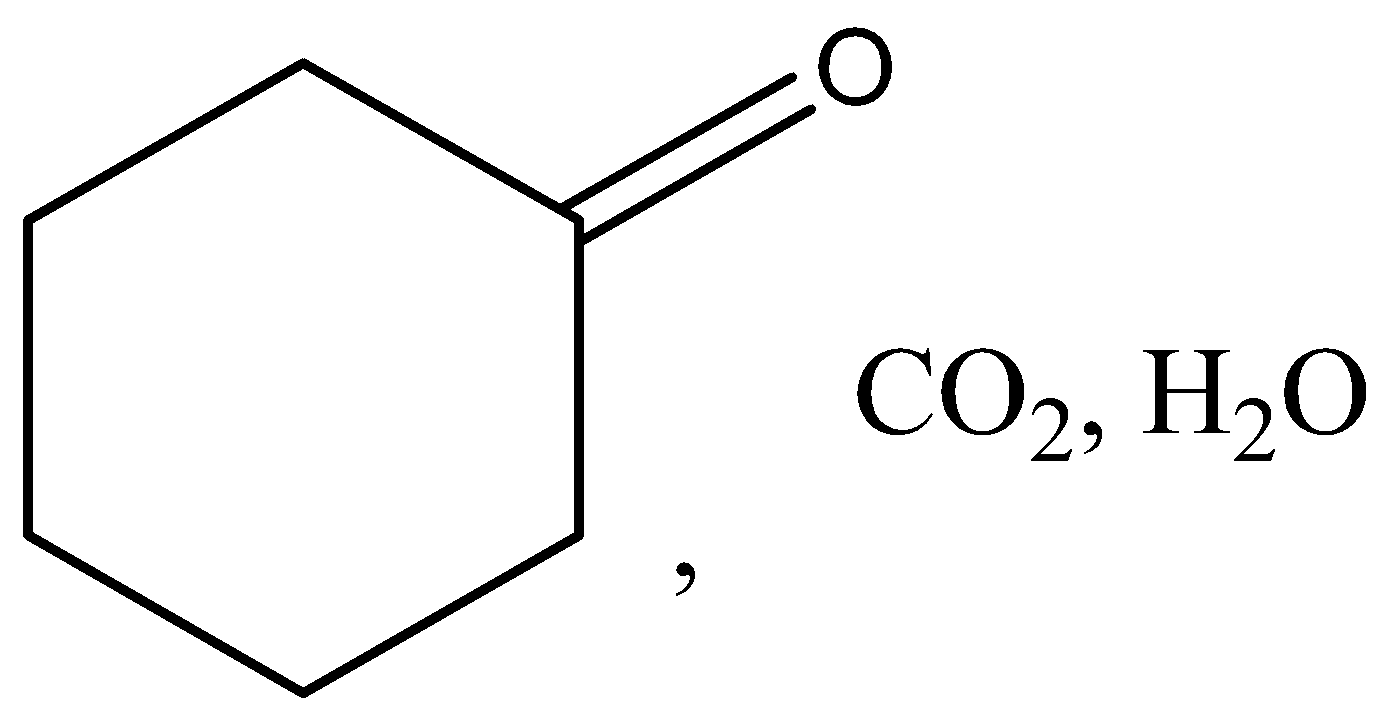
B.
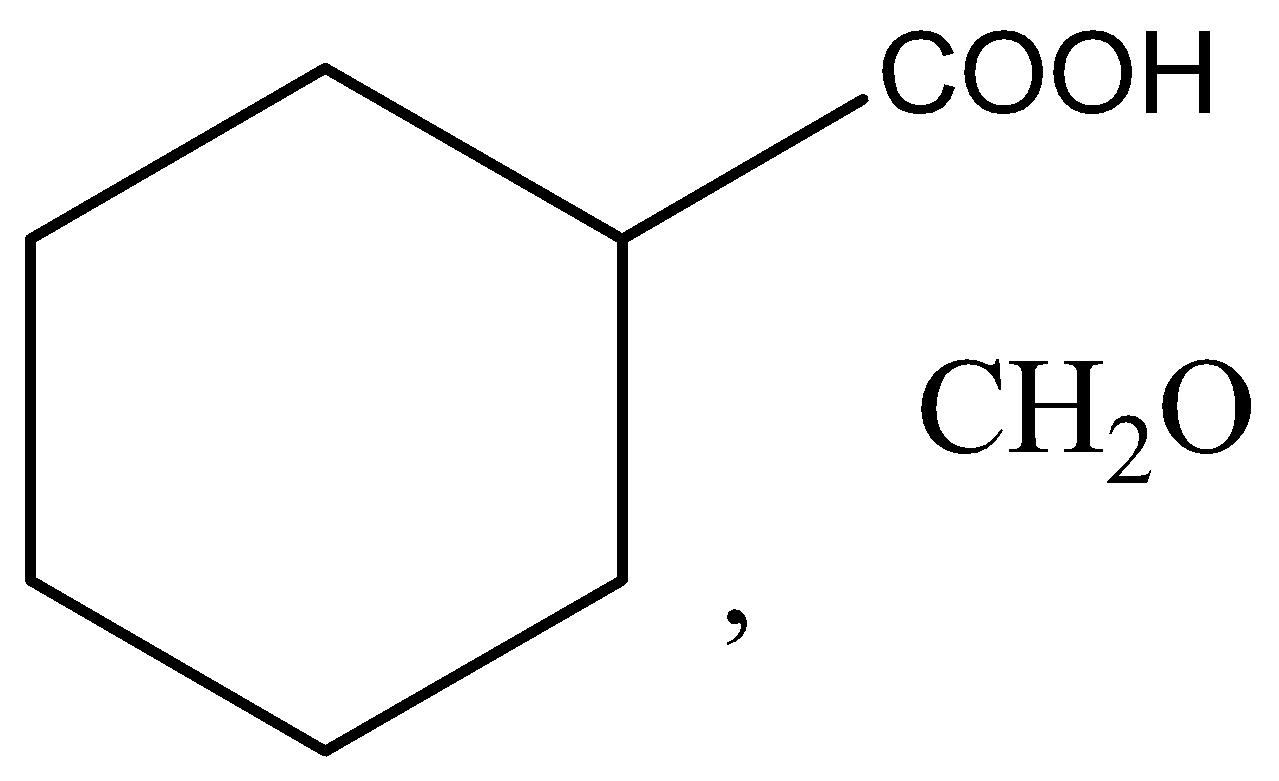
C.
D.





Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: When an alkene is treated with ozone followed by a reducing agent to break the complex double bond containing compounds into the smaller and more identifiable products. Ozonolysis is a type of weak oxidative cleavage where alkenes are cleaved (double bonds) into either ketones, aldehydes or carboxylic acid using ozone \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\].
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is a method of oxidatively cleaving alkenes or alkynes using ozone \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\], a reactive allotrope of oxygen. The process allows for carbon-carbon double or triple bonds to be replaced by double bonds with oxygen. Aldehydes (CHO), and ketones \[\left( {C{H_3}COC{H_3}} \right)\] can be formed through reductive workup.
We know that the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and we are forming a carbon-oxygen double bond on each of the two carbons that originally composed the alkene. we will end up with a ketone. And this on hydrolysis in the presence of Zinc gives aldehyde.
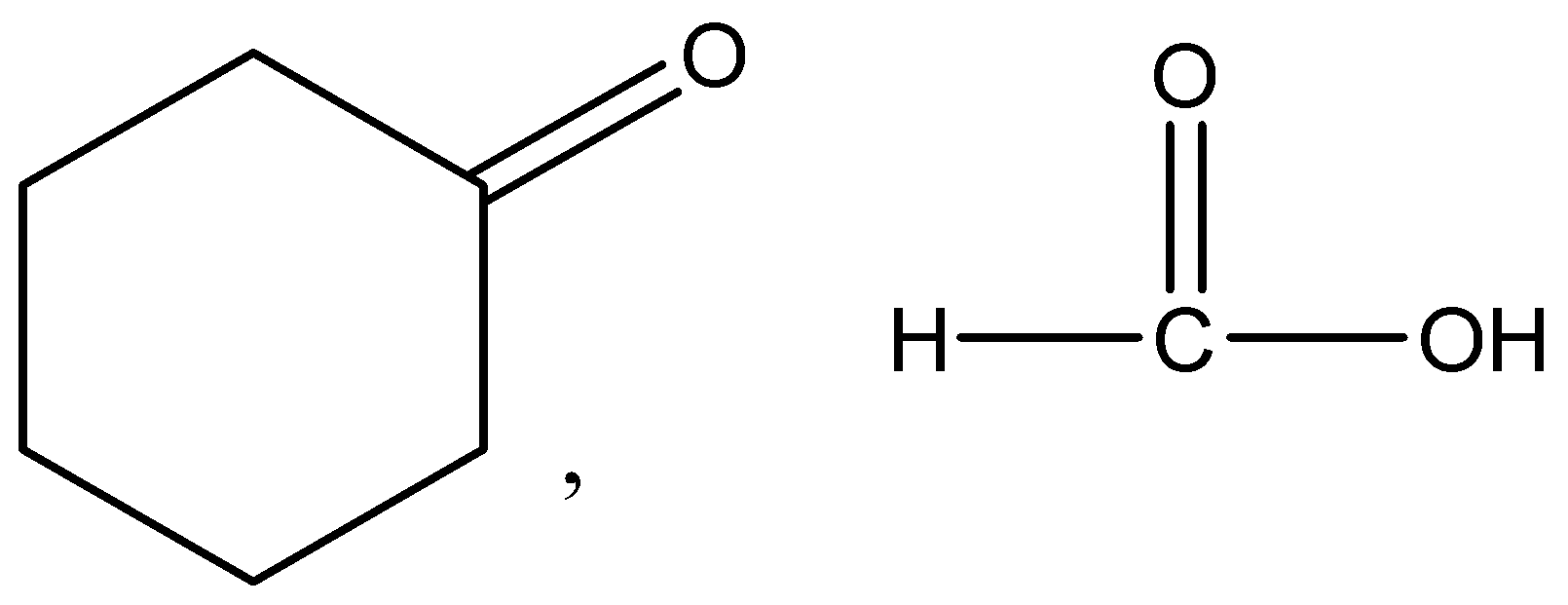
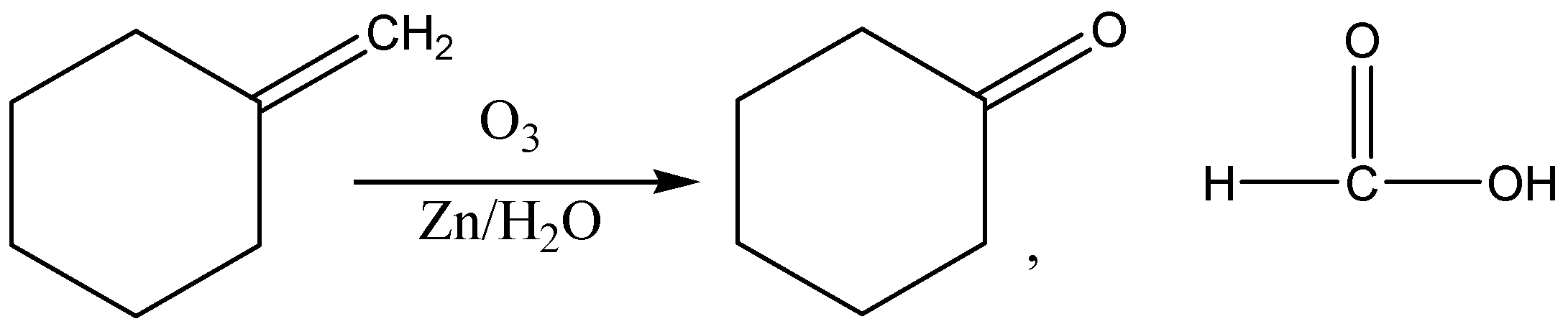
The given molecule in the question is methylene (methylene cyclohexane) and when this molecule is treated with ozone and then with \[\dfrac{{Zn}}{{{H_2}O}}\], a carbonyl group, having a carbon-to-oxygen double bond named cyclohexanone and formic acid are formed.
The reaction is shown below:
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Ozonolysis also occurs naturally and would break down repeated units used in rubber and other polymers. On an industrial scale, azelaic acid and pelargonic acids are produced from ozonolysis. Ozonolysis, or “oxidative cleavage” was originated in the 1800’s by the inventor, Christian Friedrich Schoenlein. The reaction also is attributed to Carl Dietrich Harries; therefore, we can hear a reaction termed “Harries ozonolysis”.
Complete step by step answer:
Ozonolysis is a method of oxidatively cleaving alkenes or alkynes using ozone \[\left( {{O_3}} \right)\], a reactive allotrope of oxygen. The process allows for carbon-carbon double or triple bonds to be replaced by double bonds with oxygen. Aldehydes (CHO), and ketones \[\left( {C{H_3}COC{H_3}} \right)\] can be formed through reductive workup.
We know that the carbon-carbon double bond is broken and we are forming a carbon-oxygen double bond on each of the two carbons that originally composed the alkene. we will end up with a ketone. And this on hydrolysis in the presence of Zinc gives aldehyde.
The given molecule in the question is methylene (methylene cyclohexane) and when this molecule is treated with ozone and then with \[\dfrac{{Zn}}{{{H_2}O}}\], a carbonyl group, having a carbon-to-oxygen double bond named cyclohexanone and formic acid are formed.
The reaction is shown below:

Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Ozonolysis also occurs naturally and would break down repeated units used in rubber and other polymers. On an industrial scale, azelaic acid and pelargonic acids are produced from ozonolysis. Ozonolysis, or “oxidative cleavage” was originated in the 1800’s by the inventor, Christian Friedrich Schoenlein. The reaction also is attributed to Carl Dietrich Harries; therefore, we can hear a reaction termed “Harries ozonolysis”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




