
What are the limitations of Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: The answer here is dependent on the facts about the atomic model proposed by Rutherford which described the atom as a tiny, dense and positively charged core called a nucleus and the demerits based on this gives the correct answer.
Complete answer:
In the lower classes of chemistry in the science subject, we have studied about the various models proposed to describe the atom by some scientists.
We shall see in brief about the proposed atomic model by Rutherford and then shall deduce the demerits.
> Rutherford’s atomic model was based on the experimental results that contained few features of relatively high central charge which is concentrated into very small volume when compared with the rest of the atom and also along with this central volume, bulk of atomic mass of the atom is also contained.
> This region was called as nucleus of the atom as shown below,
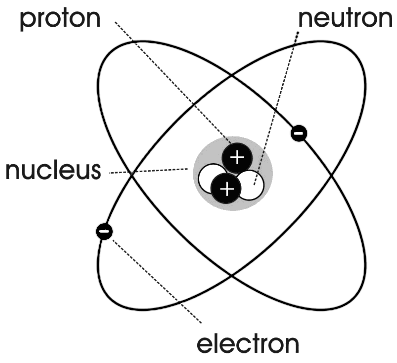
> In simple words, he described the atom as a tiny, dense positively charged core called a nucleus in which mass is concentrated and around which negative constituents called electrons revolve at some distance similar to planets revolving around the sun.
But the limitations to his model were:
> Rutherford’s model was unable to give an explanation for the stability of an atom, that is it was unable to mention anything about the arrangement of electrons in the orbit.
> According to his model, the electrons revolve at very high speed around the nucleus of an atom in a fixed orbit but Maxwell explained that accelerated charged particles release electromagnetic radiations.
Note: Note that Rutherford gave the atomic model by overturning Thomson's model with his well known gold foil experiment in which he actually demonstrated that the atom has a tiny and heavy nucleus.
Complete answer:
In the lower classes of chemistry in the science subject, we have studied about the various models proposed to describe the atom by some scientists.
We shall see in brief about the proposed atomic model by Rutherford and then shall deduce the demerits.
> Rutherford’s atomic model was based on the experimental results that contained few features of relatively high central charge which is concentrated into very small volume when compared with the rest of the atom and also along with this central volume, bulk of atomic mass of the atom is also contained.
> This region was called as nucleus of the atom as shown below,

> In simple words, he described the atom as a tiny, dense positively charged core called a nucleus in which mass is concentrated and around which negative constituents called electrons revolve at some distance similar to planets revolving around the sun.
But the limitations to his model were:
> Rutherford’s model was unable to give an explanation for the stability of an atom, that is it was unable to mention anything about the arrangement of electrons in the orbit.
> According to his model, the electrons revolve at very high speed around the nucleus of an atom in a fixed orbit but Maxwell explained that accelerated charged particles release electromagnetic radiations.
Note: Note that Rutherford gave the atomic model by overturning Thomson's model with his well known gold foil experiment in which he actually demonstrated that the atom has a tiny and heavy nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




