
What are the functions of the cornea, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve?
Answer
487.8k+ views
Hint: The eye is an organ, which is present in the protective bony socket known as orbit. Attached to the eye are six extraocular muscles. These muscles aid in moving the eye up and down and side to side, thus rotating the eye. The muscles are attached to the white portion of the eye, which is called the sclera. A strong layer of tissue covers almost the entire surface of the eyeball.Conjunctiva, a clear membrane covers the eye.
Complete answer
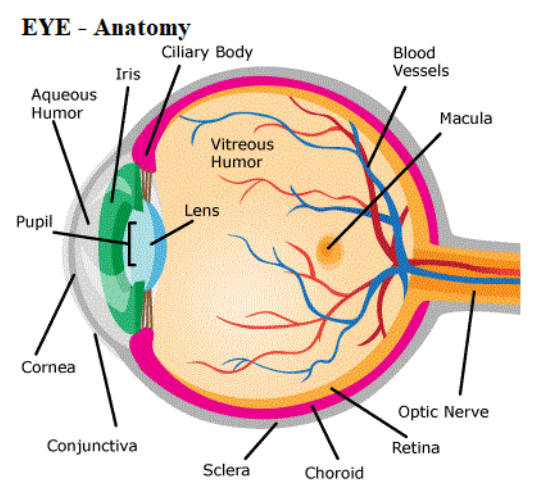
Fig: Anatomy of the Eye
There are many parts in the eye, which work in coordination for carrying out the function of providing vision. Some parts of the eye are listed and their functions are described as follows:
1. Cornea: The cornea is the front part of the tough outer coat of the eye. It is transparent and refracts light. As light enters the eye, it bends, ensuring the light is in the right place.
2. Pupil: The pupil is a hole, present in the center of the iris, which controls how much light enters the eye. The size of the pupil is controlled by the relaxation and contraction of the iris. The pupil shrinks due to the presence of higher light intensity. At the same time, it grows when there is lower light intensity. This action carried by the pupil ensures there is enough light for vision, not damaging the sensitive retinal layer.
3. Lens: Lens is a biconvex, flexible, and transparent disc present behind the iris. It focuses the light onto the retina, which is the sensitive part of the eye.
4. Retina: Retina is the lining of the back of the eye. It contains two kinds of photoreceptor cells, namely rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to dim light, black and white, while cones are sensitive to color. This aids in the detection of light in the way a camera is used in filming.
5. Optic nerve: It is a cranial nerve from the brain. It carries impulse information from the eye to the brain, where information is interpreted.
Note:
The Eye is one of the sensory organs in the body. It collects light from the visible world and converts it into nerve impulses. The optic nerve aids in the transmission of these impulses to the brain to form an image, which provides sight. The eye adjusts the amount of light it lets in constantly and focuses the objects present near and far, producing continuous images. The eye receives oxygen through the aqueous humour, nourishing cornea, iris, and lens.
Complete answer

Fig: Anatomy of the Eye
There are many parts in the eye, which work in coordination for carrying out the function of providing vision. Some parts of the eye are listed and their functions are described as follows:
1. Cornea: The cornea is the front part of the tough outer coat of the eye. It is transparent and refracts light. As light enters the eye, it bends, ensuring the light is in the right place.
2. Pupil: The pupil is a hole, present in the center of the iris, which controls how much light enters the eye. The size of the pupil is controlled by the relaxation and contraction of the iris. The pupil shrinks due to the presence of higher light intensity. At the same time, it grows when there is lower light intensity. This action carried by the pupil ensures there is enough light for vision, not damaging the sensitive retinal layer.
3. Lens: Lens is a biconvex, flexible, and transparent disc present behind the iris. It focuses the light onto the retina, which is the sensitive part of the eye.
4. Retina: Retina is the lining of the back of the eye. It contains two kinds of photoreceptor cells, namely rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to dim light, black and white, while cones are sensitive to color. This aids in the detection of light in the way a camera is used in filming.
5. Optic nerve: It is a cranial nerve from the brain. It carries impulse information from the eye to the brain, where information is interpreted.
Note:
The Eye is one of the sensory organs in the body. It collects light from the visible world and converts it into nerve impulses. The optic nerve aids in the transmission of these impulses to the brain to form an image, which provides sight. The eye adjusts the amount of light it lets in constantly and focuses the objects present near and far, producing continuous images. The eye receives oxygen through the aqueous humour, nourishing cornea, iris, and lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




