
What are the domain and range of an exponential parent function?
(a) The domain is nonnegative real numbers $\left( y\ge 0 \right)$ and the range is all real numbers.
(b) The domain is all real numbers, and the range is nonnegative real numbers $\left( y\ge 0 \right)$ .
(c) The domain is positive real numbers $\left( y>0 \right)$ and the range is all real numbers.
(d) The domain is all real numbers, and the range is positive real numbers $\left( y>0 \right)$.
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: To find the domain and range of an exponential parent function, we have to consider an exponential parent function $f\left( x \right)={{b}^{x}}$ whose base is greater than one. We have to consider the function $f\left( x \right)={{2}^{x}}$ by substituting $b=2$ . Then, we have to find the value of the function when x increases by 1. Then we have to graph this function and find the domain and range. Domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x-axis while range will be the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y-axis.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have to find the domain and range of an exponential parent function. Let us consider an exponential parent function $f\left( x \right)={{b}^{x}}$ whose base is greater than one. Let us assume $b=2$ . Therefore, the function becomes $f\left( x \right)={{2}^{x}}$ . Let us find the output values when x increases by 1.
Let us consider $x=-3$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)={{2}^{-3}}=\dfrac{1}{{{2}^{3}}}=\dfrac{1}{8}$
Now, let us consider $x=-2$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( -2 \right)={{2}^{-2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{2}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{4}$
We can find the value of the function when $x=-1$ as follows.
$\Rightarrow f\left( -1 \right)={{2}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
When $x=0$ , the value of the function will be
$\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)={{2}^{0}}=1$
Now, let us consider $x=1$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( 1 \right)={{2}^{1}}=2$
Let us consider $x=2$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{2}}=4$
Now, let us tabulate these.
Now, let us draw the graph of this function.
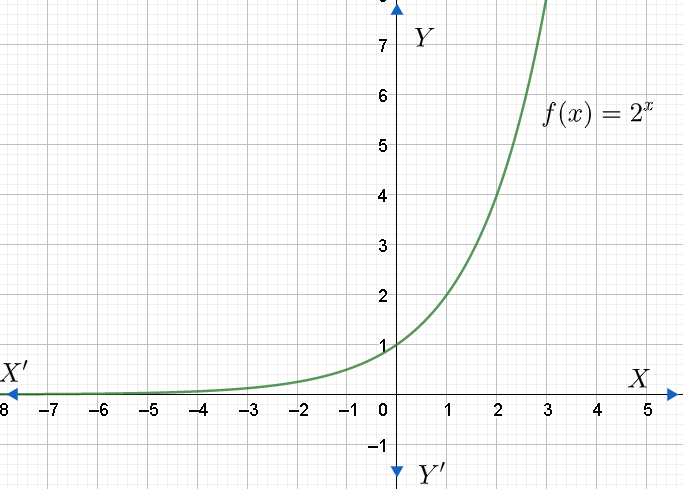
From the graph, we can see that the output values are positive for all values of x, as x increases, the output values increase without bound; and as x decreases, the output values grow smaller, approaching zero but never becomes zero.
Now, let us find the domain and range of this function. We know that domain is the set of possible input values. We can also say that the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x-axis. Here, x can be any real number. Therefore, the domain is the set of all real numbers.
Now, let us find the range. We know that range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y-axis. From the graph, we can see that y tales only positive real values, that is, $y>0$ .
Therefore, the domain is all real numbers, and the range is positive real numbers $\left( y>0 \right)$ . Hence, the correct option is d.
Note: Students must know the meaning of domain and range to find the same. From the table, we can see that output value is the product of the previous output and the base, 2. We will call the base 2 as the constant ratio. Therefore, in any exponential function $f\left( x \right)=a{{b}^{x}}$ ,b is the constant ratio of the function. We can also find the domain and range for exponential function $f\left( x \right)={{b}^{x}}$ whose base is between zero and one. The domain and the range remains the same but the graph will be an exponential decay.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have to find the domain and range of an exponential parent function. Let us consider an exponential parent function $f\left( x \right)={{b}^{x}}$ whose base is greater than one. Let us assume $b=2$ . Therefore, the function becomes $f\left( x \right)={{2}^{x}}$ . Let us find the output values when x increases by 1.
Let us consider $x=-3$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( -3 \right)={{2}^{-3}}=\dfrac{1}{{{2}^{3}}}=\dfrac{1}{8}$
Now, let us consider $x=-2$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( -2 \right)={{2}^{-2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{2}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{4}$
We can find the value of the function when $x=-1$ as follows.
$\Rightarrow f\left( -1 \right)={{2}^{-1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
When $x=0$ , the value of the function will be
$\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)={{2}^{0}}=1$
Now, let us consider $x=1$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( 1 \right)={{2}^{1}}=2$
Let us consider $x=2$ .
$\Rightarrow f\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{2}}=4$
Now, let us tabulate these.
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| $f\left( x \right)={{2}^{x}}$ | $\dfrac{1}{8}$ | $\dfrac{1}{4}$ | $\dfrac{1}{2}$ | 1 | 2 | 4 |
Now, let us draw the graph of this function.

From the graph, we can see that the output values are positive for all values of x, as x increases, the output values increase without bound; and as x decreases, the output values grow smaller, approaching zero but never becomes zero.
Now, let us find the domain and range of this function. We know that domain is the set of possible input values. We can also say that the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x-axis. Here, x can be any real number. Therefore, the domain is the set of all real numbers.
Now, let us find the range. We know that range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y-axis. From the graph, we can see that y tales only positive real values, that is, $y>0$ .
Therefore, the domain is all real numbers, and the range is positive real numbers $\left( y>0 \right)$ . Hence, the correct option is d.
Note: Students must know the meaning of domain and range to find the same. From the table, we can see that output value is the product of the previous output and the base, 2. We will call the base 2 as the constant ratio. Therefore, in any exponential function $f\left( x \right)=a{{b}^{x}}$ ,b is the constant ratio of the function. We can also find the domain and range for exponential function $f\left( x \right)={{b}^{x}}$ whose base is between zero and one. The domain and the range remains the same but the graph will be an exponential decay.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




