
What are the differences between a thorn and prickle? Describe with examples.
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Both of the parts of the plant i.e thorn and prickle are almost similar but differ only in their origin and their strength. Both help in protecting plants from insects and animals, especially herbivores.
Complete answer:
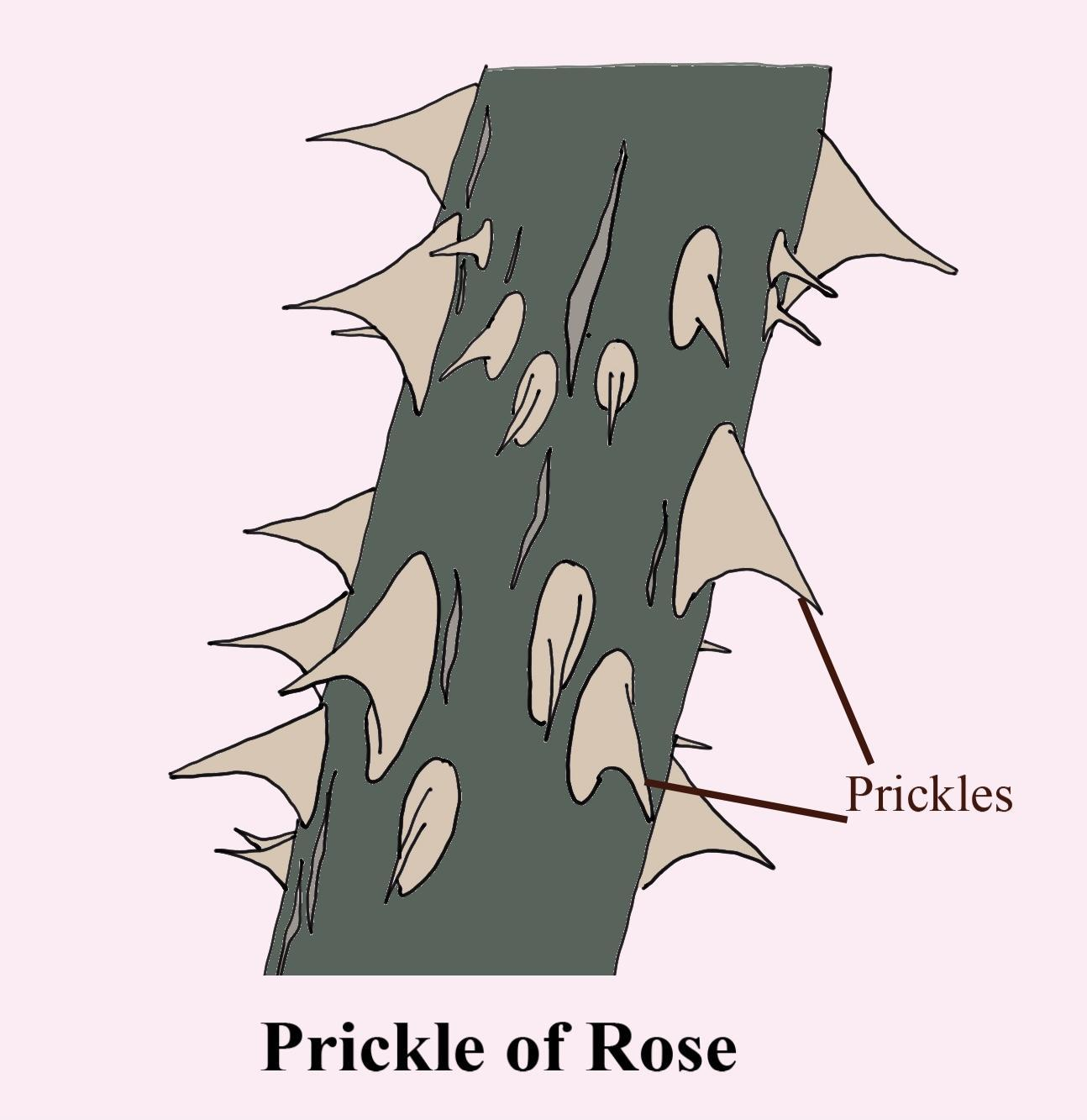
Prickles are like hairs but are often quite coarse (for example, rose prickles). They're extensions of the cortex and epidermis. Technically speaking, many plants commonly thought of as having thorns or spines but in reality, they have prickles. Roses, as an example, have prickles. Thorns are modified branches or stems. Thorns are found to be the modification of stem and formed by axillary buds and are strong in nature as seen in Bougainvillea.
Additional Information: The main function of thorns and prickles is deterring herbivory during a mechanical form. For this reason, they're classified as physical or mechanical defenses, as against chemical defenses. Not every function of thorn or prickles is limited to defense from physical attacks by herbivores and other animals. In some cases it was seen that the spines are shown to shade or helps in insulating the plants that grow them, thereby protecting them from extreme temperatures, for example, the saguaro cactus spines help in providing shade to the apical meristem in the summer season, and in members of the Opuntioideae, glochids insulate the apical meristem in winter.
Note: Other than thorn and prickle, spines are also present in the plant which is the modification of the leaves. The plants of the Cactaceae are particularly renowned for their dense covering of spines. Some cacti also have the glochids, which are defined as a specific kind of spine of some different origin, which are smaller and deciduous with numerous retrorse barbs along its length.
Complete answer:
Prickles are like hairs but are often quite coarse (for example, rose prickles). They're extensions of the cortex and epidermis. Technically speaking, many plants commonly thought of as having thorns or spines but in reality, they have prickles. Roses, as an example, have prickles. Thorns are modified branches or stems. Thorns are found to be the modification of stem and formed by axillary buds and are strong in nature as seen in Bougainvillea.
| S.NO | THORN | PRICKLE |
| 1 | Modification of stem. | Modification of cortex and epidermis. |
| 2 | Comparatively hard and strong. | Comparatively soft, can be broken down easily. |
| 3 | Example: Bougainvillea | Example Rose |

Additional Information: The main function of thorns and prickles is deterring herbivory during a mechanical form. For this reason, they're classified as physical or mechanical defenses, as against chemical defenses. Not every function of thorn or prickles is limited to defense from physical attacks by herbivores and other animals. In some cases it was seen that the spines are shown to shade or helps in insulating the plants that grow them, thereby protecting them from extreme temperatures, for example, the saguaro cactus spines help in providing shade to the apical meristem in the summer season, and in members of the Opuntioideae, glochids insulate the apical meristem in winter.
Note: Other than thorn and prickle, spines are also present in the plant which is the modification of the leaves. The plants of the Cactaceae are particularly renowned for their dense covering of spines. Some cacti also have the glochids, which are defined as a specific kind of spine of some different origin, which are smaller and deciduous with numerous retrorse barbs along its length.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




