
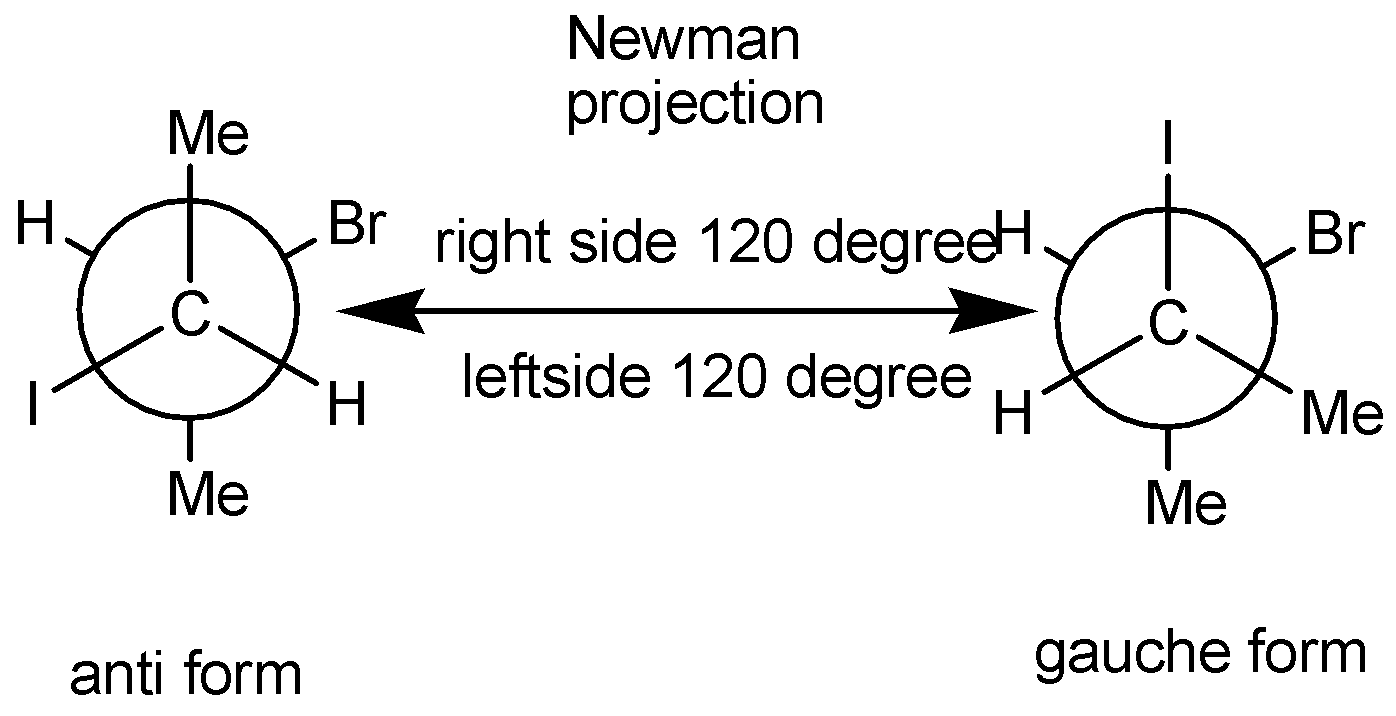
What are the Anti and Gauche Newman projections of \[\left( {2S,3R} \right) - 2bromo - 3 - iodo - butane\] ?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that in organic chemistry, \[{\text{3D}}\] view of the structure of the molecules is very important to know the reaction mechanism. It is also used to determine the stability and reactivity of the structure. The special isomers are easy to predict in this way. There are three main projections in organic chemistry \[{\text{3D}}\] view of the molecules. There are Newman projection, fischer projection and sawhorse projection.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the Newman projections are nothing but viewed the molecules from front carbon-carbon atom bonds. In this projection, two circles are there. Circles are nothing but two carbon atoms connected by a sigma bond. In this structure bond angle is \[{120^ \circ }\] between the bonds. Here one circumstance totally three bonds are formed. Out of four valence in carbon atoms one is linked with the back carbon atom through sigma bond.
In Newman projection, the Anti form of two atoms means in special arrangement two atoms are opposite to each other. The bond angle between the two atoms is \[{180^ \circ }\].
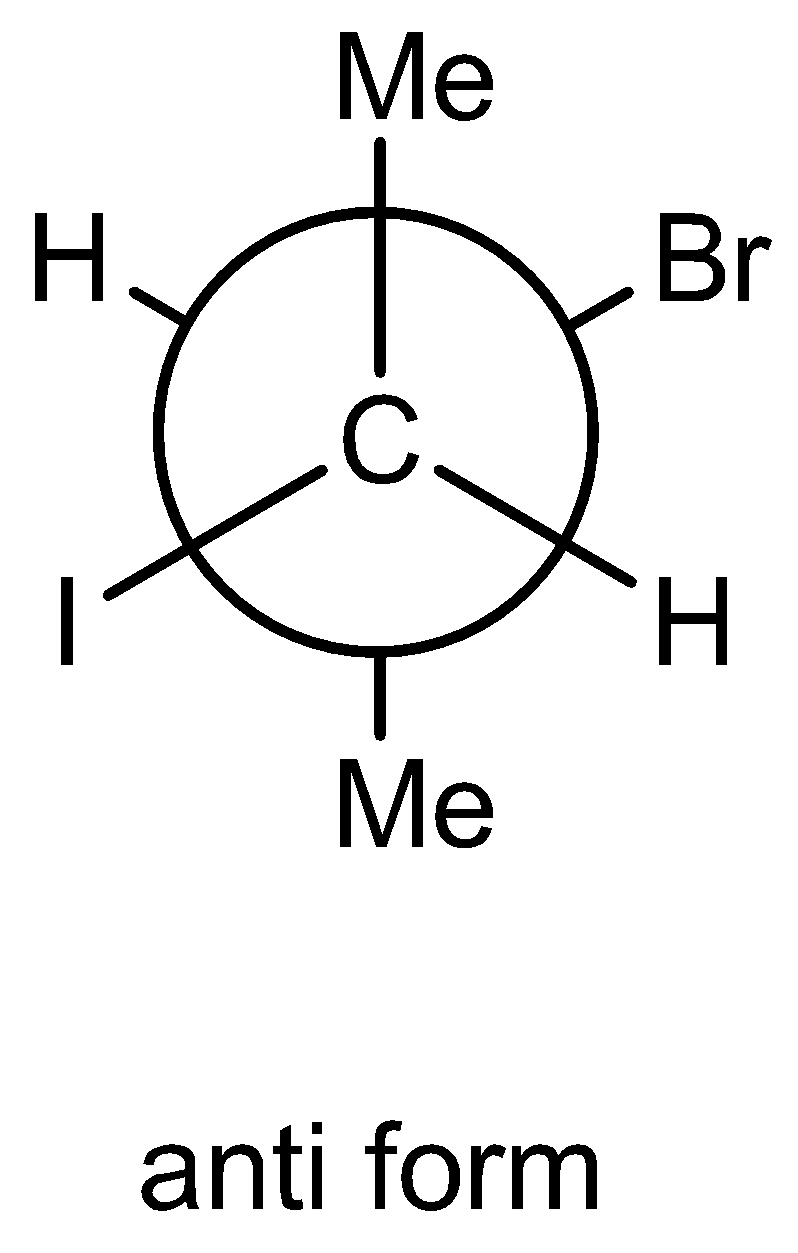
In Newman projection, gauche form means two atoms are very close in special arrangement. The bond angle between the two atoms is\[{45^ \circ }\]
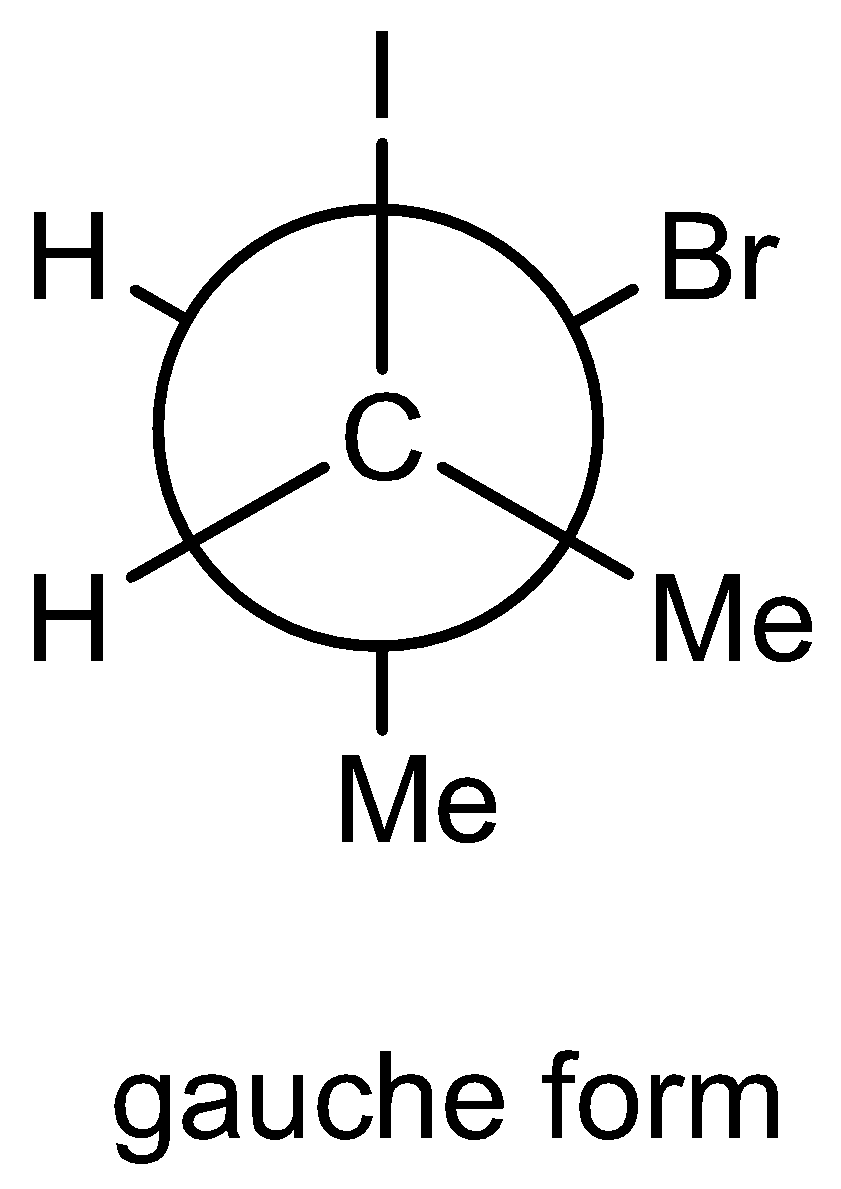
Note: We must have to know that in Newman projection, for butane two important conformations. One is skew form and staggered form. The Skew form in Newman projection means the bonds in the front carbon atom exactly placed in front side in the back carbon atom bonds. So, there is no spatial angle difference between front and back atoms. Here more steric hindrance in this form than staggered form. The Staggered form in Newman projection means the bonds in the front carbon atom exactly \[{45^ \circ }\] placed in front side in the back carbon atom bonds. So, their spatial difference between front and back carbon atoms. Here less steric hindrance in this form compared to skew form.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the Newman projections are nothing but viewed the molecules from front carbon-carbon atom bonds. In this projection, two circles are there. Circles are nothing but two carbon atoms connected by a sigma bond. In this structure bond angle is \[{120^ \circ }\] between the bonds. Here one circumstance totally three bonds are formed. Out of four valence in carbon atoms one is linked with the back carbon atom through sigma bond.
In Newman projection, the Anti form of two atoms means in special arrangement two atoms are opposite to each other. The bond angle between the two atoms is \[{180^ \circ }\].

In Newman projection, gauche form means two atoms are very close in special arrangement. The bond angle between the two atoms is\[{45^ \circ }\]


Note: We must have to know that in Newman projection, for butane two important conformations. One is skew form and staggered form. The Skew form in Newman projection means the bonds in the front carbon atom exactly placed in front side in the back carbon atom bonds. So, there is no spatial angle difference between front and back atoms. Here more steric hindrance in this form than staggered form. The Staggered form in Newman projection means the bonds in the front carbon atom exactly \[{45^ \circ }\] placed in front side in the back carbon atom bonds. So, their spatial difference between front and back carbon atoms. Here less steric hindrance in this form compared to skew form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




