
What are the 4 tissues in the stomach?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: In the upper belly, the stomach is a J-shaped organ (abdomen). It's a component of the gastrointestinal tract. It's located halfway between the end of the food pipe (oesophagus) and the beginning of the first segment of the small intestine (duodenum).
Complete answer:
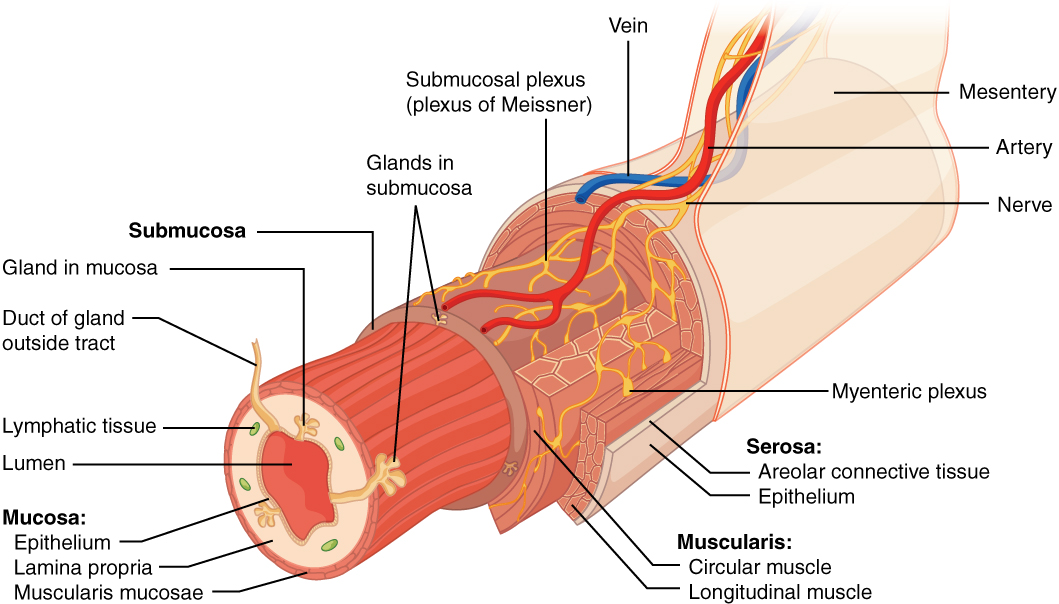
The stomach is an organ of our digestive system. It is made up of 4 layers which are as follows:
Mucosa:-This is the lining's initial and innermost layer. It's where the glands that secrete digestive juices are found. These are hydrochloric acid and pepsin, respectively. The majority of stomach cancers begin here.
Submucosa:-The mucosa is supported by this second layer. Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves abound.
Muscularis:- Thick muscles make up the third layer. This layer aids in the mixing of food with digestive fluids.
Serosa:-This is the final and most visible layer. It's the lining that encircles the stomach and keeps it contained.
Food enters your stomach through the food pipe after you chew and swallow it. Pepsin and hydrochloric acid are released at this point. The rippling motion of your stomach muscles combines the meal with the digestive juices. Partially digested food enters the small intestine after 2 to 3 hours. This is where it is further broken down and absorbed into your body over time.
Note:-
The stomach is a hollow organ that stores food while it is combined with stomach enzymes. These enzymes aid in the breakdown of food into a form that may be consumed. The stomach's lining cells secrete a strong acid as well as potent enzymes that aid in the breakdown process. Subserosa is also the stomach layer but sometimes it is not mentioned, adding this as a layer makes four layers of the stomach.
Complete answer:
The stomach is an organ of our digestive system. It is made up of 4 layers which are as follows:
Mucosa:-This is the lining's initial and innermost layer. It's where the glands that secrete digestive juices are found. These are hydrochloric acid and pepsin, respectively. The majority of stomach cancers begin here.
Submucosa:-The mucosa is supported by this second layer. Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves abound.
Muscularis:- Thick muscles make up the third layer. This layer aids in the mixing of food with digestive fluids.
Serosa:-This is the final and most visible layer. It's the lining that encircles the stomach and keeps it contained.
Food enters your stomach through the food pipe after you chew and swallow it. Pepsin and hydrochloric acid are released at this point. The rippling motion of your stomach muscles combines the meal with the digestive juices. Partially digested food enters the small intestine after 2 to 3 hours. This is where it is further broken down and absorbed into your body over time.

Note:-
The stomach is a hollow organ that stores food while it is combined with stomach enzymes. These enzymes aid in the breakdown of food into a form that may be consumed. The stomach's lining cells secrete a strong acid as well as potent enzymes that aid in the breakdown process. Subserosa is also the stomach layer but sometimes it is not mentioned, adding this as a layer makes four layers of the stomach.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




