
What are the $4$ groups of sensory relay nuclei which the alar plate contains?
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: Alar plate is a neural structure present in the embryonic nervous system. It is a portion of the dorsal part of the neural tube, where the communication of general visceral and general somatic sensory impulses take place. The caudal part of the alar plate later becomes the sensory axon portion of the spinal cord. Alar plate is otherwise known as alar lamina.
Complete answer
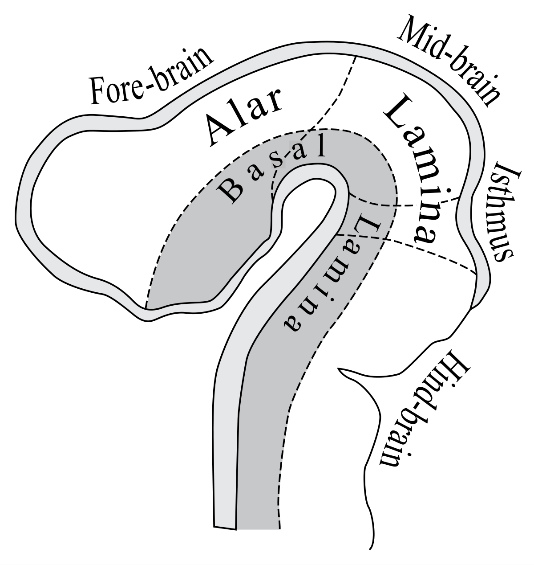
Fig.: Alar Plate
Alar plate consists of $4$ groups of sensory relay nuclei –
General visceral afferent group: It receives interoceptive information from gastrointestinal tract and heart. It is present in the organs of abdomen, pelvis and thorax. Example of its function is pain information from the digestive tract. It conducts sensory impulses from internal organs, blood vessels and glands to the central nervous system.
Special visceral afferent group: The group obtains impulses from epiglottis, taste buds of the tongue, oropharynx and palate. It consists of neurons in the tenth, ninth and seventh cranial nerves. The dendritic zones are limited to the specialized receptors for the taste. The dendritic nerves of the first cranial nerve are localized in the caudal nasal mucosa for the olfaction purpose.
General somatic afferent group: It receives impulses from head and face. The afferent fibres arise from the neurons present in the sensory ganglia. It is found in all spinal nerves except the first cranial nerve.
Special somatic afferent group: This group receives impulses from the ear through the way of vestibulocochlear nerve. It carries sensory impulses from the special senses such as equilibrium, hearing and vision.
Note:
The alar plate particularly, later on becomes the dorsal grey of the spinal cord. It develops into the sensory nuclei of cranial nerves X, IX, VIII, VII and V. The mesencephalic nucleus of V, inferior olivary nucleus and main sensory nucleus of V are too developed from the alar plate. In addition, cerebellum develops from the rhombic tip of the alar plate.
Complete answer

Fig.: Alar Plate
Alar plate consists of $4$ groups of sensory relay nuclei –
General visceral afferent group: It receives interoceptive information from gastrointestinal tract and heart. It is present in the organs of abdomen, pelvis and thorax. Example of its function is pain information from the digestive tract. It conducts sensory impulses from internal organs, blood vessels and glands to the central nervous system.
Special visceral afferent group: The group obtains impulses from epiglottis, taste buds of the tongue, oropharynx and palate. It consists of neurons in the tenth, ninth and seventh cranial nerves. The dendritic zones are limited to the specialized receptors for the taste. The dendritic nerves of the first cranial nerve are localized in the caudal nasal mucosa for the olfaction purpose.
General somatic afferent group: It receives impulses from head and face. The afferent fibres arise from the neurons present in the sensory ganglia. It is found in all spinal nerves except the first cranial nerve.
Special somatic afferent group: This group receives impulses from the ear through the way of vestibulocochlear nerve. It carries sensory impulses from the special senses such as equilibrium, hearing and vision.
Note:
The alar plate particularly, later on becomes the dorsal grey of the spinal cord. It develops into the sensory nuclei of cranial nerves X, IX, VIII, VII and V. The mesencephalic nucleus of V, inferior olivary nucleus and main sensory nucleus of V are too developed from the alar plate. In addition, cerebellum develops from the rhombic tip of the alar plate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




