
What are the +M and –M effect? What are the examples of electron releasing and electron withdrawing groups?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: We have to know that +M and –M are electromeric effect they can also be denoted by –E and +E. the only difference lies in the resonance and electromeric effect resonance is temporary while in mesomeric resonance is permanent that means permanent sharing of pi electrons.
Complete answer:
The term, though a bit outdated, is important for understanding changes in electronic density in a molecule in the presence of other species. This also involves movement of electrons but in this case due to some external agent. For example if a positive charge like H+ is brought near a double bond (say \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]), the double bond which is electron rich, the bond is polarized towards the proton, which can be shown as follows: the given below is showing +E effect.
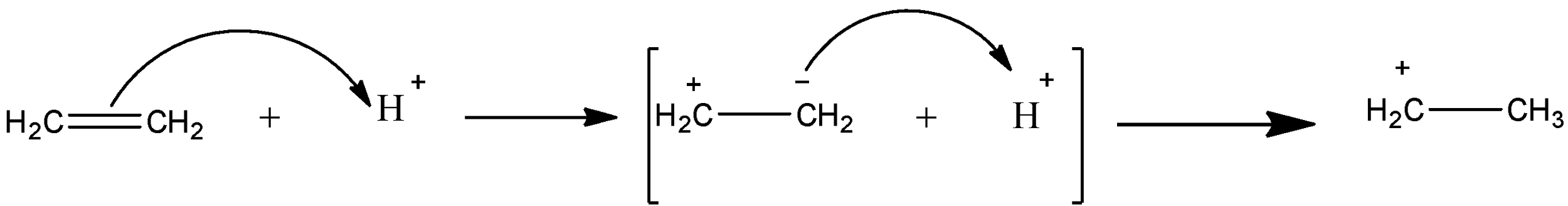
This shifting of electrons or polarization of the covalent bond is termed as Electromeric effect. This case is called +E, as the polarization occurs due to the presence of a positive charge. A –E effect can be seen when some negatively charged species like OH– attacks a double bond: the given below is showing –E effect.
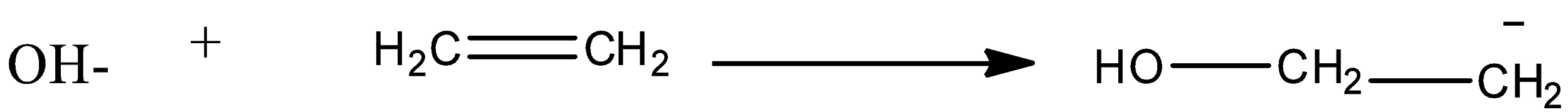
Electron releasing groups: $ - C{H_3}, - OH$
Electron withdrawing groups: $ - N{O_2}, - CN$
Note:
We have to know that the mesomeric effect in chemistry is a property of substituent or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom.
Complete answer:
The term, though a bit outdated, is important for understanding changes in electronic density in a molecule in the presence of other species. This also involves movement of electrons but in this case due to some external agent. For example if a positive charge like H+ is brought near a double bond (say \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]), the double bond which is electron rich, the bond is polarized towards the proton, which can be shown as follows: the given below is showing +E effect.

This shifting of electrons or polarization of the covalent bond is termed as Electromeric effect. This case is called +E, as the polarization occurs due to the presence of a positive charge. A –E effect can be seen when some negatively charged species like OH– attacks a double bond: the given below is showing –E effect.
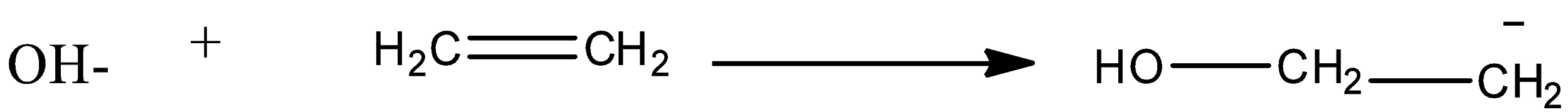
Electron releasing groups: $ - C{H_3}, - OH$
Electron withdrawing groups: $ - N{O_2}, - CN$
Note:
We have to know that the mesomeric effect in chemistry is a property of substituent or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




