
What are stomata? Give two functions of stomata.
Answer
535.4k+ views
Hint: They are pores in the leaves that regulate the exchange of gases and also control the rate of water vapour leaving the plants.
Complete answer:
Stomata are tiny openings or pores that enable gaseous exchange. Stomata are usually found in plant leaves, but they can also be found in some stems. When it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, the plant closes these pores.
The stomata in plants are enclosed by bean shaped cells called guard cells. The opening and closing of the pore is regulated by the guard cells. As water flows through them, the guard cells swell allowing the stomatal pore to expand. The pore often closes as the guard cells shrink. Apart from water vapour loss in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through these stomata. Stomata are usually open in daytime and close at night.
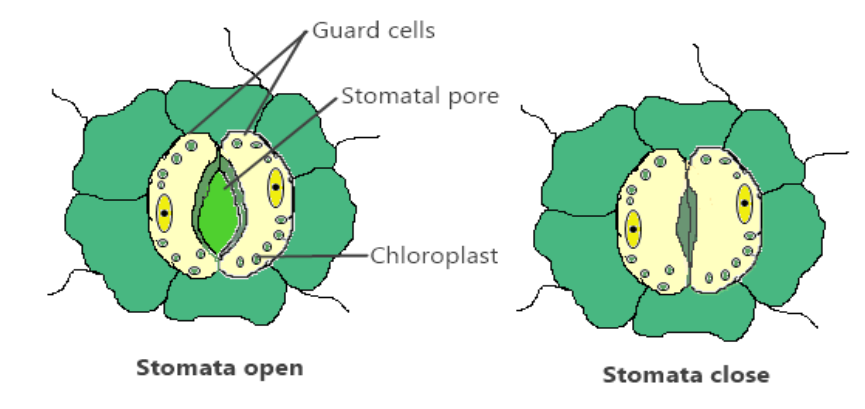
Fig: Diagram showing the closing and opening of stomata
Factors including carbon dioxide levels, light, and environmental factors control the opening and closing of stomata. Humidity is an instance of an environmental condition that controls when stomata are open or close. Stomata are open when the humidity levels are at maximum.
Two functions of stomata are:
1. It controls the amount of water entering and leaving the plants.
2. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
Note: When humidity levels in the air around the plant drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Complete answer:
Stomata are tiny openings or pores that enable gaseous exchange. Stomata are usually found in plant leaves, but they can also be found in some stems. When it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, the plant closes these pores.
The stomata in plants are enclosed by bean shaped cells called guard cells. The opening and closing of the pore is regulated by the guard cells. As water flows through them, the guard cells swell allowing the stomatal pore to expand. The pore often closes as the guard cells shrink. Apart from water vapour loss in transpiration, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through these stomata. Stomata are usually open in daytime and close at night.

Fig: Diagram showing the closing and opening of stomata
Factors including carbon dioxide levels, light, and environmental factors control the opening and closing of stomata. Humidity is an instance of an environmental condition that controls when stomata are open or close. Stomata are open when the humidity levels are at maximum.
Two functions of stomata are:
1. It controls the amount of water entering and leaving the plants.
2. It allows the plant to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
Note: When humidity levels in the air around the plant drop due to higher temperatures or windy weather, more water vapour will disperse out into the air from the plant. Under these conditions, plants must close their stomata to prevent the loss of excess water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




