
What are some examples of hydrogen bonds?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint : Hydrogen bonds are formed due to dipole–dipole interaction between hydrogen and a highly electronegative element. Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular or intramolecular. It depends on the nature of donor and acceptor atoms that constitute the bond.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A hydrogen bond is a special attractive bond which occurs when a hydrogen atom undergoes dipole – dipole attraction to a highly electronegative atom. It usually occurs between hydrogen and fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen.
Some examples of hydrogen bonds:
Water \[({H_2}O)\] : Water is the most basic example of hydrogen bonds. Here, the bonds are formed between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule as shown in the following diagram.
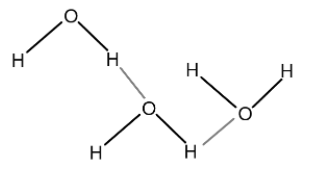
Here the bonds in the black color show one water molecule while bonds in grey color show the hydrogen bonding. Here oxygen atom of one hydrogen molecule attracts the hydrogen atom of another water molecule. Since one hydrogen molecule is shared between two oxygen atoms, therefore, the hydrogen atom becomes positive while the oxygen atoms become negative.
Ammonia \[(N{H_3})\] : Here, hydrogen bonds are formed between the hydrogen of one molecule and nitrogen of another molecule.
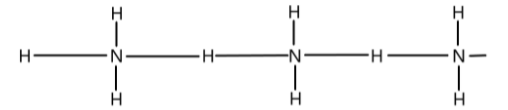
The hydrogen bonds formed here are very weak in nature.
Chloroform \[(CHC{l_3})\] : In chloroform, the central atom is a carbon atom along with one hydrogen atom and three chlorine atoms. The electronegativity difference between carbon and a hydrogen atom is very low. But chlorine is a more electronegative element than carbon and it develops a \[\delta - \]positive charge on carbon. The positive charge on carbon gets more defined due to the presence of three chlorine atoms. This carbon atom with such large \[\delta - \]positive charge makes it almost equal to the size of a neutral nitrogen atom and thus due to this it is able to show hydrogen bonding.
DNA: Here hydrogen bonds are formed between the base pairs. Due to hydrogen bonding, the shape of DNA becomes that of the helix and makes the replication of DNA strands possible.
Note :
The electronegativity of an element depends on the size of that element. The electronegativity increases on going from left to right in a periodic table. Since the size of carbon is larger than nitrogen, therefore, its electronegativity is lower than nitrogen. However, in the case of chloroform, the carbon atom has a \[3{\text{ }}\delta - \]positive charge, which reduces its size hence making it electronegative almost identical to nitrogen.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A hydrogen bond is a special attractive bond which occurs when a hydrogen atom undergoes dipole – dipole attraction to a highly electronegative atom. It usually occurs between hydrogen and fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen.
Some examples of hydrogen bonds:
Water \[({H_2}O)\] : Water is the most basic example of hydrogen bonds. Here, the bonds are formed between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule as shown in the following diagram.

Here the bonds in the black color show one water molecule while bonds in grey color show the hydrogen bonding. Here oxygen atom of one hydrogen molecule attracts the hydrogen atom of another water molecule. Since one hydrogen molecule is shared between two oxygen atoms, therefore, the hydrogen atom becomes positive while the oxygen atoms become negative.
Ammonia \[(N{H_3})\] : Here, hydrogen bonds are formed between the hydrogen of one molecule and nitrogen of another molecule.

The hydrogen bonds formed here are very weak in nature.
Chloroform \[(CHC{l_3})\] : In chloroform, the central atom is a carbon atom along with one hydrogen atom and three chlorine atoms. The electronegativity difference between carbon and a hydrogen atom is very low. But chlorine is a more electronegative element than carbon and it develops a \[\delta - \]positive charge on carbon. The positive charge on carbon gets more defined due to the presence of three chlorine atoms. This carbon atom with such large \[\delta - \]positive charge makes it almost equal to the size of a neutral nitrogen atom and thus due to this it is able to show hydrogen bonding.
DNA: Here hydrogen bonds are formed between the base pairs. Due to hydrogen bonding, the shape of DNA becomes that of the helix and makes the replication of DNA strands possible.
Note :
The electronegativity of an element depends on the size of that element. The electronegativity increases on going from left to right in a periodic table. Since the size of carbon is larger than nitrogen, therefore, its electronegativity is lower than nitrogen. However, in the case of chloroform, the carbon atom has a \[3{\text{ }}\delta - \]positive charge, which reduces its size hence making it electronegative almost identical to nitrogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




