
Why are punnett squares useful in genetics?
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: The Punnett Square is named after geneticist Reginald Punnett. It is used as a tool for the determination of possible genotypic and phenotypic outcomes of offspring given the genotypes of their parents. In the Punnett Square, the top of the table displays the alleles provided by one parent. On the left side of the table, the alleles from the other parent are placed.
Complete answer:
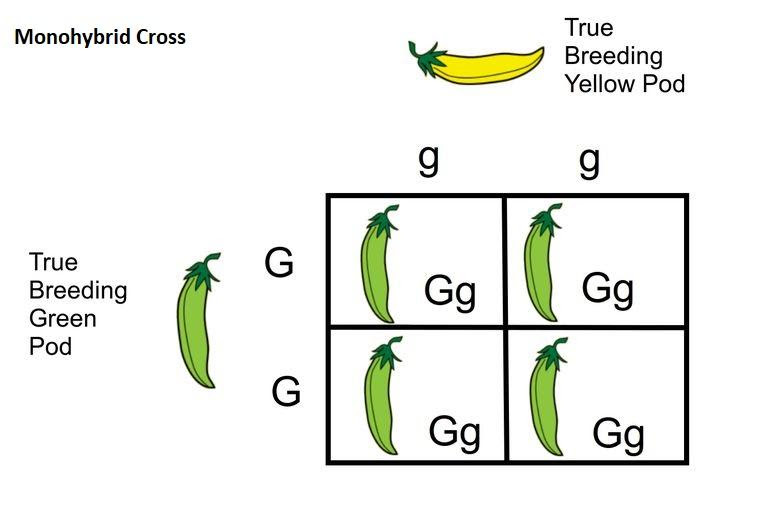
Fig.: Punnett Square Representing a Monohybrid Cross in Pea Color
Punnett Squares are used for prediction of the genetic probability of a specific phenotype, which arises in a couple’s offspring. It tells about the expression of alleles in offspring when the genotypes of the parents are provided. It also tells whether a particular offspring possesses a certain trait or not.
Each offspring inherits two versions of the same chromosome, one from the mother and another from the father. So, different versions of the same genes or different alleles are received. One is the dominant allele and another allele is recessive. As the dominant allele always shuns out the recessive allele, the only time the recessive allele gets expressed is when an individual inherits two recessive alleles from the parents.
When the genotypes of the parents are given, Punnett squares tell the information about what alleles are likely to be expressed in the offspring.
An example is Mendel’s pea experiment. For the color of the pod, there are two different alleles, green and yellow, with yellow dominant to green. The yellow allele is represented as G and the green allele is depicted as g. The probability of an individual with a GG configuration and a gg configuration to produce a green or yellow offspring, then the Punnett Square is used.
Note:
In the Punnett Square, one allele from each parent is placed inside the individual squares, forming a new gene pair. The table is highly useful for biologists. It is used in the prediction of the percentage of particular phenotypes obtained after the cross. It is also used in determining a missing genotype based on other genotypes involved in the cross. Thus, it serves as an indispensable tool in genetics.
Complete answer:

Fig.: Punnett Square Representing a Monohybrid Cross in Pea Color
Punnett Squares are used for prediction of the genetic probability of a specific phenotype, which arises in a couple’s offspring. It tells about the expression of alleles in offspring when the genotypes of the parents are provided. It also tells whether a particular offspring possesses a certain trait or not.
Each offspring inherits two versions of the same chromosome, one from the mother and another from the father. So, different versions of the same genes or different alleles are received. One is the dominant allele and another allele is recessive. As the dominant allele always shuns out the recessive allele, the only time the recessive allele gets expressed is when an individual inherits two recessive alleles from the parents.
When the genotypes of the parents are given, Punnett squares tell the information about what alleles are likely to be expressed in the offspring.
An example is Mendel’s pea experiment. For the color of the pod, there are two different alleles, green and yellow, with yellow dominant to green. The yellow allele is represented as G and the green allele is depicted as g. The probability of an individual with a GG configuration and a gg configuration to produce a green or yellow offspring, then the Punnett Square is used.
Note:
In the Punnett Square, one allele from each parent is placed inside the individual squares, forming a new gene pair. The table is highly useful for biologists. It is used in the prediction of the percentage of particular phenotypes obtained after the cross. It is also used in determining a missing genotype based on other genotypes involved in the cross. Thus, it serves as an indispensable tool in genetics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




