
How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested?
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Carbohydrates are the most abundant biomolecules.It is the combination of carbon and water.We intake a lot of carbohydrates through many food sources.In biological term carbohydrates are referred as saccharides.The saccharides are classified based on the number of carbons in a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharide molecules bond chemically.Hundreds of monosaccharide monomers are present in larger polymers in the form of polysaccharides or glycans.Polysaccharides shows diversity in their structure and biologically important polysaccharides are starch, glycogen and cellulose
Polysaccharides and disaccharides are digested by different enzymes produced in the digestive tract.The polysaccharides are broken down to oligosaccharides and the simple sugars are disaccharides that are further digested to form monosaccharides.
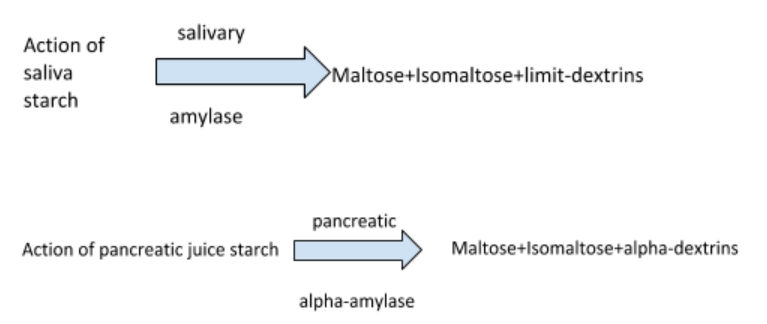
Polysaccharides Digestion
Disaccharides Digestion:
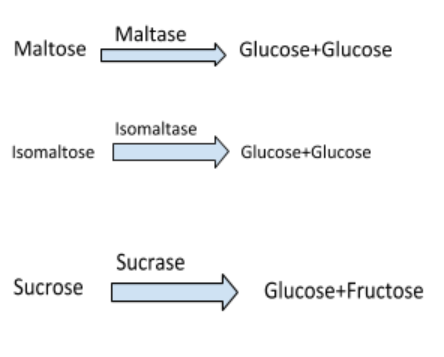
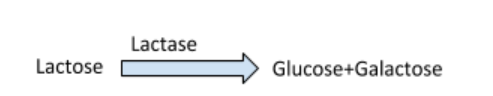
The carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth and ends at the region of the alimentary canal in the small intestine.The enzymes which act on the carbohydrates are known as carbohydrases.The food gets mixed with saliva when it enters the mouth.Salivary amylase also called as ptyalin a digestive enzyme secreted by the salivary glands are responsible for breaking down the starch into sugar of pH 6.8.The action of salivary amylase stops after oesophagus when the carbohydrate reaches the stomach.The digestion of carbohydrates resumes in small intestine.In this region the pancreatic juice and the intestine juice are mixed with the food for digestion.The former has pancreatic amylase that converts polysaccharides to disaccharides.
Note:
The various enzymes such as maltase,lactase,sucrase are present in the intestine juice which helps in digestion of disaccharides.The digestion stops in the small intestine.
Complete step by step answer:
Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharide molecules bond chemically.Hundreds of monosaccharide monomers are present in larger polymers in the form of polysaccharides or glycans.Polysaccharides shows diversity in their structure and biologically important polysaccharides are starch, glycogen and cellulose
Polysaccharides and disaccharides are digested by different enzymes produced in the digestive tract.The polysaccharides are broken down to oligosaccharides and the simple sugars are disaccharides that are further digested to form monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides Digestion

Disaccharides Digestion:


The carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth and ends at the region of the alimentary canal in the small intestine.The enzymes which act on the carbohydrates are known as carbohydrases.The food gets mixed with saliva when it enters the mouth.Salivary amylase also called as ptyalin a digestive enzyme secreted by the salivary glands are responsible for breaking down the starch into sugar of pH 6.8.The action of salivary amylase stops after oesophagus when the carbohydrate reaches the stomach.The digestion of carbohydrates resumes in small intestine.In this region the pancreatic juice and the intestine juice are mixed with the food for digestion.The former has pancreatic amylase that converts polysaccharides to disaccharides.
Note:
The various enzymes such as maltase,lactase,sucrase are present in the intestine juice which helps in digestion of disaccharides.The digestion stops in the small intestine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




