
What are phospholipids? Briefly discuss their structure, properties, and functions.
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Essential elements of the cell membranes are phospholipid bilayers. A significant function of the cell membrane is to enable certain substances to be selectively transferred into and out of cells.
Complete answer:
A phospholipid may also be a sort of lipid molecule that is an essential cell membrane portion. Two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule are used to create each phospholipid.
Structure of phospholipids:
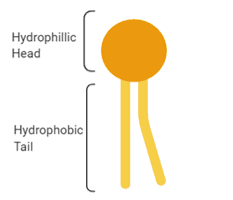
A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule that means that it is both a hydrophobic element and a hydrophilic element.
The phosphate group is hydrophilic, or "water-loving." Hence, the phosphate heads are curious about their environment's water molecules.
On the other side, the lipid tails are hydrophobic, or "water-fearing." A hydrophobic molecule repels water and is repelled.
Two neighboring layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer, compose the cell membrane. Phospholipids' acid tails face inside, away from water, while the outer aqueous side faces the phosphate heads. One layer is exposed to the inside of the cell since the heads face outward, and one layer is exposed to the outside. The lipid bilayer behaves as a semipermeable membrane; the phospholipid bilayer can easily pass through only lipophilic solutes.
Properties and Functions of phospholipids:
Since membranes are selectively permeable (also referred to as semi-permeable), only certain molecules can enter or exit the cell. Molecules that dissolve in fat can quickly pass through, whereas molecules that dissolve in water can not pass through. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and urea are some of the things that quickly go through the cell wall. It is not possible for large molecules such as glucose or ions such as sodium and potassium to move through.
Note: Phospholipids can act as emulsifiers in the food industry. Egg yolks, for instance, contain phospholipids and are used in mayonnaise to keep them from separating. In many other animal and plant sources, such as soybeans, sunflowers, cotton seeds, maize, and even cow brains, phospholipids are present in high concentrations.
Complete answer:
A phospholipid may also be a sort of lipid molecule that is an essential cell membrane portion. Two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule are used to create each phospholipid.
Structure of phospholipids:

A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule that means that it is both a hydrophobic element and a hydrophilic element.
The phosphate group is hydrophilic, or "water-loving." Hence, the phosphate heads are curious about their environment's water molecules.
On the other side, the lipid tails are hydrophobic, or "water-fearing." A hydrophobic molecule repels water and is repelled.
Two neighboring layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer, compose the cell membrane. Phospholipids' acid tails face inside, away from water, while the outer aqueous side faces the phosphate heads. One layer is exposed to the inside of the cell since the heads face outward, and one layer is exposed to the outside. The lipid bilayer behaves as a semipermeable membrane; the phospholipid bilayer can easily pass through only lipophilic solutes.
Properties and Functions of phospholipids:
Since membranes are selectively permeable (also referred to as semi-permeable), only certain molecules can enter or exit the cell. Molecules that dissolve in fat can quickly pass through, whereas molecules that dissolve in water can not pass through. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and urea are some of the things that quickly go through the cell wall. It is not possible for large molecules such as glucose or ions such as sodium and potassium to move through.
Note: Phospholipids can act as emulsifiers in the food industry. Egg yolks, for instance, contain phospholipids and are used in mayonnaise to keep them from separating. In many other animal and plant sources, such as soybeans, sunflowers, cotton seeds, maize, and even cow brains, phospholipids are present in high concentrations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




