
What are free radicals? Draw the structure of various types of free radicals and arrange them in increasing order of their stability.
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: We have heard about free radicals several times. They have a major role in the atmospheric industry, combustion, polymerization, biochemistry etc. They are also useful in several biological processes. They have a role in biological metabolism.
Complete step by step answer:
As it is familiar that the species of molecules having an unpaired electron are termed as free radicals. They are represented as \[{{{X}}^ \bullet }\] and are highly reactive species. Photo irradiation is a common method to produce free radicals. Light or heat in the form of energy is needed for the production of free radicals. Free radicals are classified into $\sigma $ and $\pi $ radicals. The unpaired electron is in $\sigma $ orbitals in $\sigma $ radicals. E.g. phenyl radical, vinyl radical etc. While the unpaired electron is in $\pi $ orbitals in $\pi $ radicals. E.g. t-butyl radical. $\pi $ radicals are generally stabilized by hyperconjugation effect or resonance effect. While there is no such stabilizing effect in $\sigma $ radicals.
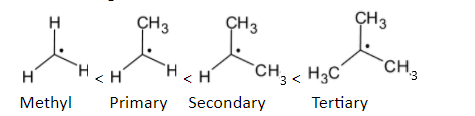
In the case of alkyl groups, when the number of alkyl groups on the carbon having free radicals is increased, the stability is increased.
The order of stability is given below:
Methyl radicalThe electron-deficient radical can be delocalized on the multiple bonds with carbon atoms. Stability is increased when a partially filled p orbital is participated in resonance with the adjacent p orbitals. The structure is given below:
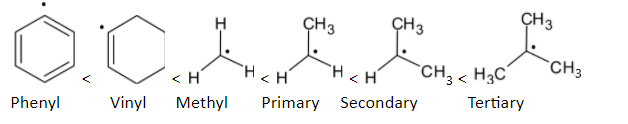
When we compare the stability of phenyl and vinyl radicals, the order is given below:
Note: The stability of free radicals depends upon three factors:
Increase in the number of alkyl groups on the carbon atom which has free radical.
Delocalization or resonance
Geometry of free radicals
Complete step by step answer:
As it is familiar that the species of molecules having an unpaired electron are termed as free radicals. They are represented as \[{{{X}}^ \bullet }\] and are highly reactive species. Photo irradiation is a common method to produce free radicals. Light or heat in the form of energy is needed for the production of free radicals. Free radicals are classified into $\sigma $ and $\pi $ radicals. The unpaired electron is in $\sigma $ orbitals in $\sigma $ radicals. E.g. phenyl radical, vinyl radical etc. While the unpaired electron is in $\pi $ orbitals in $\pi $ radicals. E.g. t-butyl radical. $\pi $ radicals are generally stabilized by hyperconjugation effect or resonance effect. While there is no such stabilizing effect in $\sigma $ radicals.
In the case of alkyl groups, when the number of alkyl groups on the carbon having free radicals is increased, the stability is increased.
The order of stability is given below:
Methyl radical

When we compare the stability of phenyl and vinyl radicals, the order is given below:

Note: The stability of free radicals depends upon three factors:
Increase in the number of alkyl groups on the carbon atom which has free radical.
Delocalization or resonance
Geometry of free radicals
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




