
What are examples of beta-lactam antibiotics?
Answer
525k+ views
Hint : Antibiotics with a beta-lactam ring in their molecular structure are known as beta-lactam antibiotics. The most commonly used antibiotic class is Beta-lactam antibiotics, which function by inhibiting bacterial cell wall biosynthesis.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A lactam is a cyclic amide in which the N atom is bound to the chain's beta carbon to form a four-membered ring.
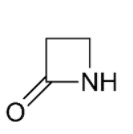
This is a function that all beta-lactam antibiotics share.
The central ring structures of beta-lactams are used to classify them.
1. Beta-lactam rings fused to a saturated five-membered ring
Penams: A thiazolidine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Penicillin G
2. Beta-lactam rings fused to unsaturated five-membered rings
Penems: A dihydrothiazole ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Faropenem
Carbapenems: A dihydropyrrole ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Meropenem
3. Beta-lactam rings fused to unsaturated six-membered rings
Cephems: A dihydrothiazine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Cefalexin
Carbacephems: A tetrahydropyridine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Loracarbef
Oxacephems: A dihydro oxazine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Flomoxef
Additional Information:
Bacteria often gain resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics by producing a beta-lactamase enzyme, which attacks the beta-lactam ring. Beta-lactam antibiotics can be combined with beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid to overcome this resistance.
Note :
Beta-lactam antibiotics were originally only effective against Gram-positive bacteria, but the production of broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics that are effective against a variety of Gram-negative bacteria has expanded their utility. Antibiotics belonging to the beta-lactam family are currently the most commonly used universal antibiotics.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A lactam is a cyclic amide in which the N atom is bound to the chain's beta carbon to form a four-membered ring.

This is a function that all beta-lactam antibiotics share.
The central ring structures of beta-lactams are used to classify them.
1. Beta-lactam rings fused to a saturated five-membered ring
Penams: A thiazolidine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Penicillin G
2. Beta-lactam rings fused to unsaturated five-membered rings
Penems: A dihydrothiazole ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Faropenem
Carbapenems: A dihydropyrrole ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Meropenem
3. Beta-lactam rings fused to unsaturated six-membered rings
Cephems: A dihydrothiazine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Cefalexin
Carbacephems: A tetrahydropyridine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Loracarbef
Oxacephems: A dihydro oxazine ring fused to the Beta-lactam ring
Example: Flomoxef
Additional Information:
Bacteria often gain resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics by producing a beta-lactamase enzyme, which attacks the beta-lactam ring. Beta-lactam antibiotics can be combined with beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid to overcome this resistance.
Note :
Beta-lactam antibiotics were originally only effective against Gram-positive bacteria, but the production of broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics that are effective against a variety of Gram-negative bacteria has expanded their utility. Antibiotics belonging to the beta-lactam family are currently the most commonly used universal antibiotics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




