
Why are chromosomes called the hereditary vehicle?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: During cell division, DNA undergoes replication and further condenses into a highly compact structure with the help of certain basic proteins. The structure so formed is termed as a chromosome. Every species carries a different set of chromosomes.
Complete answer:
Chromosomes are formed of DNA and proteins. Chromosomes are carriers of genes. They are called the hereditary vehicle because they are the condensed forms of DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid which is the genetic material of eukaryotes. All the morphological as well as physiological forms are the result of the information coded in the genome in the form of the nucleotide sequence. During sexual reproduction, the genetic material from a parent to its offspring is passed via these condensed structures known as chromosomes.
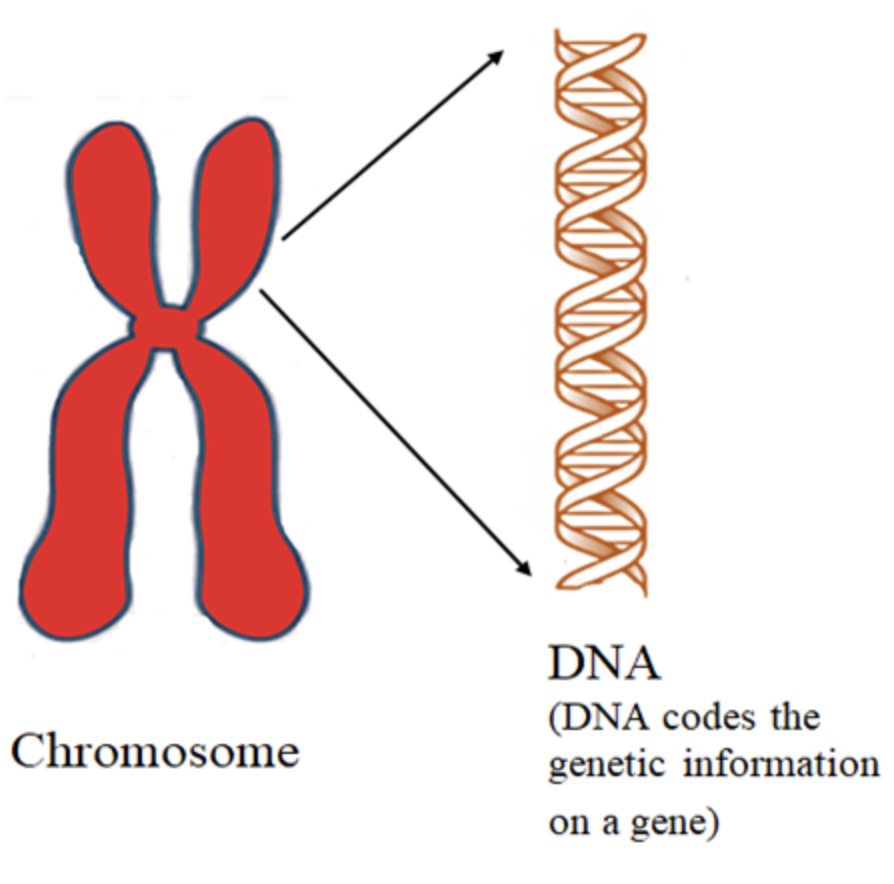
They are a carrier of genes and genes are responsible for the expression of traits such as height, color, etc. Thus, the genes bearing traits from a parent are transferred to their offsprings via chromosomes.
Additional Information:
- DNA is wrapped around eight histone proteins similar to form a structure referred to as the nucleosome.
- Many nucleosomes join to form chromatin which resembles a beaded structure on a string. Each nucleosome wraps around two turns of DNA helix around it.
- The chromatin further condenses to form a highly compact structure known as chromosomes. The formation of chromosomes is observed in the metaphase stage of the cell cycle.
- Each chromosome has a constriction point known as centromere which divides the chromosome into two parts. Each part is referred to as an arm. Their terminal ends are covered by a highly repetitive sequence called telomeres.
- Telomeres are significant in that they form the termini of chromosomes, protect chromosomes from nuclease activity, and maintain the stability of chromosomes.
Note:
- A chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids. A pair of chromosomes, one from each parent is known as homologous chromosomes.
- Each part of a gene i.e alleles is located on the same position or locus of each homologous chromosome.
Complete answer:
Chromosomes are formed of DNA and proteins. Chromosomes are carriers of genes. They are called the hereditary vehicle because they are the condensed forms of DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid which is the genetic material of eukaryotes. All the morphological as well as physiological forms are the result of the information coded in the genome in the form of the nucleotide sequence. During sexual reproduction, the genetic material from a parent to its offspring is passed via these condensed structures known as chromosomes.

They are a carrier of genes and genes are responsible for the expression of traits such as height, color, etc. Thus, the genes bearing traits from a parent are transferred to their offsprings via chromosomes.
Additional Information:
- DNA is wrapped around eight histone proteins similar to form a structure referred to as the nucleosome.
- Many nucleosomes join to form chromatin which resembles a beaded structure on a string. Each nucleosome wraps around two turns of DNA helix around it.
- The chromatin further condenses to form a highly compact structure known as chromosomes. The formation of chromosomes is observed in the metaphase stage of the cell cycle.
- Each chromosome has a constriction point known as centromere which divides the chromosome into two parts. Each part is referred to as an arm. Their terminal ends are covered by a highly repetitive sequence called telomeres.
- Telomeres are significant in that they form the termini of chromosomes, protect chromosomes from nuclease activity, and maintain the stability of chromosomes.
Note:
- A chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids. A pair of chromosomes, one from each parent is known as homologous chromosomes.
- Each part of a gene i.e alleles is located on the same position or locus of each homologous chromosome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




