
Why are antiparallel beta-sheets more stable?
Answer
393.6k+ views
Hint: Polypeptide chains of proteins are folded into secondary structures. They may be in the form of an alpha helix or beta-pleated sheets. Other forms include omega loops and beta turns.
Complete step-by-step anwer:
The secondary structure of linear proteins is primarily made of beta-strands. These adjacently placed strands constitute a beta-sheet, also called a beta-pleated sheet.
These bonds are formed due to hydrogen bonds formed between the amino and carbonyl groups of the polypeptide backbone. The functional group of the amino acids extend below and above the plane of the sheet.
Different types of beta-sheets seen in secondary protein structures are parallel beta-sheets, antiparallel beta-sheets, and mixed beta-sheets.
In parallel beta-pleated sheets, the bonded strands are in the same direction- N to C. Thus, they are separated by a long stretched sequence and hydrogen bonds are equally distanced.
In antiparallel beta-pleated sheets, the strands run in an alternate direction. Thus, the hydrogen bonds have alternating short and long distances.
In mixed beta-pleated sheets, parallel and antiparallel hydrogen bonding is seen. Around 20% of all beta-sheets are found mixed.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets have the polypeptide strands arranged in opposite directions, with well-oriented, stable, and strong hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen-bonded rings have 14 and 10 atoms in an alternating fashion. This gives an overall linear structure and makes it more stable compared to parallel beta-sheets.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets are found in various native proteins like the silk of spiders and silkworms.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets are found to occur more twisted. Thus they are able to withstand twisting, beta-bulging, and solvent exposure as compared to parallel beta-pleated sheets.
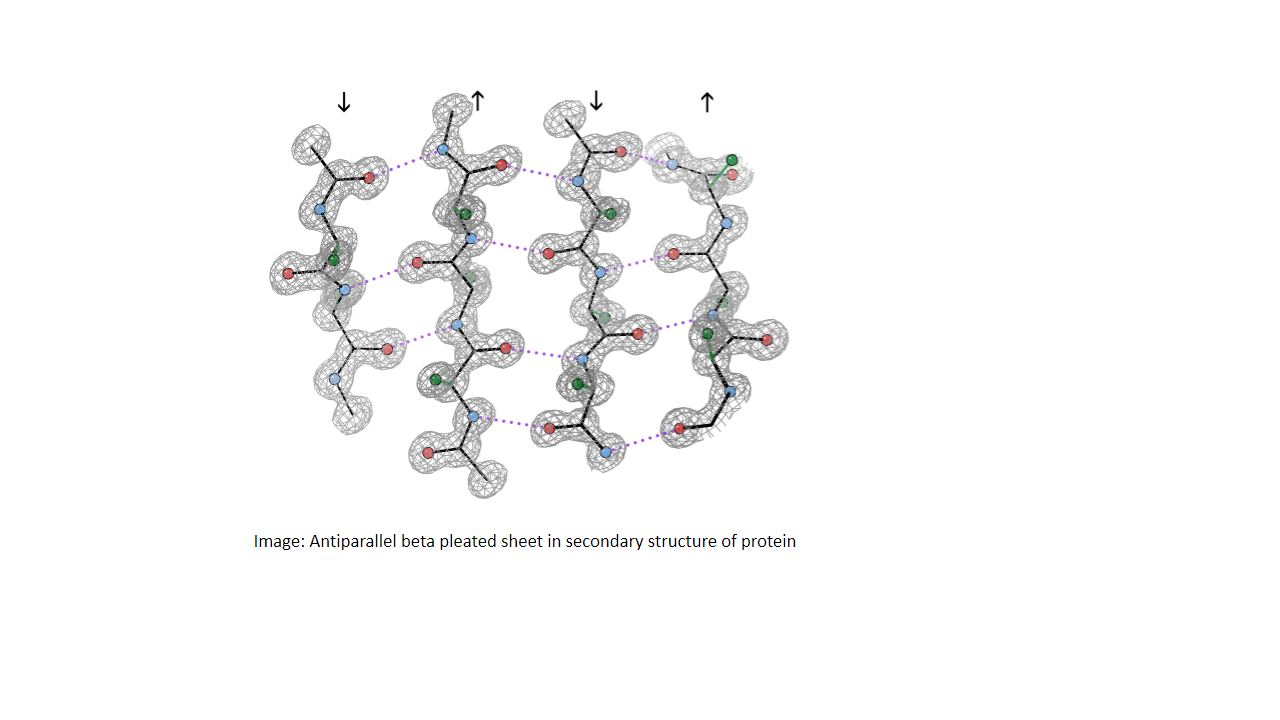
Image: Antiparallel beta-pleated sheet in secondary structure of protein
Note: The secondary structure of beta-pleated sheets was first given by Pauling and Corey.
Complete step-by-step anwer:
The secondary structure of linear proteins is primarily made of beta-strands. These adjacently placed strands constitute a beta-sheet, also called a beta-pleated sheet.
These bonds are formed due to hydrogen bonds formed between the amino and carbonyl groups of the polypeptide backbone. The functional group of the amino acids extend below and above the plane of the sheet.
Different types of beta-sheets seen in secondary protein structures are parallel beta-sheets, antiparallel beta-sheets, and mixed beta-sheets.
In parallel beta-pleated sheets, the bonded strands are in the same direction- N to C. Thus, they are separated by a long stretched sequence and hydrogen bonds are equally distanced.
In antiparallel beta-pleated sheets, the strands run in an alternate direction. Thus, the hydrogen bonds have alternating short and long distances.
In mixed beta-pleated sheets, parallel and antiparallel hydrogen bonding is seen. Around 20% of all beta-sheets are found mixed.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets have the polypeptide strands arranged in opposite directions, with well-oriented, stable, and strong hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen-bonded rings have 14 and 10 atoms in an alternating fashion. This gives an overall linear structure and makes it more stable compared to parallel beta-sheets.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets are found in various native proteins like the silk of spiders and silkworms.
Antiparallel beta-pleated sheets are found to occur more twisted. Thus they are able to withstand twisting, beta-bulging, and solvent exposure as compared to parallel beta-pleated sheets.

Image: Antiparallel beta-pleated sheet in secondary structure of protein
Note: The secondary structure of beta-pleated sheets was first given by Pauling and Corey.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Hybrid seeds have to be produced every year because class 12 biology NEET_UG

Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE




