
Are animal cells and plant cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic? Why do you say so?
Answer
479.4k+ views
Hint: Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of any living organism. Some organisms are made of only a single cell and are known as unicellular organisms. While other organisms are made of a number of cells that work together to carry out basic structural and functional mechanisms of the body.
Complete answer:
There are two types of cells present in organisms- prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are primitive cells that do not have a proper nucleus or any membrane-bound cell organelles. The basic cell components present in prokaryotic cells are cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes and a central opaque structure known as the nucleoid.
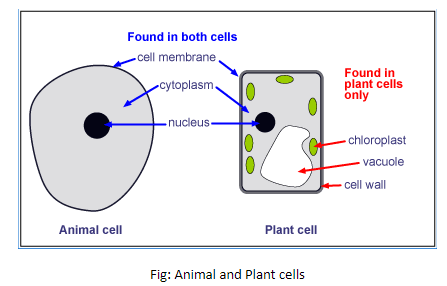
On the other hand, eukaryotic cells are those cells that have a well-developed nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane, and other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi bodies and lysosomes which carry out their own different functions in the cells. In animal and plant cells, there is a well-defined nucleus as well as membrane-bound organelles. Therefore, plant and animal cells are eukaryotic in nature and not prokaryotic.
The basic structures present in these cells are cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus, as well as other membrane-bound organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, and mitochondria. Plant cells have an extra cell wall that covers the cell membrane, and cell organelles called chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis. While animal cells have an organelle called lysosomes which helps in the degradation of waste materials.
Note: Prokaryotic cells are present in primitive unicellular organisms belonging to Kingdom Protista. All the members of the Bacterial kingdom have prokaryotic cells. The genetic material in these organisms is present outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. And ribosomes are scattered in the cytoplasm.
Complete answer:
There are two types of cells present in organisms- prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are primitive cells that do not have a proper nucleus or any membrane-bound cell organelles. The basic cell components present in prokaryotic cells are cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes and a central opaque structure known as the nucleoid.
On the other hand, eukaryotic cells are those cells that have a well-developed nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane, and other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi bodies and lysosomes which carry out their own different functions in the cells. In animal and plant cells, there is a well-defined nucleus as well as membrane-bound organelles. Therefore, plant and animal cells are eukaryotic in nature and not prokaryotic.
The basic structures present in these cells are cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus, as well as other membrane-bound organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, and mitochondria. Plant cells have an extra cell wall that covers the cell membrane, and cell organelles called chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis. While animal cells have an organelle called lysosomes which helps in the degradation of waste materials.

Note: Prokaryotic cells are present in primitive unicellular organisms belonging to Kingdom Protista. All the members of the Bacterial kingdom have prokaryotic cells. The genetic material in these organisms is present outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. And ribosomes are scattered in the cytoplasm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




