
Why are alveoli so small and uncountable in numbers?
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Alveoli are a vital component of the respiratory system which is a biological system in animals and plants that consists of distinct organs and structures utilised for gas exchange or in simple terms, it helps the living organisms to breathe.
Complete answer:
Alveoli are little balloon-like formations or structures present in our lungs. They are the tiniest components of the respiratory system. The alveoli are clustered throughout the lungs. They are located at the tips of your respiratory tree's branches.
Image showing Pulmonary Alveolus/ Alveoli
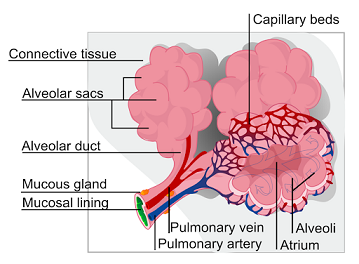
The alveolar walls are quite thin. This allows oxygen and $CO_2$ to readily flow between the alveoli and capillaries, which are extremely small blood vessels. Alveoli are considered to be the respiratory system's terminus.
Surfactant is a fluid that lines alveoli. This fluid keeps the air sac open and preserves its form, allowing oxygen and $CO_2$ to flow through. The alveoli's primary purpose is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. The body's cells require oxygen to produce energy. Carbon dioxide is emitted as a by-product of this activity.
Alveoli are infinite in number and serve to promote diffusion of gases in the lungs. They are too small to increase alveolar concentrations and therefore improve gas exchange. If the lungs were merely two just big 'empty bags' then the body couldn't absorb far more oxygen. Due to the obvious increased number of alveoli, the surface area of our lungs is considerably bigger, and gas diffusion is easier and more efficient.
Note:
On an average, the formation of alveoli begins at 16 weeks of gestation, when bronchioles first form. The cells that will become the alveoli begin to emerge at either end of these bronchioles. Foetal breathing motions may begin around week 20. They begin to develop at about 32 weeks gestation and continue to grow until about 8 years of age, and potentially even into adolescence.
Complete answer:
Alveoli are little balloon-like formations or structures present in our lungs. They are the tiniest components of the respiratory system. The alveoli are clustered throughout the lungs. They are located at the tips of your respiratory tree's branches.
Image showing Pulmonary Alveolus/ Alveoli

The alveolar walls are quite thin. This allows oxygen and $CO_2$ to readily flow between the alveoli and capillaries, which are extremely small blood vessels. Alveoli are considered to be the respiratory system's terminus.
Surfactant is a fluid that lines alveoli. This fluid keeps the air sac open and preserves its form, allowing oxygen and $CO_2$ to flow through. The alveoli's primary purpose is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. The body's cells require oxygen to produce energy. Carbon dioxide is emitted as a by-product of this activity.
Alveoli are infinite in number and serve to promote diffusion of gases in the lungs. They are too small to increase alveolar concentrations and therefore improve gas exchange. If the lungs were merely two just big 'empty bags' then the body couldn't absorb far more oxygen. Due to the obvious increased number of alveoli, the surface area of our lungs is considerably bigger, and gas diffusion is easier and more efficient.
Note:
On an average, the formation of alveoli begins at 16 weeks of gestation, when bronchioles first form. The cells that will become the alveoli begin to emerge at either end of these bronchioles. Foetal breathing motions may begin around week 20. They begin to develop at about 32 weeks gestation and continue to grow until about 8 years of age, and potentially even into adolescence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




