
Archegoniate plants belong to
(a)Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, gymnosperms, angiosperms
(b)Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta
(c)Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, angiosperms
(d)Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, gymnosperms
Answer
521.5k+ views
Hint: During the process of evolution in plants, there is a steady reduction in the growth of gametophyte with the elaboration of the sporophyte. The presence of Archegonium is an ancient feature.
Complete answer:
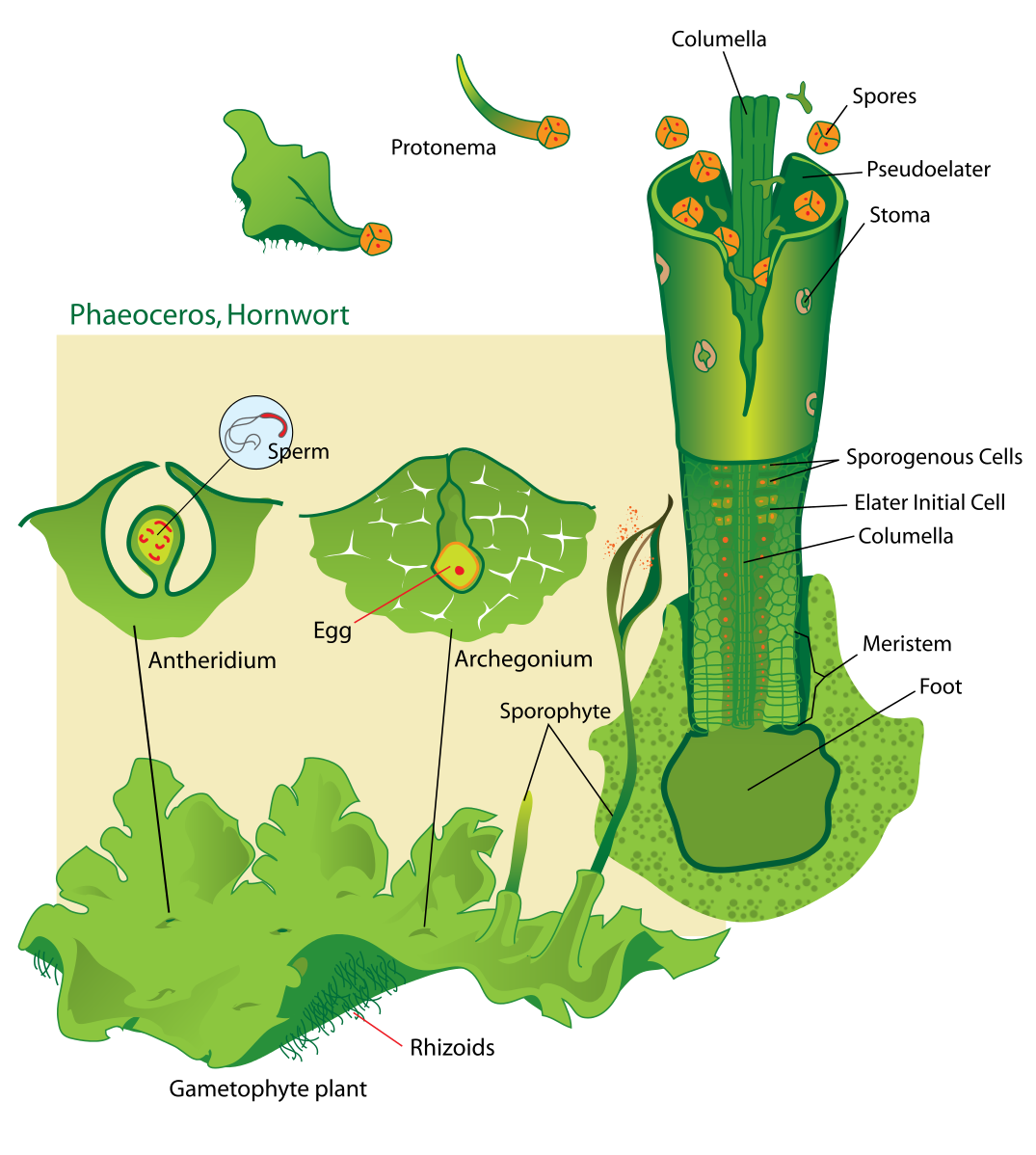
Archegoniate plants belong to the bryophytes, pteridophytes, and gymnosperms. The gymnosperms have the least developed archegonium while bryophytes possess a well-developed archegonium.
-Archegoniate plants are the plants bearing an Archegonium. Archegonium is the female sex organ.
-They are multicellular flask-shaped cells with neck canal cells that produce a single egg (oosphere) at a time. The base is usually swollen and is known as ‘venter'. The neck canal cells degenerate upon maturation. The top of the archegonium is covered by four cover cells which disappear upon the gelatinization of neck cells.
-In gymnosperms such as cycads and conifers, there are two or more archegonia or the female sex organs born from the gametophyte. The female gametophyte is multicellular and is formed by a megaspore enclosed within the megasporangium or nucellus.
-They can either be present at the surface of thallus or remain embedded as in hornworts.
So, the correct answer is ‘Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, gymnosperms.
Note: -Gnetum and Welwitschia group of gymnosperms are devoid of archegonia. Instead, they have a well-developed sporophyte.
-The male sex organ complimentary to archegonium is the Antheridium.
-The archegonium is dependent on the female gametophyte for its nutrition so it remains attached to it.
Complete answer:
Archegoniate plants belong to the bryophytes, pteridophytes, and gymnosperms. The gymnosperms have the least developed archegonium while bryophytes possess a well-developed archegonium.
-Archegoniate plants are the plants bearing an Archegonium. Archegonium is the female sex organ.
-They are multicellular flask-shaped cells with neck canal cells that produce a single egg (oosphere) at a time. The base is usually swollen and is known as ‘venter'. The neck canal cells degenerate upon maturation. The top of the archegonium is covered by four cover cells which disappear upon the gelatinization of neck cells.
-In gymnosperms such as cycads and conifers, there are two or more archegonia or the female sex organs born from the gametophyte. The female gametophyte is multicellular and is formed by a megaspore enclosed within the megasporangium or nucellus.
-They can either be present at the surface of thallus or remain embedded as in hornworts.
So, the correct answer is ‘Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, gymnosperms.

Note: -Gnetum and Welwitschia group of gymnosperms are devoid of archegonia. Instead, they have a well-developed sporophyte.
-The male sex organ complimentary to archegonium is the Antheridium.
-The archegonium is dependent on the female gametophyte for its nutrition so it remains attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




