
Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule for addition reaction is not observed by which of the following compound
A. Propene
B. 1-Butene
C. But-2-ene
D. Pent-2-ene
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint: Anti-Markovnikov rule, also known as the Kharasch Effect, states that when a polar molecule is added to an unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of a peroxide bond, the negative part of the polar compound gets attached to the C-atom having more number of H-atoms compared to the other unsaturated C-atom.
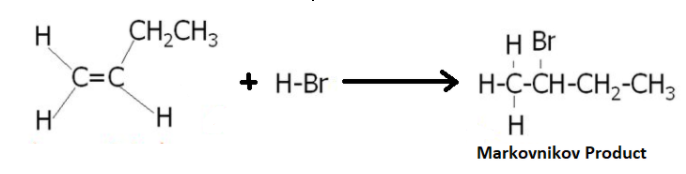
Complete Step by step answer: We know that whenever a polar molecule is added to an unsymmetrical alkene the general product that is formed when the negative part attacks the C-atom having more number of substituents(lesser no. of H-atoms) which is due to the higher hyperconjugative and inductive effects reducing the positive charge density on the given C-atom. The product obtained in this case is called Markovnikov product.
This can be shown by the following reaction:
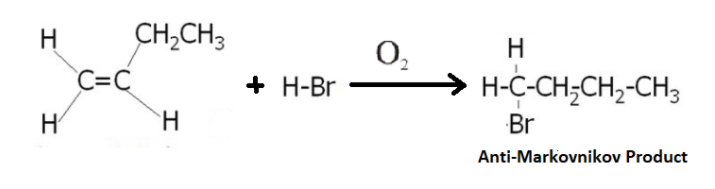
When we use Benzoyl peroxide or $O_2$, the product obtained changes from Markovnikov Product to Anti-Markovnikov product as shown below
Now in this question we have been asked to find the alkene which does not observe the Anti-Markovnikov Rule. We Know that this rule is observed in unsymmetrical alkenes. So we will check each and every option.
A. Propene: Propene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-1$ and $C-2$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option A is incorrect.
B. 1-Butene: 1-Butene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-1$ and $C-2$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option B is incorrect.
C. But-2-ene: But-2-ene is a symmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-2$ and $C-3$, so this will give only one product and therefore does not observe the Anti-Markovnikov rule for additional reaction. So option C is Correct.
D. Pent-2-ene: Pent-2-ene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-2$ and $C-3$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option D is incorrect.
So, the correct option is C. But-2-ene.
Note: In the case of anti-markovnikov products, the stability of carbocation is irrelevant as the mechanism involved in this case is the Free radical addition mechanism. It generally represents the exact opposite of that of markovnikov rule.
Complete Step by step answer: We know that whenever a polar molecule is added to an unsymmetrical alkene the general product that is formed when the negative part attacks the C-atom having more number of substituents(lesser no. of H-atoms) which is due to the higher hyperconjugative and inductive effects reducing the positive charge density on the given C-atom. The product obtained in this case is called Markovnikov product.
This can be shown by the following reaction:

When we use Benzoyl peroxide or $O_2$, the product obtained changes from Markovnikov Product to Anti-Markovnikov product as shown below

Now in this question we have been asked to find the alkene which does not observe the Anti-Markovnikov Rule. We Know that this rule is observed in unsymmetrical alkenes. So we will check each and every option.
A. Propene: Propene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-1$ and $C-2$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option A is incorrect.
B. 1-Butene: 1-Butene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-1$ and $C-2$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option B is incorrect.
C. But-2-ene: But-2-ene is a symmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-2$ and $C-3$, so this will give only one product and therefore does not observe the Anti-Markovnikov rule for additional reaction. So option C is Correct.
D. Pent-2-ene: Pent-2-ene is an unsymmetrical alkene with double bond between $C-2$ and $C-3$, so this will give both Markovnikov as well as Anti-Markovnikov product. So option D is incorrect.
So, the correct option is C. But-2-ene.
Note: In the case of anti-markovnikov products, the stability of carbocation is irrelevant as the mechanism involved in this case is the Free radical addition mechanism. It generally represents the exact opposite of that of markovnikov rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




