
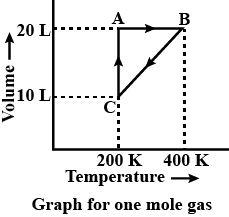
Answer the questions based on the diagram.
The pressure at A and B in the atmosphere are respectively:
(A) 0.821 and 1.642
(B) 1.642 and 0.821
(C) 1 and 2
(D) 0.082 and 0.164

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: The given illustration is based on the equations of ideal gas laws. The given VT diagram is being evaluated for one mole of gas molecules present.
Complete Solution :
Let us first discuss the ideal gas law to properly answer the given question;
Ideal gas equation-
This is the empirical relationship between the volume of the gas, pressure of the gas, temperature of the gas and amount of the gas present. This can be represented as;
\[PV=nRT\]
where,
P = pressure
V = volume
n = amount of the substance
R = ideal gas constant
T = temperature
The ideal gas law is also called as general gas equation which is derived considering basic gas laws i.e. Boyle’s law and Charles law.
Now, considering this law, we solve illustration as:
At A-
Volume = 20 L
Temperature = 200 K
Pressure can be given as,
$\begin{align}
& P=\frac{nRT}{V} \\
& P=\frac{1\times 0.0821\times 200}{20}=0.821 \\
\end{align}$
So, pressure at A is 0.821 atm.
At B-
Volume = 20 L
Temperature = 400 K
Pressure can be similarly calculated as,
$\begin{align}
& P=\frac{nRT}{V} \\
& P=\frac{1\times 0.0821\times 400}{20}=1.642 \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Do note that here, nowhere is mentioned about the units of the quantities contributing the equation required to solve the given illustration. But we need to consider them properly by looking at the given data. As any mistake in the value of the ideal gas constant, It would result in chaos.
Complete Solution :
Let us first discuss the ideal gas law to properly answer the given question;
Ideal gas equation-
This is the empirical relationship between the volume of the gas, pressure of the gas, temperature of the gas and amount of the gas present. This can be represented as;
\[PV=nRT\]
where,
P = pressure
V = volume
n = amount of the substance
R = ideal gas constant
T = temperature
The ideal gas law is also called as general gas equation which is derived considering basic gas laws i.e. Boyle’s law and Charles law.
Now, considering this law, we solve illustration as:
At A-
Volume = 20 L
Temperature = 200 K
Pressure can be given as,
$\begin{align}
& P=\frac{nRT}{V} \\
& P=\frac{1\times 0.0821\times 200}{20}=0.821 \\
\end{align}$
So, pressure at A is 0.821 atm.
At B-
Volume = 20 L
Temperature = 400 K
Pressure can be similarly calculated as,
$\begin{align}
& P=\frac{nRT}{V} \\
& P=\frac{1\times 0.0821\times 400}{20}=1.642 \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Do note that here, nowhere is mentioned about the units of the quantities contributing the equation required to solve the given illustration. But we need to consider them properly by looking at the given data. As any mistake in the value of the ideal gas constant, It would result in chaos.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




