
Answer the following questions.
(i) Draw a well-labeled diagram of a neuron and name the following parts.
(1) Node of Ranvier
(2) Nissl granules
(3) Cyton
(ii) Name the part of the human brain which is concerned with the following.
(1) Seat of memory
(2) Coordinates muscular activity
(iii) Mention any three major activities of the WHO.
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: A neuron is a specialized cell, mainly takes place in transmitting information by electrical and chemical signals. They are found within the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. A neuron is also well known as the nerve cell.
Complete answer:
(i)
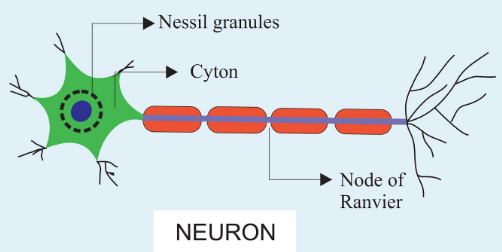
(1) Node of Ranvier: They are microscopic gaps found within myelinated axons
(2) Nissl granules: They are a large granular body found in neurons.
(3) Cyton: They are the central or cell body of a neuron containing the nucleus and excluding its processes.
(ii) Part of the human brain
(1) Seat of memory: Cerebrum
(2) Coordinates muscular activity: Cerebellum
(iii) The three major activities of WHO are-
-To collect and provide information about the occurrence of diseases of epidemic
nature such as cholera, plague, etc.
-To promote and help projects for research on diseases.
-To supply information on the newest developments about the utilization of vaccines.
Additional information:
Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals all over the body. Neurons have long extensions that reach out from the cell body called dendrites and axons. Dendrites are extensions of the neuron's cell body or soma that receive signals and conduct them toward the cell body. The cell body extends into the axon which is roofed by a myelin sheath. The myelin sheath acts as an insulator that prevents short-circuiting within the neurons. This way an impulse is maintained within a single neuron and doesn’t go haywire. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath known as Nodes of Ranvier. An impulse leap from node to node on its way of growth towards the axon terminals. At the terminals, depending on the composition of the neuron, the impulse is transmitted to the dendrites of the next neuron via a junction termed as a synapse, in a chemical or electric manner.
Note:
The structure of a neuron varies with its shape and size and it mainly depends upon its functions and location. Neurons are the structural and functional elements of the nervous system. A group of neurons forms a nerve.
Complete answer:
(i)

(1) Node of Ranvier: They are microscopic gaps found within myelinated axons
(2) Nissl granules: They are a large granular body found in neurons.
(3) Cyton: They are the central or cell body of a neuron containing the nucleus and excluding its processes.
(ii) Part of the human brain
(1) Seat of memory: Cerebrum
(2) Coordinates muscular activity: Cerebellum
(iii) The three major activities of WHO are-
-To collect and provide information about the occurrence of diseases of epidemic
nature such as cholera, plague, etc.
-To promote and help projects for research on diseases.
-To supply information on the newest developments about the utilization of vaccines.
Additional information:
Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that transmit signals all over the body. Neurons have long extensions that reach out from the cell body called dendrites and axons. Dendrites are extensions of the neuron's cell body or soma that receive signals and conduct them toward the cell body. The cell body extends into the axon which is roofed by a myelin sheath. The myelin sheath acts as an insulator that prevents short-circuiting within the neurons. This way an impulse is maintained within a single neuron and doesn’t go haywire. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath known as Nodes of Ranvier. An impulse leap from node to node on its way of growth towards the axon terminals. At the terminals, depending on the composition of the neuron, the impulse is transmitted to the dendrites of the next neuron via a junction termed as a synapse, in a chemical or electric manner.
Note:
The structure of a neuron varies with its shape and size and it mainly depends upon its functions and location. Neurons are the structural and functional elements of the nervous system. A group of neurons forms a nerve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




