
Anisole on reaction with $HI$ produces only phenol and methyl iodide. Give a reason?
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: In organic chemistry, the electrophilic substitution reactions are the type of chemical reactions in which an electrophile displaces a group in a compound. This reaction involves the initial attack of an electrophile followed by the reaction with a nucleophile in order to form the final product. Most of the aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions due to the nucleophilic nature of the benzene ring.
Complete answer:
The reaction mechanism for the given substitution reaction is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of hydrogen iodide takes place into hydrogen and iodide ions respectively. The reaction is as follows:
$HI \to {H^ + } + {I^ - }$
Step-2: The lone pair present on the oxygen atom of the anisole will act as a nucleophile and an attack of hydrogen ion will take place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
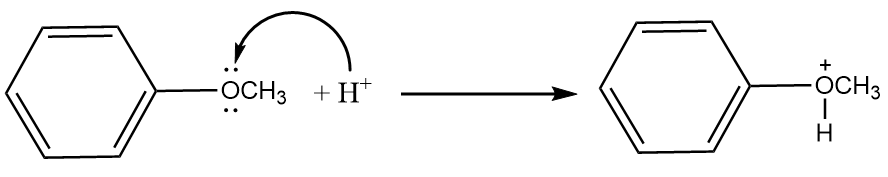
Step-3: Iodide ions will attack the methyl group and formation of phenol and methyl iodide will take place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
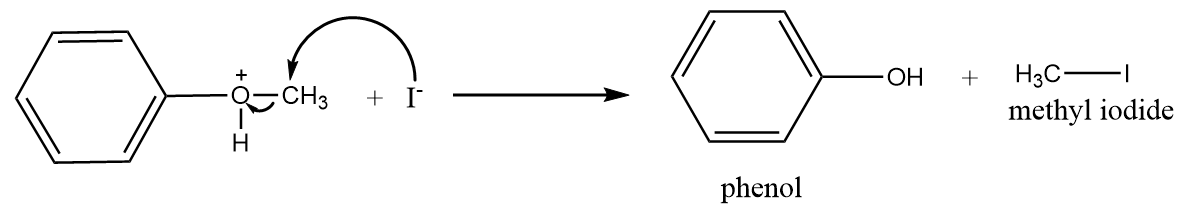
In the reaction process, only phenol and methyl iodide are formed because the bond between $O - C{H_3}$ is weaker as compared to $O - {C_6}{H_5}$ due to the presence of partial double bond character. Therefore, when iodide ion attacks the cleavage of $O - C{H_3}$ bonds take place to form methyl iodide instead of cleavage of $O - {C_6}{H_5}$ to form iodobenzene and methyl alcohol.
Note:
It is important to note that phenols do not further react to give halides because the carbon atoms of the ring are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and consist of a cloud of pi electrons over the bonds. So, it cannot undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction to form respective halides.
Complete answer:
The reaction mechanism for the given substitution reaction is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of hydrogen iodide takes place into hydrogen and iodide ions respectively. The reaction is as follows:
$HI \to {H^ + } + {I^ - }$
Step-2: The lone pair present on the oxygen atom of the anisole will act as a nucleophile and an attack of hydrogen ion will take place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
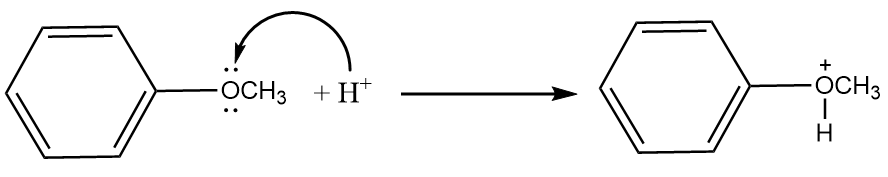
Step-3: Iodide ions will attack the methyl group and formation of phenol and methyl iodide will take place. The reaction proceeds as follows:

In the reaction process, only phenol and methyl iodide are formed because the bond between $O - C{H_3}$ is weaker as compared to $O - {C_6}{H_5}$ due to the presence of partial double bond character. Therefore, when iodide ion attacks the cleavage of $O - C{H_3}$ bonds take place to form methyl iodide instead of cleavage of $O - {C_6}{H_5}$ to form iodobenzene and methyl alcohol.
Note:
It is important to note that phenols do not further react to give halides because the carbon atoms of the ring are $s{p^2}$ hybridized and consist of a cloud of pi electrons over the bonds. So, it cannot undergo a nucleophilic substitution reaction to form respective halides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




