
Angle strain cyclopropane is:
A.$24^\circ 44'$
B.$9^\circ 44'$
C.$44'$
D.$ - 5^\circ 16'$
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: A molecule experiences strain when its chemical structure undergoes some stress which raises its internal energy in comparison to strain free reference compounds. When this strain is produced due to deviation in bond angles of a molecule, it is termed as angle strain.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically angle strain is the increase in potential energy of a molecule due to deviation of bond angles from ideal values. It is also termed as ring strain because it is mostly found in cyclic structures and due to rigidity, compounds can have only one conformation as we can see in the structure of cyclopropane.
Structure of cyclopropane:
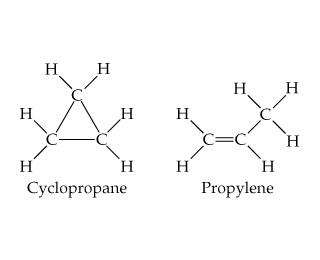
As we all know that strain is calculated by the deviation in bond angle.
In our molecule Cyclopropane, the carbon has $s{p^3}$ hybridization which tells us that it should have an angle of $109^\circ 28'$ but due to its rigid structure, it actually can’t maintain this angle so as a result there is the generation of angle strain.
This angle strain is calculated in terms of bond angle which is as follows:
Deviation,$d = \dfrac{{109^\circ 28' - \alpha }}{2}$ , where $\alpha $ is the bond angle in Cyclopropane.
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = 60^\circ $
Now put the value of $\alpha $ in deviation formula.
Deviation ,$d = \dfrac{{109^\circ 28' - 60^\circ }}{2} = + 24^\circ 44'$
$ \Rightarrow $ Angle strain in Cyclopropane is $24^\circ 44'$ .
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
When we see any deviation in a molecule from its standard structure we can predict that it is a strained molecule. Scientifically it is predicted by the energy of molecules which is enhanced because of unfavourable bond lengths, bond angles or dihedral angles.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically angle strain is the increase in potential energy of a molecule due to deviation of bond angles from ideal values. It is also termed as ring strain because it is mostly found in cyclic structures and due to rigidity, compounds can have only one conformation as we can see in the structure of cyclopropane.
Structure of cyclopropane:

As we all know that strain is calculated by the deviation in bond angle.
In our molecule Cyclopropane, the carbon has $s{p^3}$ hybridization which tells us that it should have an angle of $109^\circ 28'$ but due to its rigid structure, it actually can’t maintain this angle so as a result there is the generation of angle strain.
This angle strain is calculated in terms of bond angle which is as follows:
Deviation,$d = \dfrac{{109^\circ 28' - \alpha }}{2}$ , where $\alpha $ is the bond angle in Cyclopropane.
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = 60^\circ $
Now put the value of $\alpha $ in deviation formula.
Deviation ,$d = \dfrac{{109^\circ 28' - 60^\circ }}{2} = + 24^\circ 44'$
$ \Rightarrow $ Angle strain in Cyclopropane is $24^\circ 44'$ .
Hence option (A) is correct.
Note:
When we see any deviation in a molecule from its standard structure we can predict that it is a strained molecule. Scientifically it is predicted by the energy of molecules which is enhanced because of unfavourable bond lengths, bond angles or dihedral angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




