
What is the angle between two vectors of equal magnitude when the magnitude of their sum is the same as the magnitude of each vector?
A.$120^\circ $
B. $240^\circ $
C. $90^\circ $
D. $30^\circ $
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: This question arises from motion in a plane (vectors). Here we apply the triangle law of vector addition. It states that if two vectors are represented both in magnitude and direction by the two sides of a triangle taken in the same order then the resultant of these vectors by the third side of the triangle taken in the opposite order.
That means ${\vec R = \vec A + \vec B}$
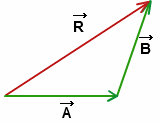
Complete step by step answer:
Let A and B be two vectors such that A=B. And the angle between two vectors A and B is$\alpha $. According to the question, the magnitude of the resultant vector R of vectors A and B is such that R=A=B.
Now according to the triangle law of vector addition, the magnitude of the resultant vector R
$R=[A^2+B^2+2ABcos \alpha]^{1/2}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^2} = {{\text{A}}^2} + {{\text{B}}^2} + 2{\text{ABcos}}\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{A}}^2} = {{\text{A}}^2} + {{\text{A}}^2} + 2{\text{AAcos}}\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\text{A}}^2} + 2{{\text{A}}^2}{\text{cos}}\alpha - {{\text{A}}^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{A}}^2}(1 + 2{\text{cos}}\alpha {\text{) = 0}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{cos }}\alpha = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}$
$\therefore \alpha = {\text{arc cos}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right) = 120^\circ $
$\therefore$ The frictional force at the contact surface is ${m_1}\omega _1^2\,R$.
The maximum angular speed $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{\mu _2^{}g}}{R}}$
Additional information:
The angle between two vectors of equal magnitude $0^\circ $, depending on the ratio of the magnitudes of the two vectors. Two vectors of equal magnitude that are pointing in opposite directions will sum to zero. Two vectors of unequal magnitude can never sum to zero.
Note:
When the vector quantities are given in magnitude they are represented in scalar form. Vector quantities cannot be added or subtracted algebraically. These quantities are specified by both magnitude and direction.
That means ${\vec R = \vec A + \vec B}$

Complete step by step answer:
Let A and B be two vectors such that A=B. And the angle between two vectors A and B is$\alpha $. According to the question, the magnitude of the resultant vector R of vectors A and B is such that R=A=B.
Now according to the triangle law of vector addition, the magnitude of the resultant vector R
$R=[A^2+B^2+2ABcos \alpha]^{1/2}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^2} = {{\text{A}}^2} + {{\text{B}}^2} + 2{\text{ABcos}}\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{A}}^2} = {{\text{A}}^2} + {{\text{A}}^2} + 2{\text{AAcos}}\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\text{A}}^2} + 2{{\text{A}}^2}{\text{cos}}\alpha - {{\text{A}}^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{A}}^2}(1 + 2{\text{cos}}\alpha {\text{) = 0}}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{cos }}\alpha = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}$
$\therefore \alpha = {\text{arc cos}}\left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right) = 120^\circ $
$\therefore$ The frictional force at the contact surface is ${m_1}\omega _1^2\,R$.
The maximum angular speed $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{\mu _2^{}g}}{R}}$
Additional information:
The angle between two vectors of equal magnitude $0^\circ $, depending on the ratio of the magnitudes of the two vectors. Two vectors of equal magnitude that are pointing in opposite directions will sum to zero. Two vectors of unequal magnitude can never sum to zero.
Note:
When the vector quantities are given in magnitude they are represented in scalar form. Vector quantities cannot be added or subtracted algebraically. These quantities are specified by both magnitude and direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




