
Angle between the tangents drawn to ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ at the points where it is cut by the line$y = 2x + c\,\,{\text{is}}\,\,\dfrac{\pi }{2}\,$then,
A). $|{\text{c}}| = \sqrt 5 $
B). $|{\text{c}}| = 2\sqrt 5 $
C). $|{\text{c}}| = \sqrt {10} $
D). $|{\text{c}}| = 2\sqrt {10} $
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: Given the equation of the circle from the angle between the tangent is drawn${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ is in the general form.
Therefore, use the formula ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$ to find the center and
radius of the given circle. Use the concept of the distance of the point $({x_1},\,\,{y_1})$ to the line $A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c = 0$ , that is $d = \dfrac{{|A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} }}$, using all this information we need to find the value of the constant c.
Complete step-by-step solution:
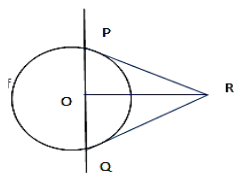
Given the equation of circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ and the circle cut by the line $y = 2x + c\,\,$. Draw the tangents at the point of intersection of the circle and the line.
Also given that the angle between the tangents drawn at the points
Where the line cuts the circle is \[{90^0}\] .
Therefore the tangents are perpendicular to each other
${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$
By completing the square method
${x^2} - 2x + 1 - 1 + {y^2} - 4y + 4 - 4 + 1 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} - 4 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} = 4$
Compare this equation with ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$ the center of this equation is (h, k) and radius is r.
Therefore, we get Centre is \[\left( {1,{\text{ }}2} \right)\] and radius is $2$ .
From the diagram angle PRQ \[ = {90^0}\] (given)
Join OR so that the angles PRO and QRO equal to ${45^0}$.
Therefore \[OR{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}cos{45^0} = {\text{ }}2\] .$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt 2 $
Now consider the line $y = 2x + c\,\, \Rightarrow 2x - y + c = 0$
We know that the perpendicular distance from the point $({x_1},\,\,{y_1})$ to the line $A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c = 0$ is
$d = \dfrac{{|A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} }}$
Therefore, the perpendicular distance from (1, 2) to the line $2x - y + c = 0$ is the radius.
Perpendicular distance = $\dfrac{{|2(1) - 1(2) + c|}}{{\sqrt {{1^2} + {2^2}} }}$
$\sqrt{2} = \dfrac{{|c|}}{{\sqrt 5 }} \Rightarrow |c| = \sqrt {10} $
Note: If instead of the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ the equation of a circle is of the form ${x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}$then directly we get center and radius. Distance is always positive, therefore if you get a negative value even though you have to consider positive value. Since radius can be framed as $r = \dfrac{d}{2}$ where d is the overall diameter.
Therefore, use the formula ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$ to find the center and
radius of the given circle. Use the concept of the distance of the point $({x_1},\,\,{y_1})$ to the line $A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c = 0$ , that is $d = \dfrac{{|A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} }}$, using all this information we need to find the value of the constant c.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Given the equation of circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ and the circle cut by the line $y = 2x + c\,\,$. Draw the tangents at the point of intersection of the circle and the line.
Also given that the angle between the tangents drawn at the points
Where the line cuts the circle is \[{90^0}\] .
Therefore the tangents are perpendicular to each other
${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$
By completing the square method
${x^2} - 2x + 1 - 1 + {y^2} - 4y + 4 - 4 + 1 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} - 4 = 0$
${(x - 1)^2} + {(y - 2)^2} = 4$
Compare this equation with ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$ the center of this equation is (h, k) and radius is r.
Therefore, we get Centre is \[\left( {1,{\text{ }}2} \right)\] and radius is $2$ .
From the diagram angle PRQ \[ = {90^0}\] (given)
Join OR so that the angles PRO and QRO equal to ${45^0}$.
Therefore \[OR{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }}cos{45^0} = {\text{ }}2\] .$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \sqrt 2 $
Now consider the line $y = 2x + c\,\, \Rightarrow 2x - y + c = 0$
We know that the perpendicular distance from the point $({x_1},\,\,{y_1})$ to the line $A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c = 0$ is
$d = \dfrac{{|A{x_1} + B{y_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} }}$
Therefore, the perpendicular distance from (1, 2) to the line $2x - y + c = 0$ is the radius.
Perpendicular distance = $\dfrac{{|2(1) - 1(2) + c|}}{{\sqrt {{1^2} + {2^2}} }}$
$\sqrt{2} = \dfrac{{|c|}}{{\sqrt 5 }} \Rightarrow |c| = \sqrt {10} $
Note: If instead of the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0$ the equation of a circle is of the form ${x^2} + {y^2} = {r^2}$then directly we get center and radius. Distance is always positive, therefore if you get a negative value even though you have to consider positive value. Since radius can be framed as $r = \dfrac{d}{2}$ where d is the overall diameter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




