
$\angle ABC$ and $\angle BDC$ are two right angles. If AD = 9cm, DC = 16cm and AB = 15cm, then the length of BD is?
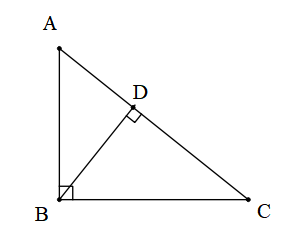
(a) 12cm
(b) 16cm
(c) 15cm
(d) 25cm

Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: We can see that all the triangles are right-angle triangles. Hence, to find the length, we need to find the pythagorean theorem. Pythagoras theorem says that, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\left( \text{side 1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{side 2} \right)}^{\text{2}}}$ where, the hypotenuse is the side opposite to ${{90}^{\circ }}$ . We then need to substitute the values given in the question and get the unknown side of BD.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to find the length of the side of a triangle.
We are given that $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle BDC={{90}^{\circ }}$ ,
It will be clear once we draw the diagram.
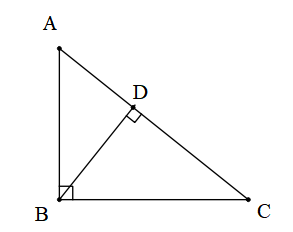
We can see that the $\Delta ABC$ is a right angle triangle and $\Delta BDC$ is also a right angle triangle.
Segment BD intersects AC at ${{90}^{\circ }}$. Therefore, $\angle ADB$ also equals ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Let us consider $\Delta ADB$.
In $\Delta ADB$, $\angle ADB={{90}^{\circ }}$, AD = 9cm, AB = 15cm,
We can use the pythagorean theorem,
Pythagoras theorem says that ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\left( \text{side 1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{side 2} \right)}^{\text{2}}}.................(i)$
The hypotenuse is the side opposite to the side with ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Therefore, we can see that hypotenuse = AB = 15cm and side 1 = AD = 9cm.
Substituting, in the equation, we get that,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AD \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 9 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Solving for BD we get,
${{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}-{{9}^{2}}=144$ .
Taking square root on both sides, we get,
BD = 12cm.
Hence, option (a) is the correct option.
Note: We need to take care of the point that side AB is not the hypotenuse of $\Delta ABC$ , so we are not applying Pythagoras theorem to $\Delta ABC$ instead we are applying the Pythagoras theorem to $\Delta ADB$. Also, the length of the hypotenuse is 15 cm. There is no other side in the right angle triangle which is greater than the hypotenuse. Therefore, the side we need to find has to be smaller than AB. Hence, option (b), (c), (d) are eliminated. The only option remaining is that option (a) is the correct option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to find the length of the side of a triangle.
We are given that $\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}$ and $\angle BDC={{90}^{\circ }}$ ,
It will be clear once we draw the diagram.

We can see that the $\Delta ABC$ is a right angle triangle and $\Delta BDC$ is also a right angle triangle.
Segment BD intersects AC at ${{90}^{\circ }}$. Therefore, $\angle ADB$ also equals ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Let us consider $\Delta ADB$.
In $\Delta ADB$, $\angle ADB={{90}^{\circ }}$, AD = 9cm, AB = 15cm,
We can use the pythagorean theorem,
Pythagoras theorem says that ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\left( \text{side 1} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\left( \text{side 2} \right)}^{\text{2}}}.................(i)$
The hypotenuse is the side opposite to the side with ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Therefore, we can see that hypotenuse = AB = 15cm and side 1 = AD = 9cm.
Substituting, in the equation, we get that,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AD \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 9 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Solving for BD we get,
${{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}={{15}^{2}}-{{9}^{2}}=144$ .
Taking square root on both sides, we get,
BD = 12cm.
Hence, option (a) is the correct option.
Note: We need to take care of the point that side AB is not the hypotenuse of $\Delta ABC$ , so we are not applying Pythagoras theorem to $\Delta ABC$ instead we are applying the Pythagoras theorem to $\Delta ADB$. Also, the length of the hypotenuse is 15 cm. There is no other side in the right angle triangle which is greater than the hypotenuse. Therefore, the side we need to find has to be smaller than AB. Hence, option (b), (c), (d) are eliminated. The only option remaining is that option (a) is the correct option.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




