
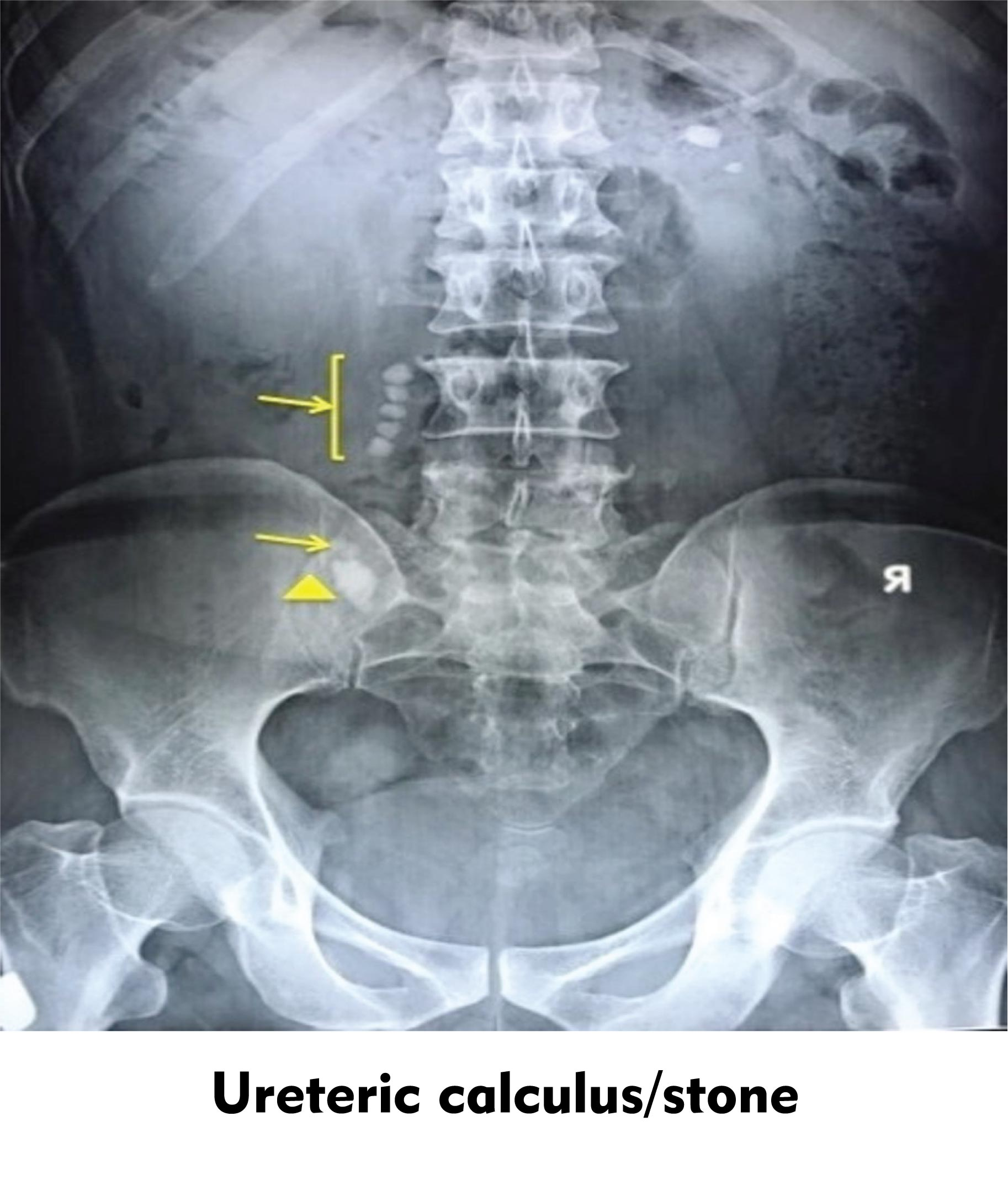
An X-ray of the lower abdomen shows a shade in the region of ureter suspected to be a ureteric calculus. Possible clinical symptoms would be
(a) Acute renal failure
(b) Anuria and hematuria
(c) Motor aphasia
(d) Chronic renal failure (CRF)
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: A possible clinical symptom of ureteric calculus is a condition of non-passage of urine. In clinical practice, this condition is defined as the passage of less than a hundred milliliters of urine during a day. Another symptom of ureteric calculus is characterized by the presence of blood in the urine.
Complete answer:
The possible clinical symptoms of ureteric calculus would be anuria and hematuria. ‘Calculus’ is a concretion of material like mineral salts. It usually forms within an organ or a duct of the body. The condition of the formation of calculus is called ‘lithiasis.’ Thus, stones possess the potential of causing a number of medical conditions.
Now let's understand what happens in a condition of ureteric calculus.
-Pain in the back and side, usually just below the ribs.
-Pain that changes places for example:
-It radiates to the lower abdomen and possibly the groin.
-It comes in a fashion of waves.
-It changes in intensity
-It shifts sites.
-The patient also feels pain while urinating.
-There may be nausea and/or vomiting.
-A frequent urge to go for urination, but there is a painful passage of lesser than normal quantity of urine, known as ‘anuria.’
-On observation, the urine is cloudy or has a strong, foul smell.
-There is blood in the urine called ‘hematuria’.
So, the correct answer is, ‘anuria and hematuria.’
Note: -Calculus in common terms is called the ‘stone.’
-Acute renal failure is characterized by decreased urine output, fluid retention causing swelling in legs, ankles, or feet.
-Motor aphasia is a neural condition in which the patient develops an inability to comprehend language. There is weakness and inability to speak spontaneously.
-Chronic renal failure is characterized by loss of appetite, weakness, high blood pressure, etc.
Complete answer:
The possible clinical symptoms of ureteric calculus would be anuria and hematuria. ‘Calculus’ is a concretion of material like mineral salts. It usually forms within an organ or a duct of the body. The condition of the formation of calculus is called ‘lithiasis.’ Thus, stones possess the potential of causing a number of medical conditions.
Now let's understand what happens in a condition of ureteric calculus.
-Pain in the back and side, usually just below the ribs.
-Pain that changes places for example:
-It radiates to the lower abdomen and possibly the groin.
-It comes in a fashion of waves.
-It changes in intensity
-It shifts sites.
-The patient also feels pain while urinating.
-There may be nausea and/or vomiting.
-A frequent urge to go for urination, but there is a painful passage of lesser than normal quantity of urine, known as ‘anuria.’
-On observation, the urine is cloudy or has a strong, foul smell.
-There is blood in the urine called ‘hematuria’.
So, the correct answer is, ‘anuria and hematuria.’
Note: -Calculus in common terms is called the ‘stone.’
-Acute renal failure is characterized by decreased urine output, fluid retention causing swelling in legs, ankles, or feet.
-Motor aphasia is a neural condition in which the patient develops an inability to comprehend language. There is weakness and inability to speak spontaneously.
-Chronic renal failure is characterized by loss of appetite, weakness, high blood pressure, etc.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




