
An unknown alcohol is treated with the “Lucas reagent” to determine whether the alcohol is primary, secondary or tertiary. Which alcohol reacts fastest and by which mechanism?
A. Tertiary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$
B. Secondary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$
C. Tertiary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$
D. Secondary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The reaction of an alcohol with Lucas reagent takes place in two steps. In the first step carbocation forms and in the second step product alkyl chloride forms. The Lucas reagent differentiates the alcohol, on the basis of their reactivity or the stability of the intermediate.
Complete Step by step answer: Lucas test is used to distinguish the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. The mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and dry anhydrous zinc chloride is known as Lucas reagent.
The test distinguishes the alcohols based on their reactivity. In this test, alcohol reacts with hydrochloric acid and forms alkyl chloride.
OH, a group of alcohol attacks on the acid and gets protonated. Then water molecules are eliminated to form a carbocation. On this carbocation the chloride ion attacks and forms alkyl chloride.
The reaction of alcohols with Lucas reagent is as follows:
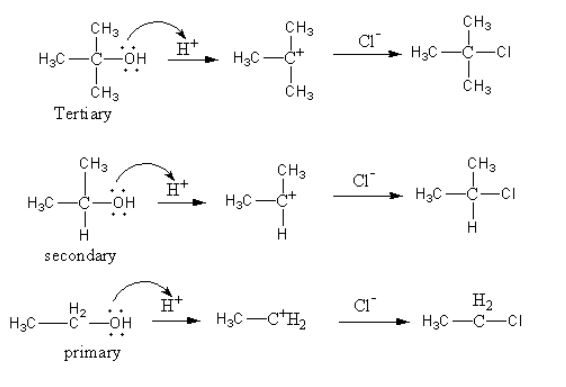
As during the reaction, a carbocation forms so, the rate of reaction depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The more stable the carbocation the more will be the rate of reaction.
The order of stability of carbocation is as follows:
${1^ \circ } < \,{2^ \circ }\, < \,{3^ \circ }$
So, the tertiary alcohol reacts faster because of the formation of tertiary carbocation during the reaction which is very stable carbocation.
The carbocation formation takes place in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction.
So, tertiary alcohol reacts fastest with Lucas reagent via ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ mechanism.
Therefore, option (C) Tertiary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$, is correct.
Note: The ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ mechanism, a carbocation form in first step. The carbocation is the intermediate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$types reactions. The tertiary carbocation is most stable due to the presence of an electron-donating alkyl group. The more the number of electron-donating groups the more stable the carbocation will be. ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ type reactions take place in one step. Only a transition state forms in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction, no intermediate forms. The –OH group removes from one side and chloride attacks form another side. Primary alcohol follows the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ mechanism due to less steric hindrance.
Complete Step by step answer: Lucas test is used to distinguish the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. The mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and dry anhydrous zinc chloride is known as Lucas reagent.
The test distinguishes the alcohols based on their reactivity. In this test, alcohol reacts with hydrochloric acid and forms alkyl chloride.
OH, a group of alcohol attacks on the acid and gets protonated. Then water molecules are eliminated to form a carbocation. On this carbocation the chloride ion attacks and forms alkyl chloride.
The reaction of alcohols with Lucas reagent is as follows:

As during the reaction, a carbocation forms so, the rate of reaction depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The more stable the carbocation the more will be the rate of reaction.
The order of stability of carbocation is as follows:
${1^ \circ } < \,{2^ \circ }\, < \,{3^ \circ }$
So, the tertiary alcohol reacts faster because of the formation of tertiary carbocation during the reaction which is very stable carbocation.
The carbocation formation takes place in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ reaction.
So, tertiary alcohol reacts fastest with Lucas reagent via ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ mechanism.
Therefore, option (C) Tertiary alcohol by ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$, is correct.
Note: The ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$ mechanism, a carbocation form in first step. The carbocation is the intermediate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}1$types reactions. The tertiary carbocation is most stable due to the presence of an electron-donating alkyl group. The more the number of electron-donating groups the more stable the carbocation will be. ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ type reactions take place in one step. Only a transition state forms in ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction, no intermediate forms. The –OH group removes from one side and chloride attacks form another side. Primary alcohol follows the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ mechanism due to less steric hindrance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




