
An organic compound ${C_4}{H_{10}}O{\text{ (X)}}$ on reaction with ${I_2}/red - P$ gives ${C_4}{H_9}I$ which on further reaction with $AgN{O_2}$ gives ${C_4}{H_9}N{O_2}{\text{ (Y)}}$. Y on treatment with $HN{O_3}$ form a blue solution which in turns to red on making the solution slightly alkaline. The possible identity of X is:
A. 1-butanol
B. 2 methyl-1-pentanol
C. 2-butanol
D. Either 1 or 2
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Follow each step of the question with options to reach the solution. Red phosphorus is a hard crystalline solid without any smell and is a bad conductor of electricity. Chemically being less reactive than white phosphorus, red phosphorus reacts with halogens, sulphur and alkali metals only when heated forms their corresponding salts and also red phosphorus does not react with caustic alkalis.
Complete answer:
The organic compound (X) given is ${C_4}{H_{10}}O$.
1-butanol on reaction with ${I_2}/red - P$ gives Butyl iodide. (given ${C_4}{H_9}I$)
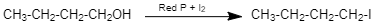
Silver nitrite is a covalent compound and the bond between Ag-O is covalent.Therefore it does not have a negative charge on the oxygen atom. Hence, the nucleophilic attack occurs through the lone pair on nitrogen forming nitroalkanes. So, When this haloalkane (1-iodobutane) is treated with silver nitrite, $(AgN{O_2})$, the halogen atom is replaced by nitro group $( - N{O_2})$ to give Nitroalkane (1-Nitrobutane). (Given ${C_4}{H_9}N{O_2}{\text{ is }}(Y)$)
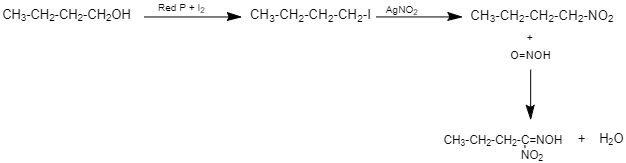
This 1-Nitrobutane on treatment with nitrous acid forms Nitrolic acid, (a blue coloured solution) which dissolves in alkali to give a red coloured solution.
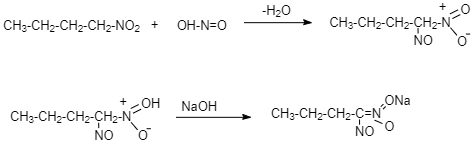
The answer cannot be 2-butanol as 2-Nitrobutane reacts with nitrous acid to produce Pseudo nitrole which gives blue colour with alkali.
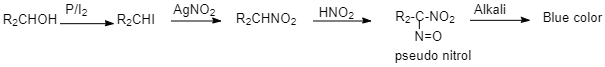
So the organic compound(X) is 1-butanol
Therefore the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
The Victor Meyer apparatus is the usual laboratory method of determining the molecular weight of a volatile liquid.It was developed by Viktor Meyer, who spelled his name Victor in publications at the time of its development. In this method, a known mass of a volatile solid or liquid under examination is converted into its vapour form by heating in a Victor Meyer's tube.
Complete answer:
The organic compound (X) given is ${C_4}{H_{10}}O$.
1-butanol on reaction with ${I_2}/red - P$ gives Butyl iodide. (given ${C_4}{H_9}I$)
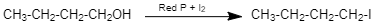
Silver nitrite is a covalent compound and the bond between Ag-O is covalent.Therefore it does not have a negative charge on the oxygen atom. Hence, the nucleophilic attack occurs through the lone pair on nitrogen forming nitroalkanes. So, When this haloalkane (1-iodobutane) is treated with silver nitrite, $(AgN{O_2})$, the halogen atom is replaced by nitro group $( - N{O_2})$ to give Nitroalkane (1-Nitrobutane). (Given ${C_4}{H_9}N{O_2}{\text{ is }}(Y)$)

This 1-Nitrobutane on treatment with nitrous acid forms Nitrolic acid, (a blue coloured solution) which dissolves in alkali to give a red coloured solution.

The answer cannot be 2-butanol as 2-Nitrobutane reacts with nitrous acid to produce Pseudo nitrole which gives blue colour with alkali.
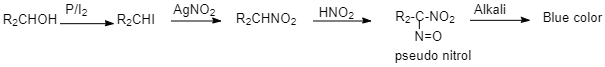
So the organic compound(X) is 1-butanol
Therefore the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
The Victor Meyer apparatus is the usual laboratory method of determining the molecular weight of a volatile liquid.It was developed by Viktor Meyer, who spelled his name Victor in publications at the time of its development. In this method, a known mass of a volatile solid or liquid under examination is converted into its vapour form by heating in a Victor Meyer's tube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




